A Divided Nation: Germany and the Cold War
Related Articles: A Divided Nation: Germany and the Cold War
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Divided Nation: Germany and the Cold War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Divided Nation: Germany and the Cold War
The Cold War, a period of geopolitical tension and ideological rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, profoundly impacted Germany. The nation, once a powerful force in Europe, emerged from World War II deeply divided, both geographically and ideologically. This division, enshrined in the "Iron Curtain" that separated East and West, became a stark symbol of the Cold War’s impact on Europe.
From Defeat to Division:
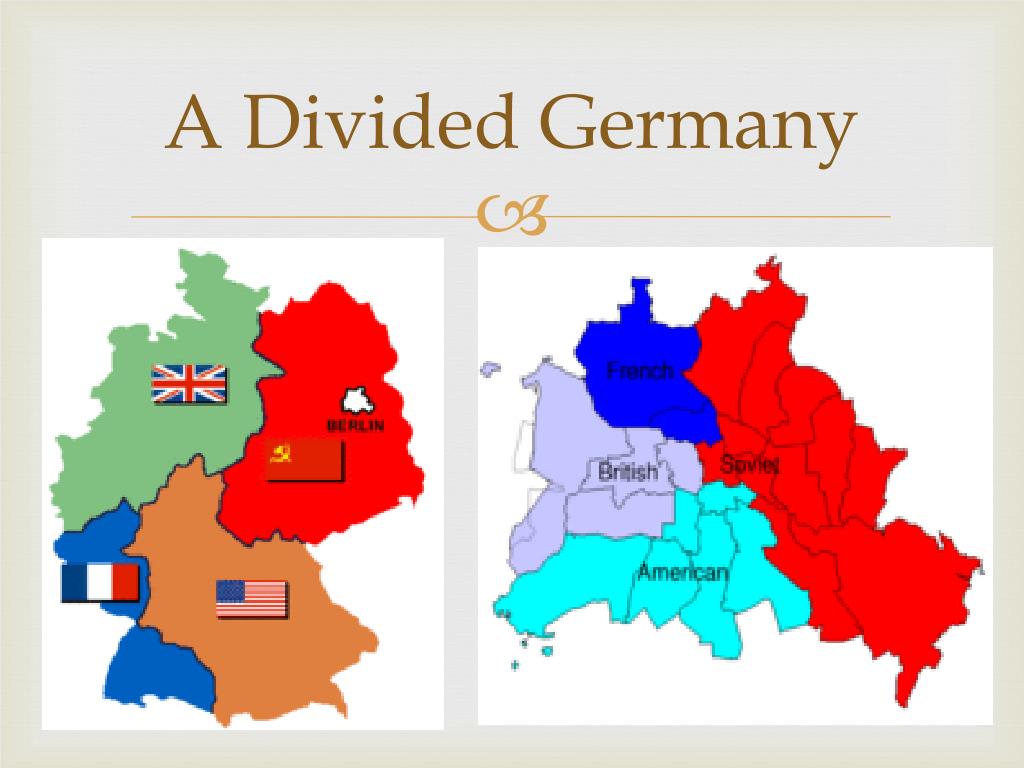
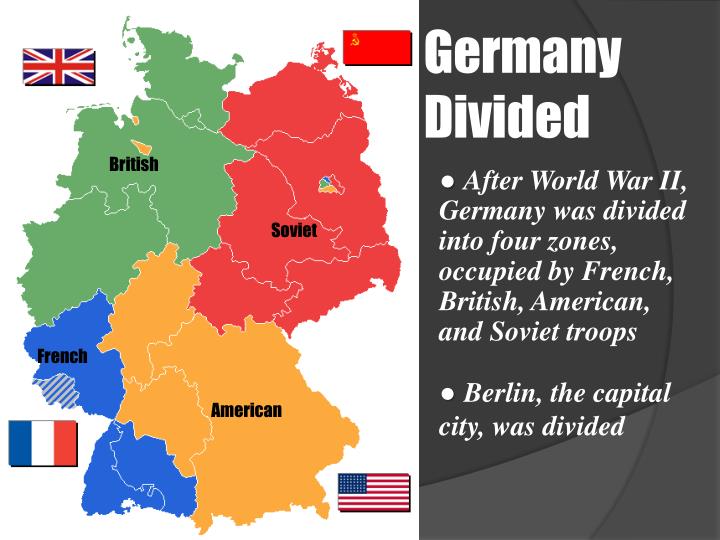
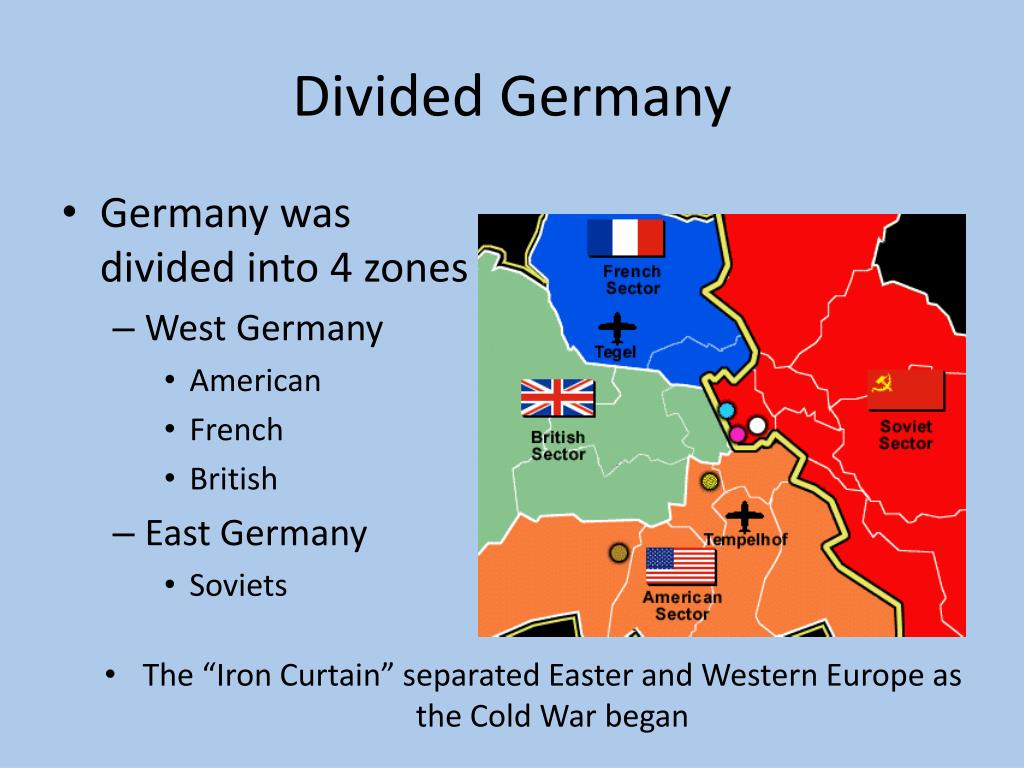
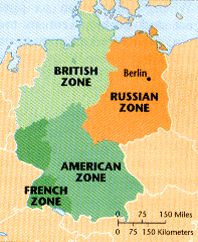
Following the Allied victory in World War II, Germany was occupied by the victorious powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France. This occupation, initially intended to be temporary, transformed into a permanent division. The Soviet Union, having liberated eastern Germany from Nazi control, established a communist regime in the Soviet Occupation Zone (SOZ). The western Allies, meanwhile, fostered democratic governance in their zones, eventually merging them into the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) in 1949. The SOZ, under Soviet control, became the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in the same year.
The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Symbol of Division:
The division of Germany was most dramatically illustrated by the Berlin Wall. Built in 1961, the wall physically separated East and West Berlin, severing families and friends, and becoming a powerful symbol of the Cold War’s division. It served as a stark reminder of the ideological and political gulf that separated the two Germanys and the broader East and West blocs.
The Cold War’s Impact on East Germany:
East Germany, under the control of the Soviet Union, became a communist state, heavily influenced by Soviet policies and ideology. The country’s economy was tightly controlled, with centralized planning and state-owned enterprises. The GDR’s political system was characterized by a single-party rule under the Socialist Unity Party (SED), with limited individual freedoms and suppression of dissent. This system, while achieving relative economic stability, often came at the cost of individual liberties and stifled creativity.
West Germany’s Economic Miracle:
In contrast to East Germany, West Germany experienced a remarkable economic recovery in the post-war era. The Marshall Plan, a massive American aid program, provided much-needed financial assistance to rebuild the nation’s infrastructure and stimulate economic growth. This, coupled with the implementation of free-market policies and a skilled workforce, led to the "Wirtschaftswunder" – the "Economic Miracle" – a period of sustained economic growth and prosperity.
The Cold War’s Shadow on Germany:
The Cold War cast a long shadow over Germany. The country became a crucial battleground in the ideological struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union. The presence of NATO forces in West Germany and the Warsaw Pact forces in East Germany created a constant tension, fueling fears of a potential conflict. The Berlin Wall, a constant reminder of the division, became a focal point of Cold War tensions.
The Fall of the Wall and Reunification:
The Cold War’s grip on Germany finally loosened in the late 1980s. The rise of Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union and his policies of "perestroika" (restructuring) and "glasnost" (openness) led to a period of political and economic liberalization in the Soviet bloc. These changes, coupled with the growing discontent within East Germany, culminated in the dismantling of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989.
The fall of the wall paved the way for the reunification of Germany, which took place on October 3, 1990. The two Germanys, once separated by ideology and a physical barrier, finally became one nation. This reunification, however, was not without its challenges. The integration of East Germany’s economy and society into the West presented significant hurdles, requiring substantial investment and economic restructuring.
The Legacy of the Cold War:
The Cold War’s impact on Germany continues to resonate today. The experience of division, the legacy of the Berlin Wall, and the challenges of reunification have shaped the nation’s political and social landscape. The Cold War also left a lasting mark on German foreign policy, with the nation playing a crucial role in the European Union and advocating for peace and cooperation within Europe.
FAQs about Germany and the Cold War:
1. What were the main reasons for the division of Germany after World War II?
The division of Germany was a result of conflicting ideologies and power struggles between the victorious Allied powers. The Soviet Union sought to establish a communist buffer zone in Eastern Europe, while the Western Allies aimed to prevent Soviet expansion and promote democracy. The division of Germany was a reflection of this geopolitical tension.
2. What was the significance of the Berlin Wall?
The Berlin Wall served as a tangible symbol of the Cold War division, physically separating East and West Berlin and representing the ideological and political gulf between the two blocs. It was a stark reminder of the restrictions imposed on East Germans and the suppression of individual freedoms.
3. How did the Cold War impact the economies of East and West Germany?
The Cold War had a profound impact on the economies of both Germanys. East Germany, under Soviet control, experienced a centrally planned economy with limited individual freedom and economic growth. West Germany, on the other hand, benefited from the Marshall Plan and implemented free-market policies, leading to an economic boom known as the "Wirtschaftswunder."
4. What were the key events that led to the fall of the Berlin Wall and the reunification of Germany?
The fall of the Berlin Wall and the reunification of Germany were a culmination of several factors, including the rise of Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union and his policies of "perestroika" and "glasnost," growing discontent within East Germany, and the pressure from the West for political and economic reforms.
5. What are some of the lasting impacts of the Cold War on Germany?
The Cold War’s impact on Germany continues to be felt today. The experience of division, the legacy of the Berlin Wall, and the challenges of reunification have shaped the nation’s political and social landscape. The Cold War also left a lasting mark on German foreign policy, with the nation playing a crucial role in the European Union and advocating for peace and cooperation within Europe.
Tips for Understanding Germany and the Cold War:
- Study the history of the Cold War: Understanding the global context of the Cold War is essential to comprehending its impact on Germany.
- Explore the history of the division of Germany: Research the events leading to the division, the establishment of the two Germanys, and the significance of the Berlin Wall.
- Learn about the economic and social systems of East and West Germany: Compare and contrast the economic and social conditions in the two Germanys during the Cold War.
- Examine the role of the Cold War in German foreign policy: Understand how the Cold War shaped Germany’s relationship with other countries and its role in international organizations.
- Read primary sources: Explore personal accounts, diaries, and memoirs from individuals who lived through the Cold War in Germany.
Conclusion:
The Cold War left an indelible mark on Germany, shaping its history, politics, and society. The division of the nation, the construction of the Berlin Wall, and the experience of reunification are all testament to the profound impact of this global conflict. While the Cold War ended decades ago, its legacy continues to inform Germany’s place in the world, emphasizing the importance of peace, cooperation, and the pursuit of a unified and prosperous Europe.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Divided Nation: Germany and the Cold War. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
