A Tapestry of Green: Understanding the Global Distribution of Grasslands
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Green: Understanding the Global Distribution of Grasslands
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Green: Understanding the Global Distribution of Grasslands. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Green: Understanding the Global Distribution of Grasslands

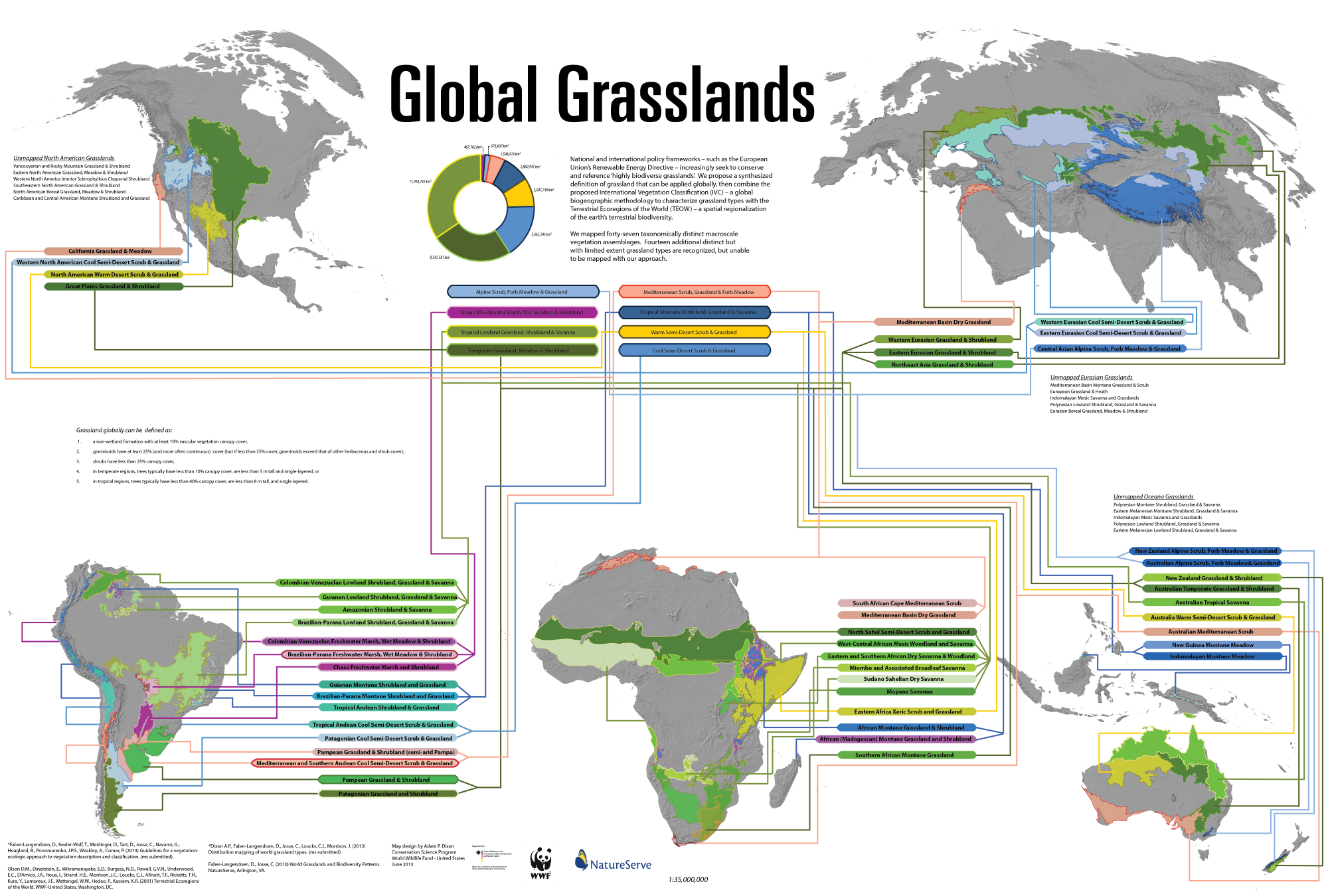
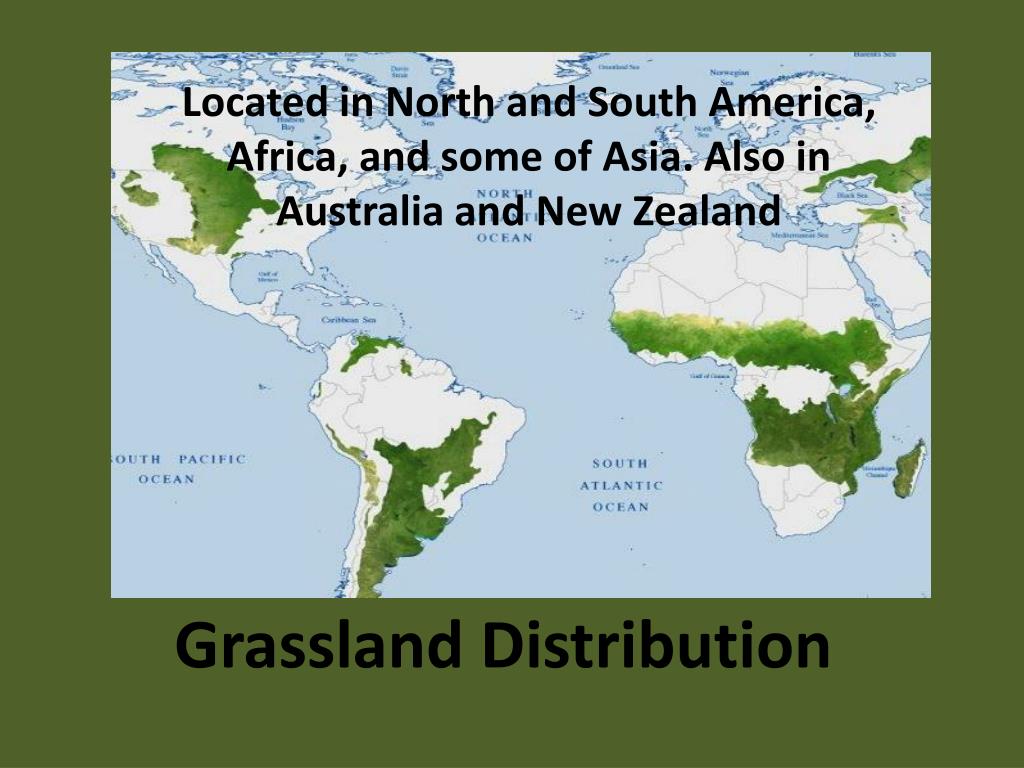
Grasslands, often referred to as prairies, savannas, or steppes, are vast ecosystems characterized by a dominant presence of grasses, with varying proportions of herbaceous plants and scattered trees. They are found on every continent except Antarctica, covering a significant portion of the Earth’s land surface. These diverse ecosystems play a critical role in global biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and human sustenance. Understanding their distribution and the factors influencing their unique characteristics is crucial for their conservation and management.
Mapping the Green Canvas: A Global Perspective
Visualizing the global distribution of grasslands is essential for comprehending their ecological significance and the threats they face. Maps serve as powerful tools for showcasing the vast expanse of these ecosystems, highlighting their diverse forms, and revealing their geographic connections.
A Spectrum of Grasslands:
The world’s grasslands exhibit remarkable diversity, reflecting the interplay of climate, soil conditions, and geographic location. This diversity is reflected in the various names given to these ecosystems:
-
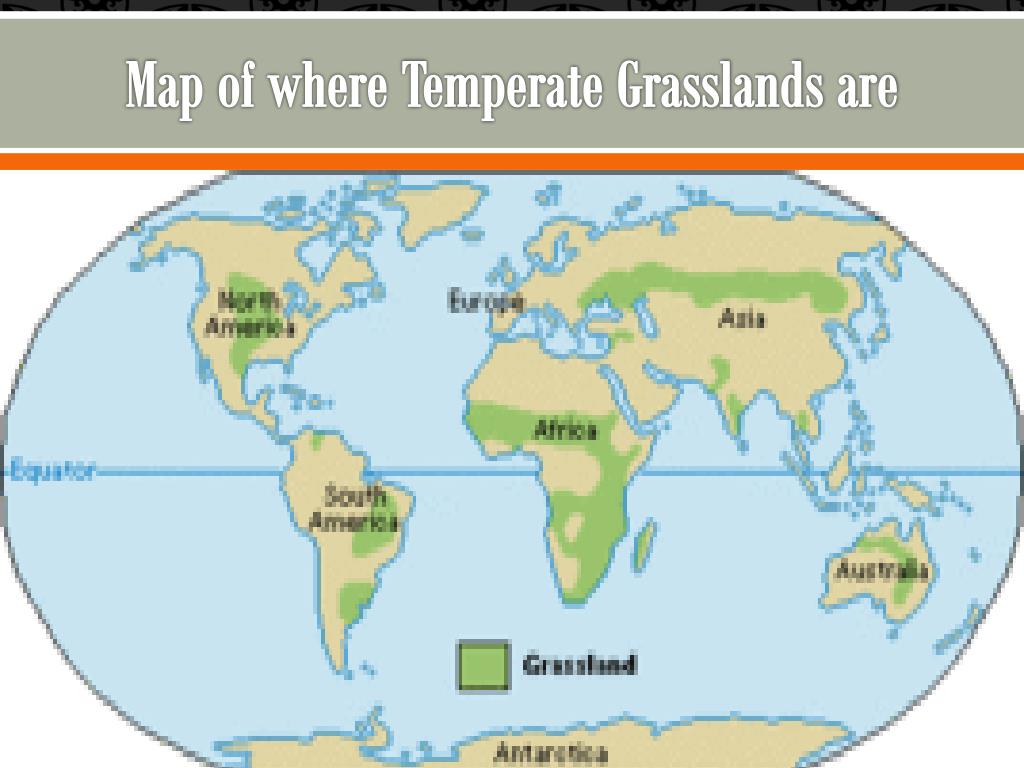
Temperate Grasslands: Found in mid-latitude regions with moderate rainfall and distinct seasons, these grasslands are often characterized by tall grasses and a rich diversity of wildflowers. Examples include the North American prairies, the Eurasian steppes, and the Pampas of South America.
-
Tropical Savannas: Occurring in tropical and subtropical regions with distinct wet and dry seasons, these grasslands feature scattered trees and shrubs amidst a sea of grasses. The African savannas, with their iconic herds of grazing animals, are a prime example.
-
Mediterranean Grasslands: Located in regions with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, these grasslands are characterized by drought-tolerant grasses and a diverse array of wildflowers. The Mediterranean Basin and parts of California showcase this type of grassland.
-
Alpine Grasslands: Found at high altitudes, these grasslands are characterized by low-growing grasses and a harsh climate. The alpine meadows of the Himalayas and the Andes are prime examples.
Factors Shaping the Grassland Tapestry:
Several key factors influence the distribution and characteristics of grasslands worldwide:
-
Climate: Rainfall patterns, temperature fluctuations, and seasonal variation play a crucial role in determining the type of grasses that can thrive in a given region.
-
Soil: Soil type, fertility, and drainage influence the composition and productivity of grassland vegetation.
-
Fire: Natural fires are a significant factor in many grasslands, playing a role in shaping plant communities and maintaining the openness of the ecosystem.
-
Herbivory: Grazing animals, such as bison, zebras, and kangaroos, are important drivers of grassland structure and dynamics.
The Importance of Grasslands:
Grasslands are more than just vast expanses of green. They provide a multitude of ecological and economic benefits:
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: Grasslands harbor a remarkable diversity of plant and animal life, including many endemic species.
-
Carbon Sequestration: Grasslands play a vital role in absorbing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide, contributing to climate regulation.
-
Water Regulation: Grassland ecosystems help regulate water cycles, contributing to groundwater recharge and flood control.
-
Food and Fiber Production: Grasslands are essential for livestock grazing and the production of hay and other agricultural products.
-
Recreation and Tourism: Grasslands offer opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing.
Threats to Grassland Ecosystems:
Despite their importance, grasslands face a range of threats:
-
Land Use Change: Conversion of grasslands to agricultural land, urban development, and infrastructure projects are major drivers of habitat loss.
-
Overgrazing: Excessive grazing pressure can degrade grasslands, leading to soil erosion and loss of biodiversity.
-
Invasive Species: Introduction of non-native plant and animal species can disrupt grassland ecosystems.
-
Climate Change: Changes in precipitation patterns, temperature extremes, and increased drought can negatively impact grassland ecosystems.
Conservation and Management:
Protecting and managing grasslands requires a multifaceted approach:
-
Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas helps conserve grassland biodiversity and maintain ecosystem services.
-
Sustainable Land Management: Implementing practices that promote soil health, reduce grazing pressure, and control invasive species are crucial for grassland conservation.
-
Restoration: Restoring degraded grasslands can help revitalize these ecosystems and enhance their resilience.
-
Public Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of grasslands and the threats they face is essential for promoting conservation efforts.
FAQs about Grasslands:
Q: What is the largest grassland in the world?
A: The largest contiguous grassland in the world is the Eurasian Steppe, stretching across vast swathes of Eastern Europe and Asia.
Q: Are all grasslands similar?
A: No, grasslands exhibit significant variation in their plant and animal communities, reflecting the unique environmental conditions of each region.
Q: Why are grasslands important for climate change mitigation?
A: Grasslands act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide, helping to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations.
Q: How can I help protect grasslands?
A: You can support grassland conservation by supporting organizations working to protect these ecosystems, choosing sustainable products, and reducing your carbon footprint.
Tips for Understanding Grasslands:
-
Explore local grasslands: Visit a nearby grassland to observe its unique features and understand the role it plays in the local ecosystem.
-
Learn about grassland plants and animals: Research the diverse plant and animal life that call grasslands home.
-
Support sustainable land management practices: Encourage farmers and ranchers to adopt practices that promote grassland health.
-
Advocate for grassland conservation: Raise awareness about the importance of grasslands and the threats they face.
Conclusion:
Grasslands, in all their diverse forms, are essential components of the global ecosystem. Their intricate web of life, their role in carbon sequestration, and their contributions to human well-being underscore their importance. By understanding their distribution, the factors shaping their characteristics, and the threats they face, we can work towards ensuring the long-term health and resilience of these vital ecosystems. Through conservation, sustainable management, and public awareness, we can ensure that the green tapestry of grasslands continues to flourish for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Green: Understanding the Global Distribution of Grasslands. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!