A Geographical Portrait of Russia: A Vast and Diverse Landscape
Related Articles: A Geographical Portrait of Russia: A Vast and Diverse Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Portrait of Russia: A Vast and Diverse Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Portrait of Russia: A Vast and Diverse Landscape

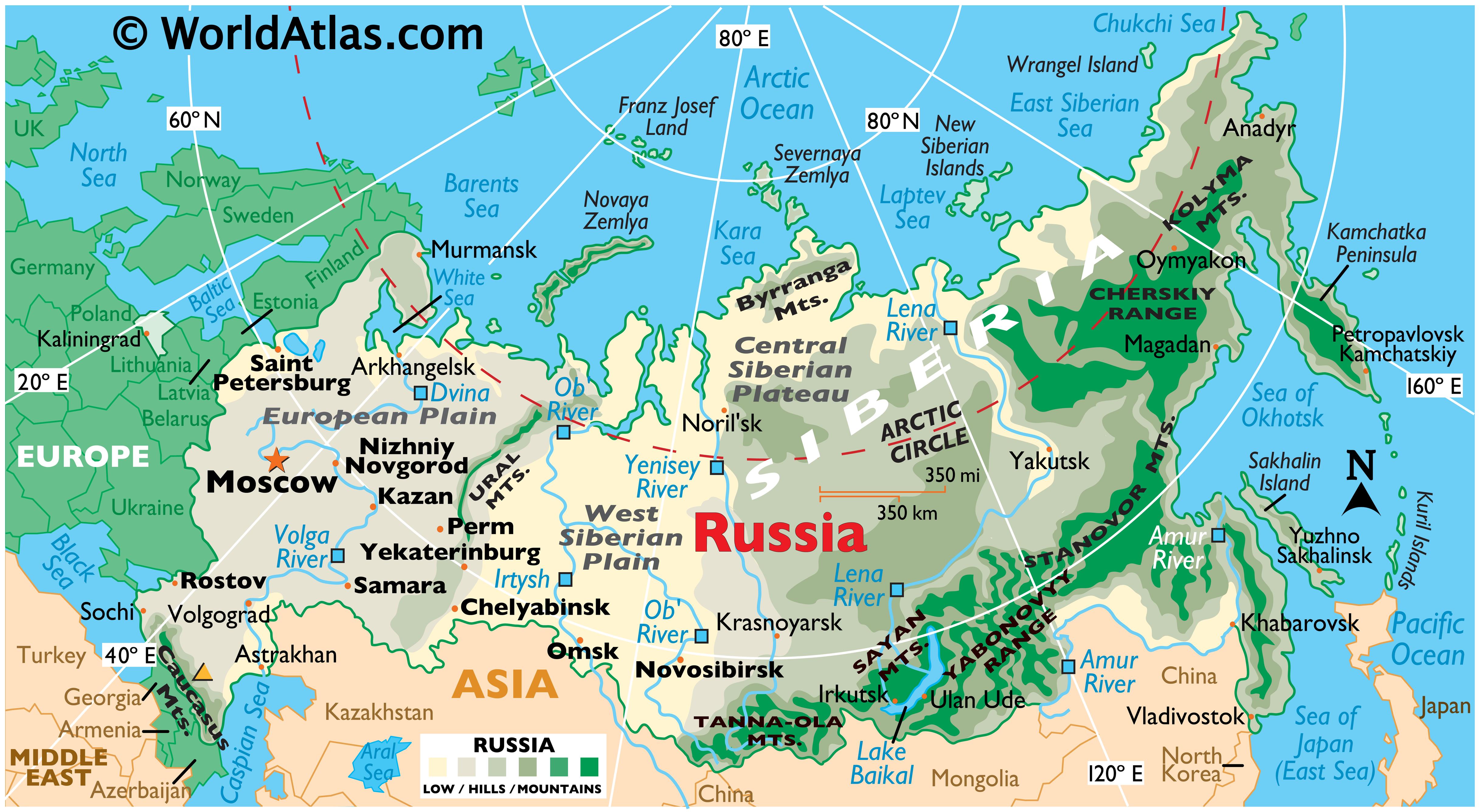
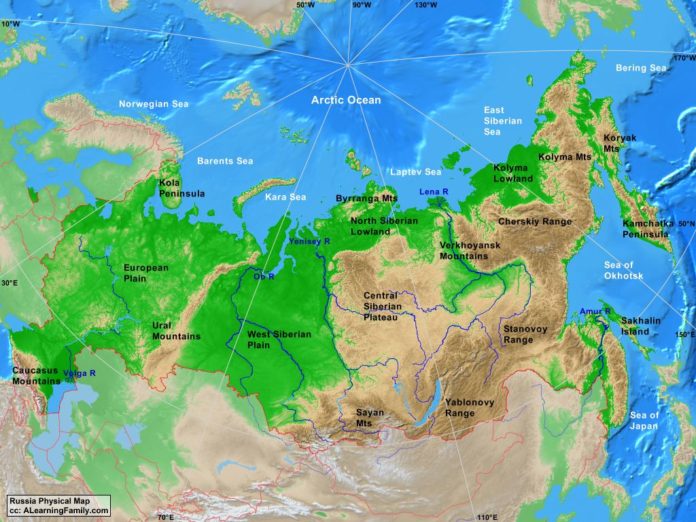
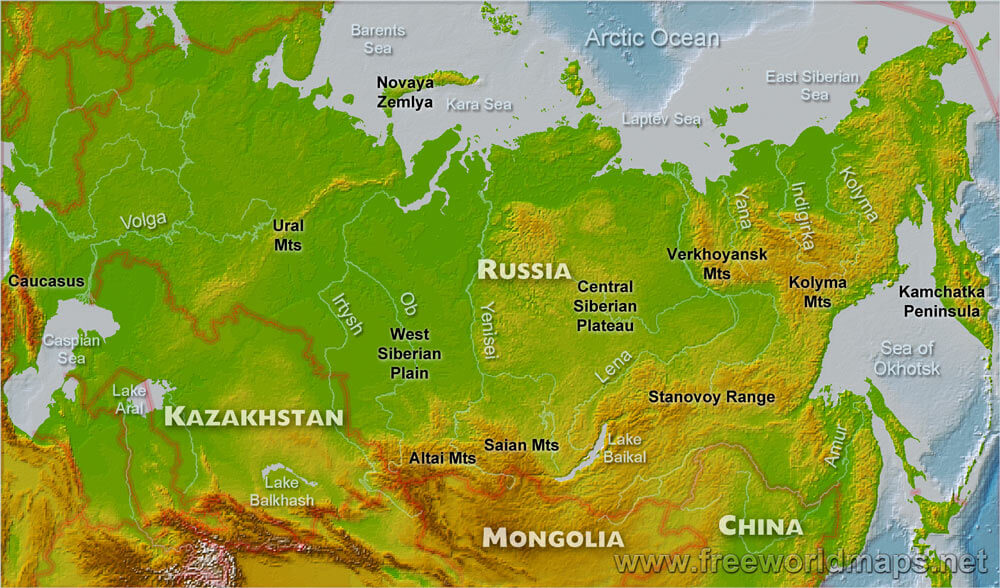
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, stretches across eleven time zones and encompasses a staggering diversity of landscapes, climates, and cultures. Understanding the geographical map of Russia is crucial for comprehending its history, politics, economy, and environmental challenges.
A Land of Extremes:
The vastness of Russia is immediately apparent on any map. Its landmass extends from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, encompassing a range of physical features that are unparalleled in scale and diversity.
-
The European Plain: This vast expanse, covering much of western Russia, is characterized by fertile black earth soils and a relatively flat topography. It is home to some of Russia’s most important agricultural regions and major cities, including Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Nizhny Novgorod.
-
The Ural Mountains: This ancient mountain range, running from north to south, marks the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia. The Urals are rich in mineral resources, particularly iron ore and coal, which have played a significant role in Russia’s industrial development.
-
The Siberian Plain: This vast, flat plain stretches east of the Urals, covering a large portion of Siberia. It is characterized by permafrost, vast coniferous forests, and a harsh, continental climate. The Siberian Plain is sparsely populated but holds significant mineral wealth and vast reserves of natural gas.
-
The Caucasus Mountains: This mountain range, located in the southwest of Russia, is home to Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe. The Caucasus region is characterized by diverse ethnicities and cultures, and its strategic location has made it a historical crossroads.
-
The Far East: This region, bordering the Pacific Ocean, is characterized by its diverse geography, including the Kamchatka Peninsula, with its active volcanoes and geothermal activity. This region is rich in marine resources and is home to unique flora and fauna.
Beyond Topography: Climate and Natural Resources:
Russia’s geography has a profound impact on its climate, which is characterized by extreme variations. The European Plain experiences a humid continental climate with warm summers and cold winters, while Siberia is dominated by a subarctic climate with long, frigid winters and short, cool summers. The Far East experiences a monsoon climate with heavy rainfall during the summer months.
This diverse climate supports a wide range of natural resources, including:
-
Forests: Russia has the largest forest reserves in the world, covering approximately 45% of its territory. These forests are crucial for the country’s timber industry and play a vital role in regulating the global climate.
-
Mineral Resources: Russia is a major producer of oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, and other minerals. These resources are essential for its economy and have fueled its industrial development.
-
Water Resources: Russia has an abundance of freshwater resources, including major rivers like the Volga, Ob, and Yenisei. These rivers are crucial for navigation, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
The Impact of Geography on Russian History and Society:
Russia’s vast geography has shaped its history and culture in profound ways:
-
Expansion and Conquest: The vastness of the Russian landmass allowed for centuries of expansion and conquest, leading to the creation of a vast empire.
-
Isolation and Centralization: Russia’s geographical isolation from Western Europe contributed to its unique cultural development and its strong central government.
-
Transportation and Infrastructure: The vast distances and challenging terrain have posed significant challenges to transportation and infrastructure development.
-
Environmental Challenges: Russia faces significant environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. These challenges are exacerbated by the country’s vast size and diverse geography.
Understanding the Geographical Map of Russia:
A geographical map of Russia is essential for understanding the country’s complexities. It provides a visual representation of its vastness, diverse landscapes, and strategic location. By studying the map, one can gain insights into:
-
The distribution of population and cities: Russia’s population is concentrated in the European part of the country, with vast stretches of Siberia and the Far East remaining sparsely populated.
-
The major transportation routes: Russia’s vast size requires extensive transportation infrastructure, including rail lines, pipelines, and roads.
-
The location of major natural resources: The map reveals the distribution of Russia’s abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and forests.
-
The geopolitical significance of Russia’s borders: Russia shares borders with 14 countries, including major powers like China and the United States. Its strategic location has made it a key player in global affairs.
FAQs about the Geographical Map of Russia:
Q: What are the major cities in Russia?
A: Some of the most significant cities in Russia include Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Chelyabinsk.
Q: What are the main natural resources found in Russia?
A: Russia is rich in oil, natural gas, coal, iron ore, timber, and other mineral resources.
Q: What are the major rivers in Russia?
A: Some of the most important rivers in Russia include the Volga, Ob, Yenisei, Lena, and Amur.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Russia?
A: The major mountain ranges in Russia include the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus Mountains, the Altai Mountains, and the Sayan Mountains.
Q: What are the major climate zones in Russia?
A: Russia experiences a wide range of climates, including humid continental, subarctic, monsoon, and steppe climates.
Tips for Using a Geographical Map of Russia:
-
Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the scale, key, and symbols used on the map.
-
Identify the major geographic features: Locate the major rivers, mountains, plains, and cities on the map.
-
Consider the context: Think about how the geography of Russia has shaped its history, culture, and politics.
-
Use the map as a tool for research: The map can be used to answer questions about Russia’s economy, environment, and society.
Conclusion:
The geographical map of Russia provides a vital tool for understanding this vast and complex country. It reveals the interplay of geography, history, and culture, shedding light on the unique challenges and opportunities that Russia faces in the 21st century. By studying the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diversity and scale of this remarkable nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Portrait of Russia: A Vast and Diverse Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!