A Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the Indian Mountain Map
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the Indian Mountain Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the Indian Mountain Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the Indian Mountain Map
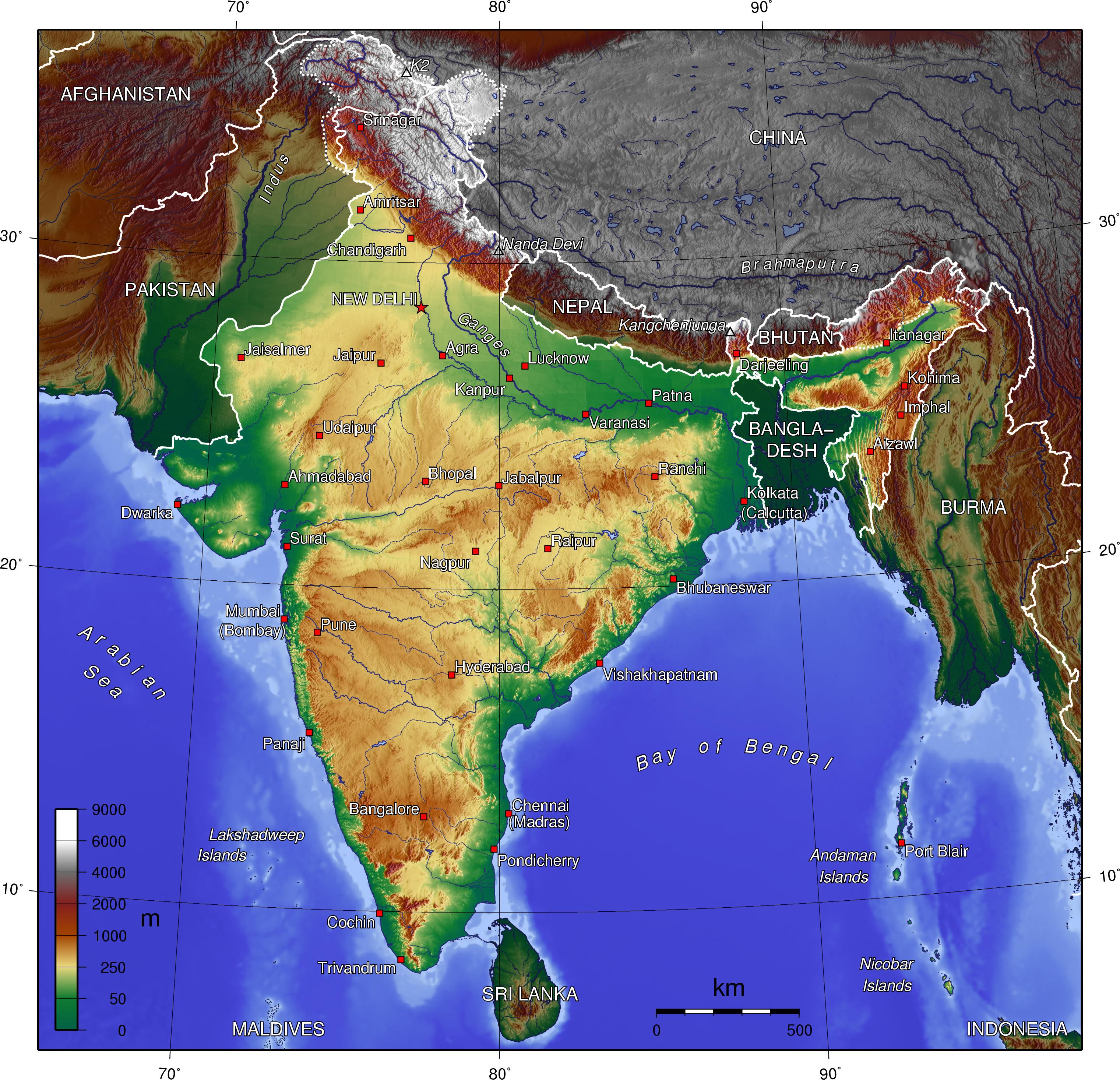
The Indian subcontinent, a land of diverse landscapes, is home to a magnificent tapestry of mountain ranges, each with its unique character and significance. These towering peaks, sculpted by tectonic forces over millions of years, define the geography, climate, and cultural identity of the nation. Understanding the Indian mountain map is crucial for appreciating the country’s rich natural heritage and its profound impact on human life.
The Himalayan Giants:
The most iconic feature of the Indian mountain map is undoubtedly the Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range. This formidable chain, stretching across the northern border of India, is a testament to the Earth’s dynamic nature. It holds the eight highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest, the "Roof of the World." The Himalayas are a vital water source, feeding major rivers like the Ganga and the Brahmaputra, which sustain millions of people downstream.
The Karakoram and the Hindu Kush:
Adjacent to the Himalayas are the Karakoram and the Hindu Kush ranges, both characterized by rugged peaks and vast glaciers. The Karakoram, which includes the second-highest peak, K2, is known for its extreme terrain and challenging climbs. The Hindu Kush, on the other hand, forms a natural boundary between Afghanistan and Pakistan, its slopes supporting diverse ecosystems and cultural traditions.
The Eastern Ranges:
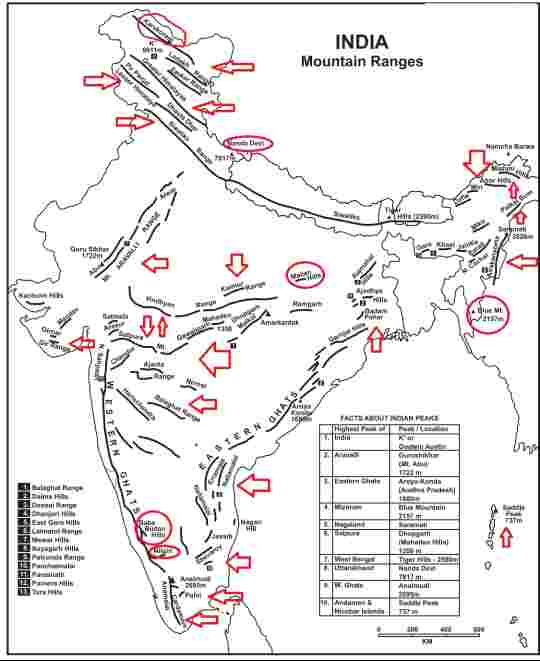
East of the Himalayas, the Indian mountain map features a series of lower but equally significant ranges. The Patkai, Naga, and Lushai hills, collectively known as the "Seven Sister Hills," are home to a rich tapestry of tribal communities, each with its own unique language, customs, and traditions. These ranges also play a crucial role in regulating rainfall patterns and supporting biodiversity.
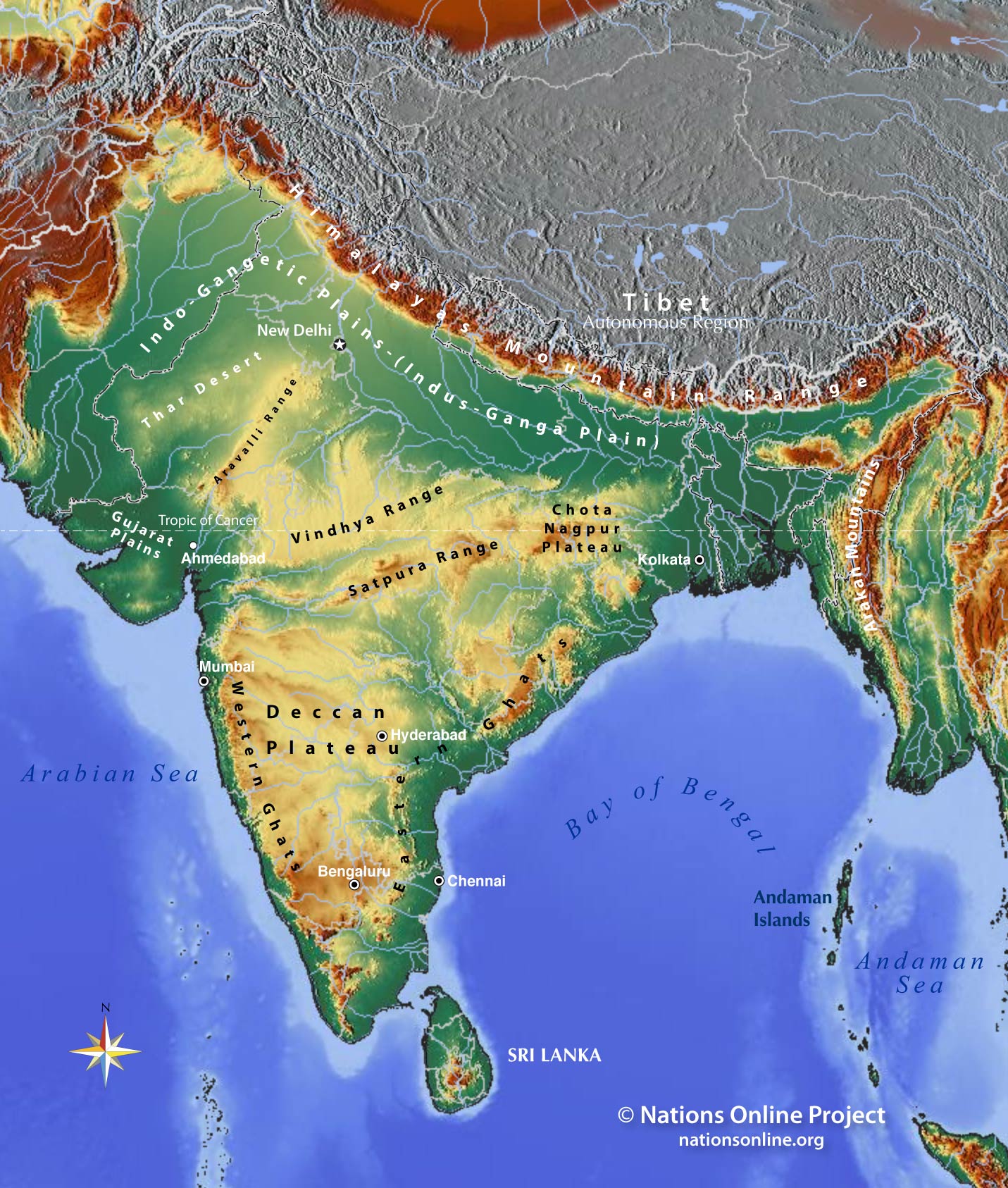
The Western Ghats:
On the western coast of India, the Western Ghats rise dramatically from the Arabian Sea. This range, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a biodiversity hotspot, harboring a wide range of flora and fauna. The Western Ghats are also vital for water security, providing water for major cities and agricultural areas.
The Vindhyas and the Satpuras:
Central India is characterized by the Vindhya and Satpura ranges, two ancient mountain systems that have shaped the region’s geology and culture. These ranges, though less imposing than the Himalayas, are nonetheless important for their mineral resources, wildlife sanctuaries, and historical significance.
Understanding the Importance:
The Indian mountain map is not merely a collection of geographical features; it is a living entity that has profoundly shaped the country’s history, culture, and economy.
Ecological Significance:
- Water Security: The mountains are the source of numerous rivers that sustain millions of people and irrigate vast agricultural lands.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The Himalayan and Western Ghat ranges are home to a vast array of flora and fauna, many of which are endemic to the region.
- Climate Regulation: The mountains play a crucial role in regulating rainfall patterns and moderating temperatures, influencing the climate of the entire subcontinent.
Cultural Significance:
- Home to Diverse Communities: The mountains are home to a multitude of tribal communities, each with its own unique culture, language, and traditions.
- Spiritual Significance: Many mountain peaks and rivers hold religious and spiritual significance for various faiths, making them pilgrimage sites for millions.
- Architectural Heritage: The mountains have inspired unique architectural styles, from the ancient cave temples of Ajanta and Ellora to the magnificent palaces of the Himalayas.
Economic Significance:
- Tourism: The mountains are a major tourist destination, attracting visitors from all over the world for their breathtaking scenery, adventure activities, and cultural experiences.
- Mineral Resources: The mountains are rich in mineral resources, including iron ore, bauxite, and copper, which contribute significantly to the Indian economy.
- Hydropower: The mountain rivers provide immense potential for hydropower generation, contributing to the country’s energy security.
Challenges and Conservation:
While the Indian mountain map is a source of immense wealth and beauty, it also faces several challenges:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and erratic rainfall patterns are threatening the delicate ecosystems and glaciers of the mountains.
- Deforestation: Unsustainable logging and agricultural practices are leading to deforestation, causing soil erosion and landslides.
- Pollution: Industrial activities and urbanization are contributing to air and water pollution, impacting the health of the mountain communities and ecosystems.
- Overtourism: The increasing influx of tourists is putting pressure on fragile ecosystems and cultural heritage sites.
Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the importance of the mountains, the Indian government has implemented several conservation initiatives, including:
- National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries: Establishing protected areas to conserve biodiversity and protect endangered species.
- Reforestation Programs: Promoting tree planting and afforestation to combat deforestation and restore degraded ecosystems.
- Sustainable Tourism Initiatives: Encouraging responsible tourism practices to minimize environmental impact and preserve cultural heritage.
- Climate Change Mitigation Strategies: Implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changing climate.
FAQs about the Indian Mountain Map:
Q: What are the highest peaks in the Indian Himalayas?
A: The highest peaks in the Indian Himalayas are:
- Mount Everest (8,848.86 m)
- Kangchenjunga (8,586 m)
- Lhotse (8,516 m)
- Makalu (8,485 m)
- Cho Oyu (8,188 m)
- Dhaulagiri I (8,167 m)
- Manaslu (8,163 m)
- Nanga Parbat (8,126 m)
Q: Which mountain range is home to the "Seven Sister Hills"?
A: The "Seven Sister Hills" refer to the Patkai, Naga, and Lushai ranges, located in the northeastern part of India.
Q: What is the significance of the Western Ghats?
A: The Western Ghats are a UNESCO World Heritage Site, known for their rich biodiversity, vital role in water security, and unique ecosystems.
Q: What are the major rivers originating from the Himalayas?
A: The major rivers originating from the Himalayas include:
- Ganga
- Brahmaputra
- Yamuna
- Indus
- Sutlej
- Beas
- Ravi
Q: What are the main challenges faced by the Indian mountains?
A: The main challenges faced by the Indian mountains include climate change, deforestation, pollution, and overtourism.
Tips for Exploring the Indian Mountain Map:
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the different regions and choose destinations that align with your interests and fitness level.
- Respect the local culture: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, and dress appropriately when visiting religious sites.
- Be prepared for the weather: Pack warm clothing, waterproof gear, and appropriate footwear, as weather conditions can change rapidly in the mountains.
- Hire a local guide: Engaging a local guide can enhance your experience, provide valuable insights, and ensure your safety.
- Leave no trace: Pack out all trash, avoid disturbing wildlife, and minimize your impact on the environment.
Conclusion:
The Indian mountain map is a testament to the country’s incredible natural beauty and diversity. These towering peaks, with their rugged landscapes and diverse ecosystems, are a vital resource for millions of people and a source of inspiration for generations to come. Understanding the Indian mountain map is crucial for appreciating the country’s rich heritage, addressing the challenges it faces, and ensuring its sustainable future. By embracing responsible practices, promoting conservation efforts, and fostering a deep appreciation for the mountains, we can preserve this precious natural legacy for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the Indian Mountain Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!