A Journey Through Earth’s Giants: Exploring the World’s Mountains on a Map
Related Articles: A Journey Through Earth’s Giants: Exploring the World’s Mountains on a Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Earth’s Giants: Exploring the World’s Mountains on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Earth’s Giants: Exploring the World’s Mountains on a Map
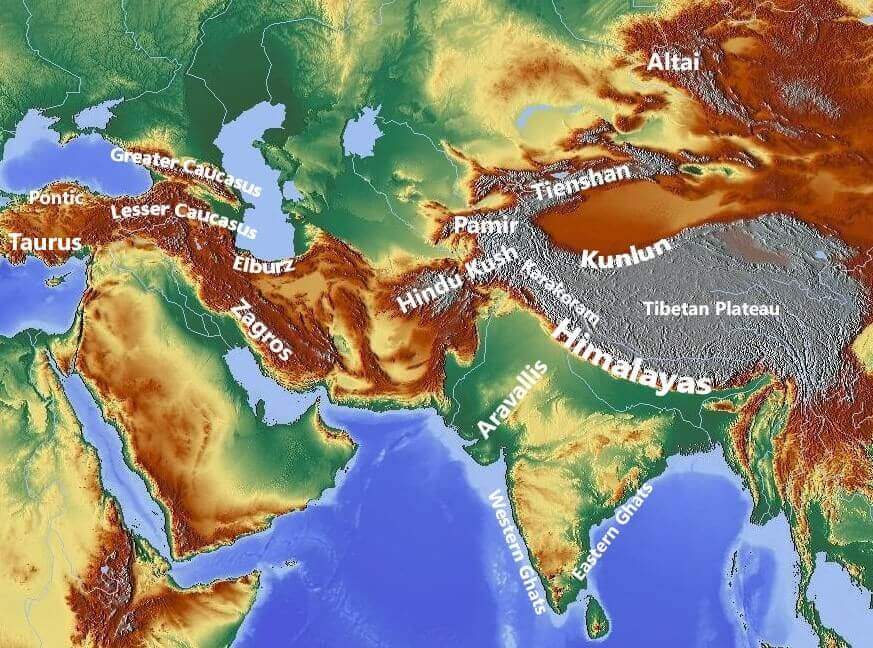
Mountains, those colossal landforms that pierce the sky, are more than just scenic backdrops. They are the products of tectonic forces, cradles of unique ecosystems, and sources of vital resources. Their presence shapes climates, influences human settlements, and inspires awe and wonder. To truly appreciate the grandeur of these natural giants, a world map atlas focused on mountains becomes an invaluable tool.
A World Map Atlas: A Visual Guide to Earth’s Mountain Ranges
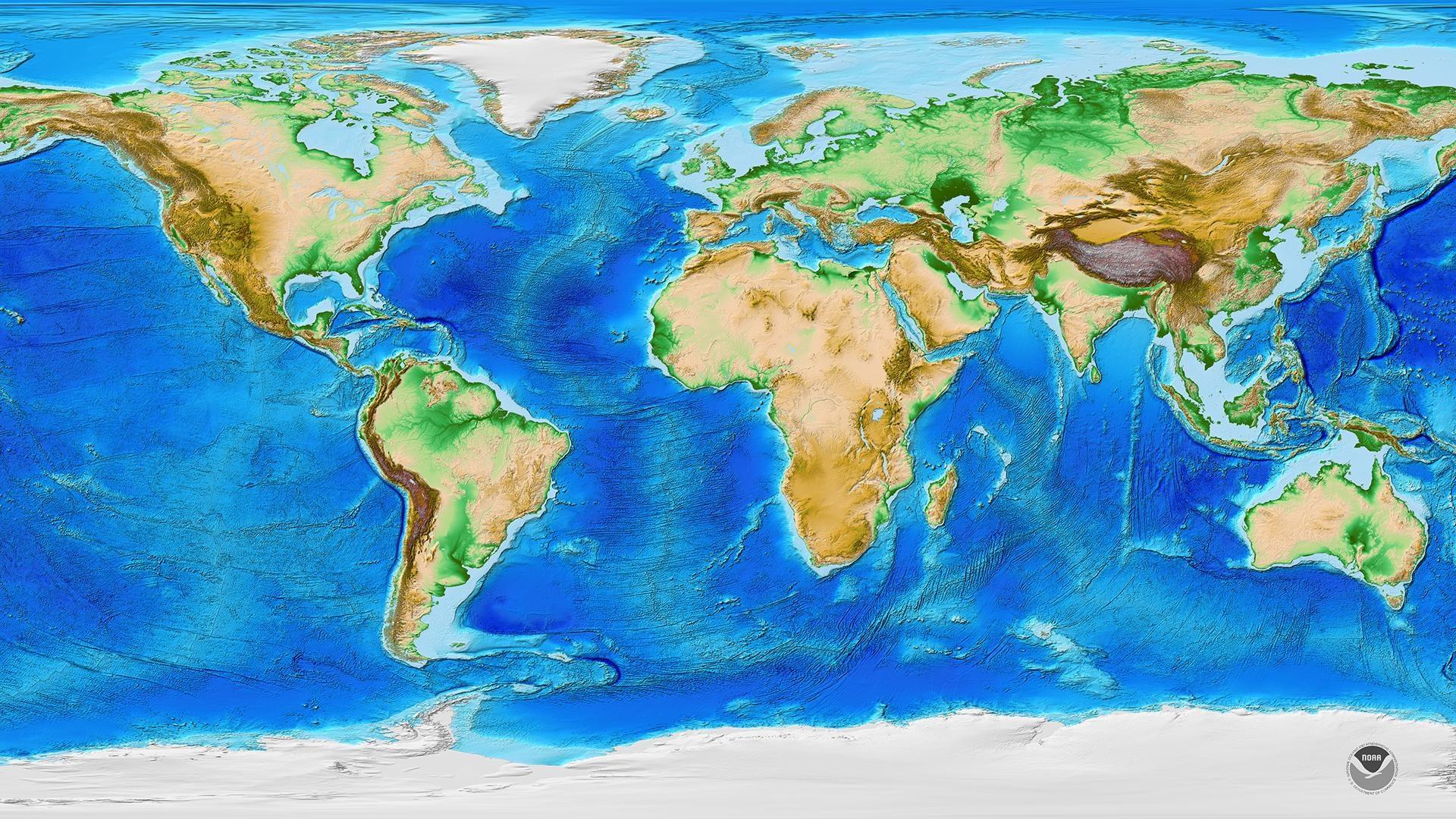
A world map atlas dedicated to mountains offers a comprehensive overview of the planet’s topography, highlighting the distribution and characteristics of major mountain ranges. This visual representation allows for an understanding of:
- Global Distribution: The atlas reveals how mountains are not randomly scattered but clustered in specific regions. The "Ring of Fire," for instance, is a prime example of how tectonic activity along plate boundaries gives rise to volcanic mountain chains.
- Height and Elevation: Atlases often use color gradients or contour lines to depict elevation, enabling a clear visualization of the highest peaks and the overall topography.
- Mountain Ranges: The atlas provides a structured framework for understanding the major mountain ranges, their locations, and their defining features. The Himalayas, the Andes, the Alps, and the Rockies are just a few examples of the diverse mountain ranges that shape the world.
- Geological Formation: Atlases may incorporate information on the geological processes that formed the mountains, including folding, faulting, and volcanic activity. This provides a deeper understanding of the forces that shaped the Earth’s surface.
Beyond the Visual: Exploring the Importance of Mountains
The significance of mountains extends far beyond their visual appeal. They play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s environment and influencing human societies:
- Climate Regulation: Mountains act as barriers to wind and moisture, creating rain shadows and influencing regional climates. They also affect air circulation patterns, leading to diverse weather conditions on different sides of the mountain range.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountains are often home to unique and endemic species, contributing significantly to global biodiversity. Their varied altitudes and microclimates support a wide range of plant and animal life.
- Water Resources: Mountain glaciers and snowfields are important sources of freshwater, providing water for agriculture, drinking, and hydropower generation. They act as natural reservoirs, regulating water flow and ensuring water availability during dry seasons.
- Economic Resources: Mountains contain valuable mineral deposits, timber resources, and hydroelectric potential. They also offer opportunities for tourism, recreation, and outdoor activities.
Challenges and Opportunities: Addressing the Impacts of Climate Change
Mountains are facing increasing challenges due to climate change. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and glacial retreat are impacting ecosystems, water resources, and human livelihoods. Addressing these challenges requires:
- Conservation Efforts: Protecting mountain ecosystems through sustainable land management practices, reducing pollution, and promoting biodiversity conservation.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit the impacts of climate change on mountain environments.
- Adaptation Strategies: Developing strategies to adapt to the changing climate, including water management, disaster preparedness, and community-based adaptation initiatives.
FAQs: Exploring the World’s Mountains
Q: What are the highest mountains in the world?
A: The highest mountains are found in the Himalayas, with Mount Everest (8,848.86 m) being the tallest peak. Other notable peaks include K2 (8,611 m), Kangchenjunga (8,586 m), Lhotse (8,516 m), and Makalu (8,485 m).
Q: How are mountains formed?
A: Mountains are formed primarily through tectonic plate collisions. When two plates collide, the denser plate subducts beneath the less dense plate, causing the crust to buckle, fold, and uplift, creating mountains. Volcanic mountains are formed when magma rises from the Earth’s mantle and erupts on the surface.
Q: What are the different types of mountains?
A: Mountains can be classified based on their formation and characteristics:
- Fold Mountains: Formed by the folding of rock layers, like the Himalayas.
- Fault-Block Mountains: Formed when blocks of rock are uplifted or dropped along faults, like the Sierra Nevada.
- Volcanic Mountains: Formed by the accumulation of lava and ash from volcanic eruptions, like Mount Fuji.
- Dome Mountains: Formed by the upward doming of rock layers, like the Black Hills.
Q: What are the environmental benefits of mountains?
A: Mountains play a crucial role in regulating climate, providing water resources, and supporting biodiversity. They also act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Q: What are the challenges facing mountains today?
A: Mountains are facing challenges such as climate change, deforestation, pollution, and overgrazing, which threaten their ecosystems, water resources, and biodiversity.
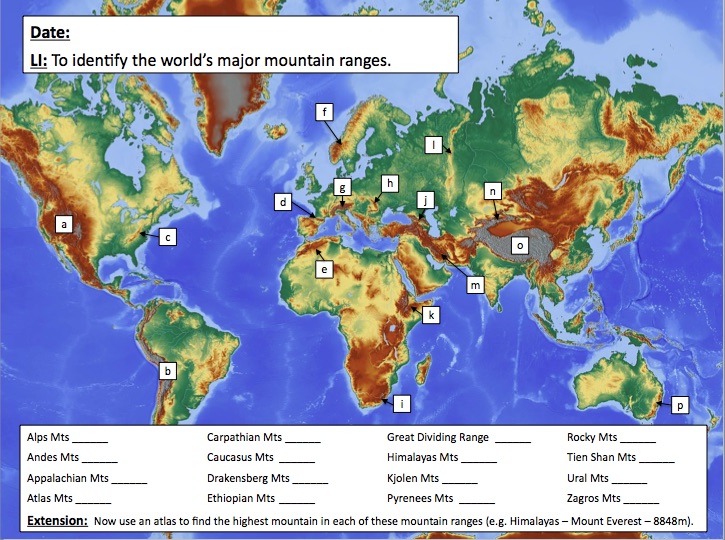
Tips for Exploring Mountains on a World Map Atlas
- Focus on Specific Regions: Instead of trying to encompass the entire world, choose a region or continent and explore its mountain ranges in detail.
- Utilize Different Scales: Use atlases with different scales to compare mountain ranges and their relative heights.
- Connect with the Landscape: Use the atlas to identify key features like rivers, lakes, and vegetation, which can help visualize the mountain environment.
- Explore Beyond the Peaks: Look beyond the tallest peaks to understand the entire mountain range, including valleys, plateaus, and foothills.
- Combine with Other Resources: Use the atlas in conjunction with other resources like travel guides, documentaries, and online maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of mountains.
Conclusion: A Window to the World’s Natural Wonders
A world map atlas focused on mountains serves as a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s topography, appreciating the grandeur of these natural wonders, and recognizing their vital role in shaping our planet and influencing our lives. By using this tool, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and the importance of protecting these magnificent landforms for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Earth’s Giants: Exploring the World’s Mountains on a Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!