A Geographic Overview of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
![U.S. Nuclear Power Plants and Production by State [1650x1275] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/IabWt3J8zmHtcCP04mPXZQaKuufPN2t7tvlvUtSatUU.png?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=35c6857a877c048ddb83a9b7b0f8b2ef93024b3b)
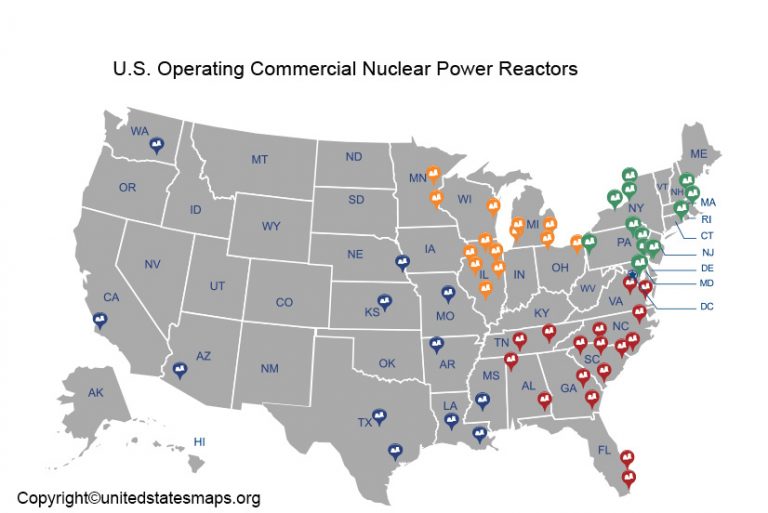
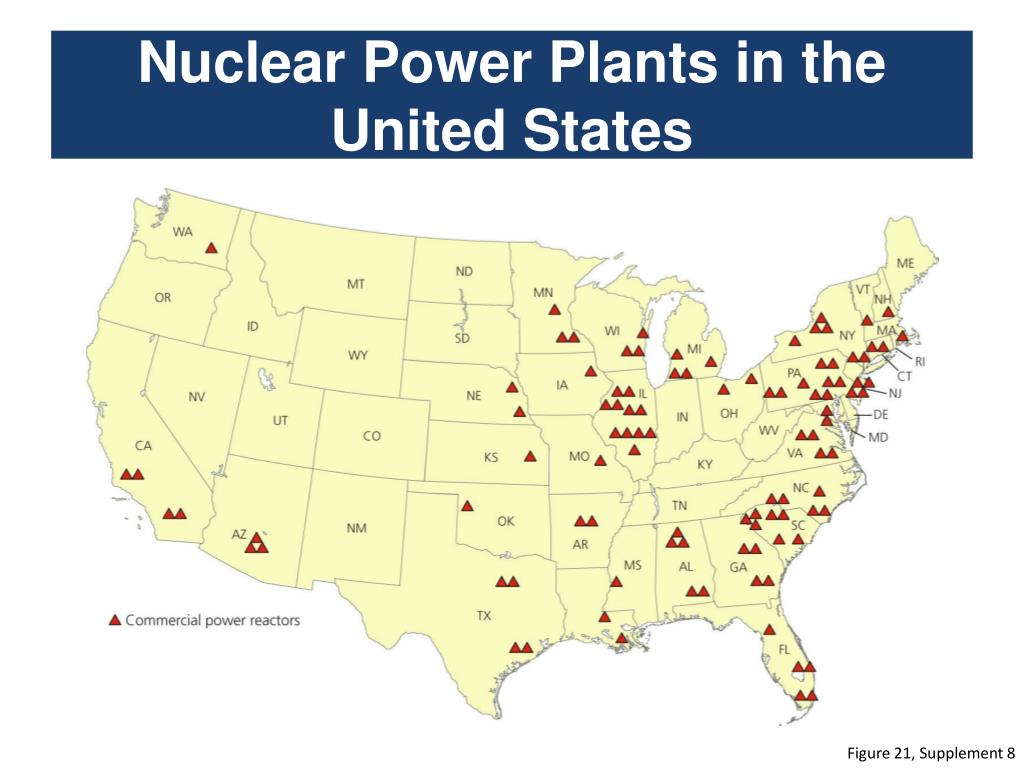
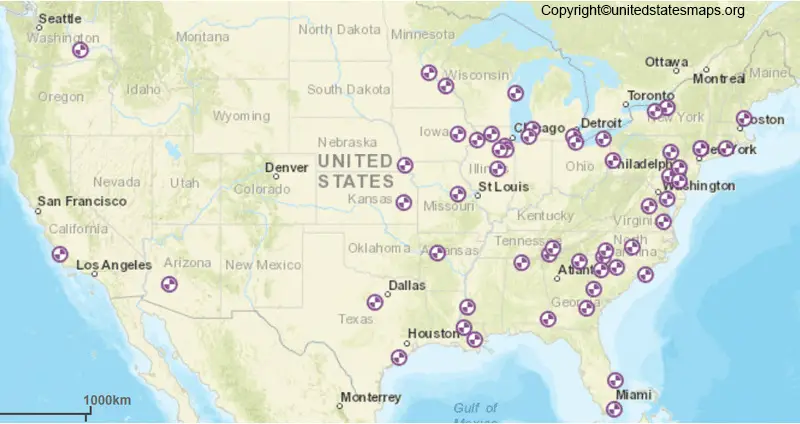
The United States currently operates 92 nuclear power plants across 28 states, generating a significant portion of the nation’s electricity. These facilities, strategically dispersed across the country, represent a vital component of the American energy landscape. Understanding their distribution and characteristics is crucial for comprehending the role of nuclear power in the nation’s energy mix and its potential future.
Geographic Distribution and Concentration:
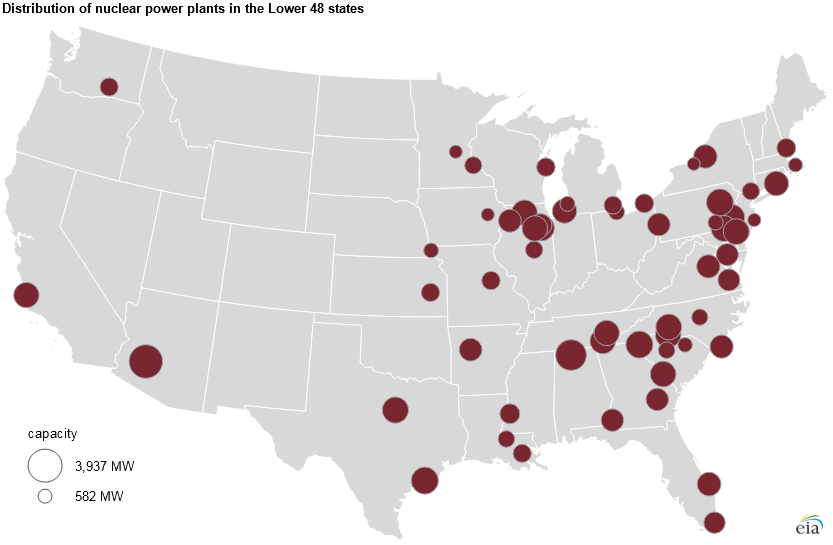
The map of US nuclear plants reveals a non-uniform distribution, with clusters concentrated in specific regions. The Southeast, particularly along the Atlantic coast, boasts a significant number of reactors, with notable concentrations in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. The Midwest, with its industrial heartland, also houses a large number of plants, notably in Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Ohio. The Northeast, particularly in New York and New England, also features a notable presence of nuclear power.
The Western United States, however, exhibits a much lower density of nuclear plants. California, with its emphasis on renewable energy, operates only one operational reactor. Arizona, Washington, and Oregon each have a limited number of plants, reflecting regional energy priorities.
Factors Influencing Plant Location:
Several factors historically influenced the location of nuclear power plants in the United States:
- Proximity to Water Sources: Nuclear power plants require vast amounts of water for cooling purposes. Therefore, they are often situated near large bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, or oceans. This explains the concentration of plants along the coastlines and near major rivers.
- Access to Transportation Infrastructure: The construction and operation of nuclear plants involve the transportation of large, heavy components, fuel, and waste. Therefore, proximity to major transportation networks, including railways and highways, was a crucial factor in site selection.
- Proximity to Population Centers: Nuclear power plants typically generate electricity for nearby urban areas. Locating them within reasonable proximity to major population centers ensured efficient distribution of energy.
- Geological Stability: The stability of the underlying geological formations is paramount for the safe operation of a nuclear power plant. Regions prone to earthquakes or other geological hazards were generally avoided.
- Political and Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment and political climate also played a role in site selection. States with supportive policies and regulations often attracted more nuclear power development.
Types of Reactors and Power Output:
The majority of nuclear power plants in the United States utilize pressurized water reactors (PWRs), which account for approximately 80% of the total capacity. Boiling water reactors (BWRs) constitute the remaining 20%, with some plants employing a combination of both types.
The power output of individual reactors varies significantly, ranging from several hundred megawatts to over 1,000 megawatts. The total generating capacity of all US nuclear power plants exceeds 100,000 megawatts, demonstrating the substantial contribution of nuclear energy to the nation’s electricity supply.
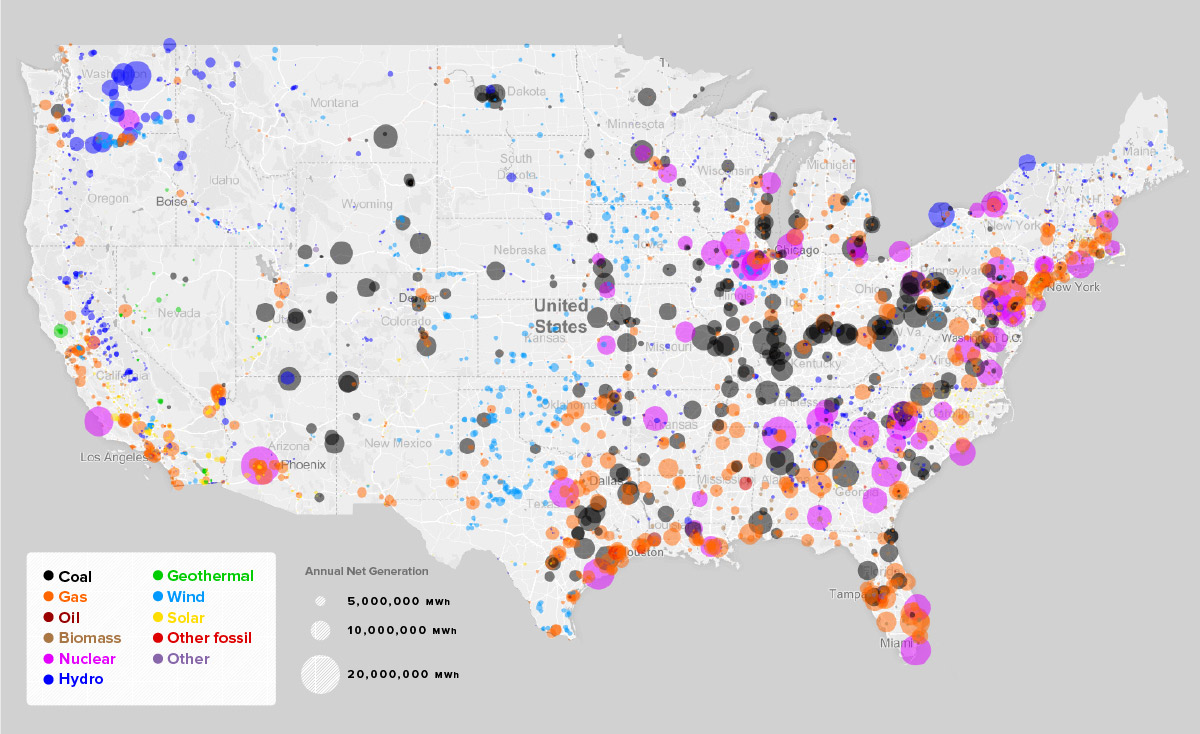
The Role of Nuclear Power in the US Energy Mix:
Nuclear power plays a vital role in the US energy mix, contributing approximately 20% of the nation’s electricity generation. It is a reliable, low-carbon source of energy, providing a significant portion of the baseload power that is essential for maintaining a stable grid.
Benefits of Nuclear Power:
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power plants generate electricity without releasing significant amounts of greenhouse gases, making them a key component of efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Reliable Baseload Power: Nuclear power plants operate consistently, providing a reliable source of baseload power that is essential for maintaining a stable electricity grid.
- Energy Security: Nuclear power reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, contributing to energy security and national independence.
- Job Creation: The construction, operation, and maintenance of nuclear power plants generate numerous jobs in various industries.
Challenges and Considerations:
While nuclear power offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges:
- Nuclear Waste Management: The safe disposal of nuclear waste remains a complex and ongoing challenge.
- Safety Concerns: The potential for accidents, although extremely low, continues to be a concern for some.
- High Initial Costs: The construction of nuclear power plants requires substantial upfront investments, making them a capital-intensive endeavor.
- Public Perception: Public perception of nuclear power remains mixed, with concerns about safety and waste disposal.
Future of Nuclear Power in the United States:
The future of nuclear power in the United States is uncertain, with a number of factors influencing its trajectory. The ongoing debate over climate change and the need for clean energy sources has renewed interest in nuclear power. However, economic factors, regulatory hurdles, and public perception continue to present challenges.
FAQs about Nuclear Power Plants in the US:
Q1: What is the average lifespan of a nuclear power plant in the US?
A: The typical lifespan of a nuclear power plant in the United States is approximately 40 years, although many plants have received extensions to operate for an additional 20 years or more.
Q2: How does the US regulate nuclear power plants?
A: The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is the primary regulatory body for nuclear power plants in the United States. The NRC establishes strict safety regulations, conducts inspections, and licenses the operation of nuclear facilities.
Q3: What are the major safety features of nuclear power plants in the US?
A: US nuclear power plants incorporate numerous safety features, including containment structures, multiple layers of redundancy in safety systems, and rigorous training and operational procedures.
Q4: How is nuclear waste managed in the US?
A: Currently, nuclear waste is stored on-site at nuclear power plants. The US Department of Energy is working on developing a permanent repository for high-level radioactive waste, but no permanent solution has been implemented yet.
Q5: What are the economic benefits of nuclear power in the US?
A: Nuclear power plants provide significant economic benefits, including job creation, tax revenues, and contributions to local economies.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Nuclear Power Plants in the US:
- Focus on the Concentration of Plants: Observe the clusters of nuclear power plants in specific regions and consider the factors that might have influenced their location.
- Consider Regional Energy Mix: Analyze the role of nuclear power in the overall energy mix of different regions, comparing it with the prevalence of other energy sources.
- Research Individual Plants: Explore the characteristics of individual nuclear power plants, including their type, power output, and operational history.
- Stay Informed about Current Events: Keep up-to-date on the latest developments in the nuclear power industry, including plant closures, new construction projects, and policy changes.
Conclusion:
The map of US nuclear power plants provides a visual representation of the significant role this technology plays in the nation’s energy landscape. Understanding its geographic distribution, the factors that influenced plant location, and the benefits and challenges of nuclear power is essential for informed discussions about the future of energy in the United States. As the nation seeks to address climate change and ensure energy security, nuclear power will undoubtedly continue to be a subject of debate and a crucial element of the energy mix.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!