A Visual Guide to the Global Landscape: Understanding the Map of Developing Countries
Related Articles: A Visual Guide to the Global Landscape: Understanding the Map of Developing Countries
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Visual Guide to the Global Landscape: Understanding the Map of Developing Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Guide to the Global Landscape: Understanding the Map of Developing Countries
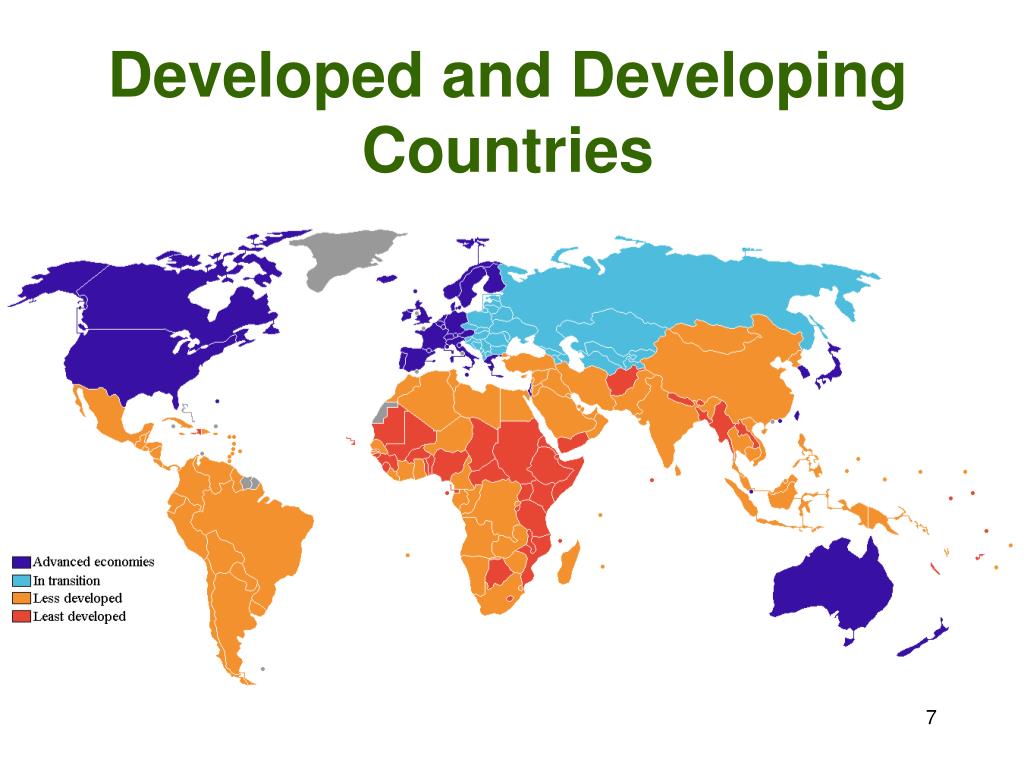
The world is a tapestry of diverse nations, each with its unique story of development. While some countries have achieved high levels of economic prosperity and social well-being, others are still navigating the path towards progress. This journey is often visualized through the categorization of countries into "developed" and "developing," a classification that, while simplified, provides a valuable framework for understanding global disparities and opportunities.
A map of developing countries serves as a powerful tool for visualizing this global landscape. It offers a spatial representation of the challenges and potential of nations undergoing economic and social transformation. Examining this map reveals crucial insights into the distribution of development across the globe, highlighting geographical patterns and regional disparities.
Understanding the Terminology
The terms "developed" and "developing" are often used interchangeably with "high-income" and "low- and middle-income" countries, respectively. These classifications are based on economic indicators such as Gross National Income (GNI) per capita, Human Development Index (HDI), and other measures of social and economic progress. While these classifications provide a starting point for analysis, it is crucial to acknowledge their limitations. They do not capture the nuances of individual countries’ development journeys, and many nations fall within a spectrum of development, defying simplistic binary categorizations.
Visualizing Development: Insights from the Map
The map of developing countries reveals several key observations:
- Geographical Distribution: The majority of developing countries are located in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. This geographical clustering suggests that historical factors, colonial legacies, and geopolitical dynamics have shaped the current development landscape.
- Regional Disparities: Within continents, significant disparities exist in development levels. For instance, within Africa, countries like Botswana and Mauritius have achieved remarkable progress, while others face significant challenges.
- Emerging Economies: The map also highlights the rise of emerging economies, particularly in Asia, such as China, India, and Indonesia. These countries are rapidly transitioning towards higher levels of economic activity and technological advancement.
- Focus on Sustainable Development: The map emphasizes the importance of sustainable development goals, recognizing the need for economic growth that is environmentally responsible and socially inclusive.
The Importance of the Map
The map of developing countries serves as a valuable tool for various stakeholders:
- Policymakers: The map provides a visual representation of development priorities and allows policymakers to identify areas requiring targeted interventions and investment.
- International Organizations: International organizations like the United Nations and the World Bank use the map to allocate resources and tailor development programs to specific contexts.
- Researchers: Academics and researchers use the map to analyze development trends, identify patterns, and conduct comparative studies across countries.
- Businesses: The map helps businesses identify potential markets, assess investment opportunities, and understand the social and economic landscape of developing countries.
- Civil Society: Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and other civil society groups utilize the map to understand the needs of communities and prioritize their efforts in promoting development and social justice.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Map of Developing Countries:
1. Why are some countries classified as "developing"?
Countries are classified as "developing" based on a combination of factors, including economic indicators (GNI per capita), social indicators (literacy rates, life expectancy), and human development indicators (HDI). These factors reflect the level of economic activity, social progress, and overall well-being within a nation.
2. Does the map accurately reflect the complexities of development?
The map provides a simplified snapshot of the global development landscape. It is crucial to recognize that development is a multi-faceted process, and individual countries may face unique challenges and opportunities. The map should be used as a starting point for further analysis and understanding of specific contexts.
3. How can the map be used to promote development?
The map can serve as a visual guide for policymakers, international organizations, and other stakeholders to identify areas requiring targeted interventions, allocate resources effectively, and design development programs tailored to specific needs.
4. What are the limitations of using the map?
The map does not capture the nuances of individual countries’ development journeys. It is a static representation of a dynamic process, and development indicators can change over time. Additionally, the map does not account for factors such as social inequality, political instability, and environmental challenges, which can significantly impact development outcomes.
Tips for Using the Map of Developing Countries Effectively:
- Consider the context: Recognize the limitations of the map and avoid making generalizations about entire countries based solely on their classification.
- Focus on specific indicators: Explore data beyond the simple "developed" or "developing" categorization to gain a deeper understanding of individual countries’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Engage with local communities: Seek perspectives from individuals and communities within developing countries to understand their unique experiences and priorities.
- Promote collaboration and partnerships: Recognize that development is a collaborative process, and encourage partnerships between governments, international organizations, businesses, and civil society to address shared challenges.
Conclusion
The map of developing countries is a powerful visual tool for understanding the global landscape and the challenges and opportunities facing nations in their pursuit of progress. It highlights the need for a nuanced understanding of development, recognizing the diversity of experiences and the importance of tailored solutions. By utilizing the map effectively and engaging with local perspectives, we can contribute to a more equitable and sustainable future for all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Guide to the Global Landscape: Understanding the Map of Developing Countries. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!