Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Significance
Related Articles: Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Significance
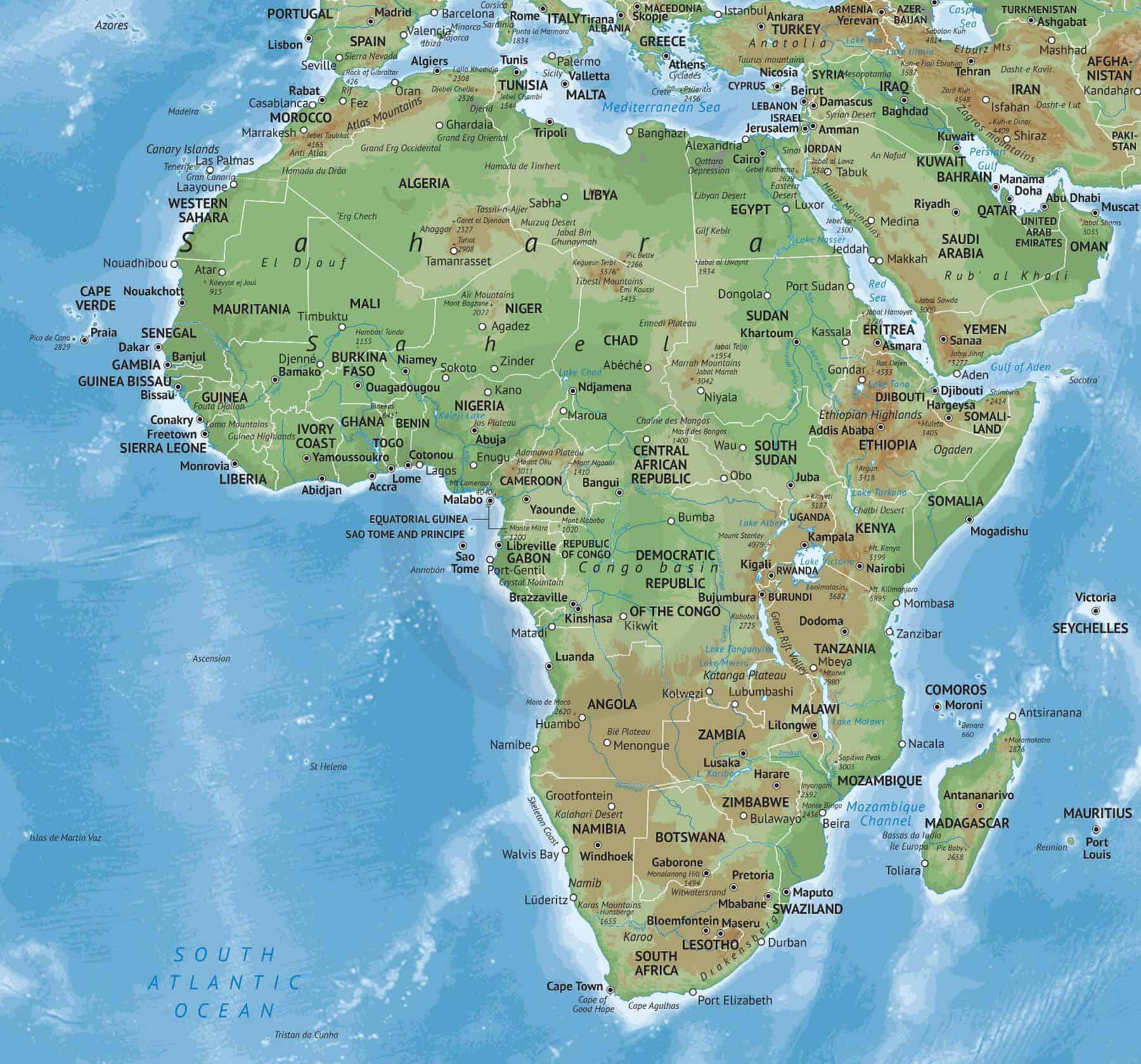
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a vast and diverse landmass situated in the eastern hemisphere. Its geographical location, spanning both the northern and southern hemispheres, plays a pivotal role in its unique characteristics and global significance.
Location and Boundaries:
Africa is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Indian Ocean to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south. It is strategically positioned between Europe and Asia, making it a crossroads of history, culture, and trade. The continent’s geographical coordinates range from approximately 37° North to 35° South latitude and from 17° West to 51° East longitude.
Geographical Features:
Africa’s varied landscape is a testament to its vast size and complex geological history. It encompasses a wide range of geographical features, including:
- Deserts: The Sahara, the world’s largest hot desert, dominates North Africa. Other notable deserts include the Namib and Kalahari in southern Africa.
- Mountains: The Atlas Mountains in North Africa and the Drakensberg Mountains in southern Africa are prominent mountain ranges. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak, is located in Tanzania.
- Rivers: The Nile River, the longest river in the world, flows through eastern Africa. Other major rivers include the Congo, Niger, and Zambezi.
- Lakes: Africa is home to numerous lakes, including Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa and the second-largest freshwater lake in the world. Lake Tanganyika and Lake Malawi are also significant.
- Plateaus: The Ethiopian Highlands and the East African Plateau are vast elevated regions with diverse ecosystems.
Climate Zones:
Africa’s geographical location and varied topography give rise to a wide range of climate zones:
- Tropical Rainforest: Found in the equatorial regions, characterized by high rainfall and humidity.
- Savanna: A vast grassland region with distinct wet and dry seasons, supporting a diverse range of wildlife.
- Desert: Characterized by extreme temperatures, low rainfall, and arid conditions.
- Mediterranean: Found in the northern and southern tips of the continent, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
Biodiversity and Resources:
Africa is renowned for its exceptional biodiversity, boasting a wide variety of flora and fauna. It is home to an estimated 20% of the world’s bird species and a significant portion of the world’s mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. The continent’s rich natural resources include vast reserves of minerals, oil, and gas.
Human Geography:
Africa is the second-most populous continent, with a diverse population of over 1.3 billion people. It is home to over 1,500 distinct ethnic groups, each with its own unique language, culture, and traditions. The continent’s history is marked by a complex tapestry of empires, kingdoms, and colonial influences.
Economic and Political Landscape:
Africa’s economic landscape is diverse, ranging from resource-rich nations to developing economies. The continent faces challenges such as poverty, inequality, and political instability, but also possesses significant potential for growth and development.
Global Significance:
Africa’s strategic location and vast resources make it a key player in the global economy and political landscape. The continent is a major producer of agricultural commodities, minerals, and energy resources. Its growing population and expanding markets present significant opportunities for investment and trade.
FAQs about Africa’s Location:
-
Q: What is the most northern point of Africa?
- A: Cape Blanc, located in Tunisia, is the northernmost point of the African continent.
-
Q: What is the most southern point of Africa?
- A: Cape Agulhas, located in South Africa, is the southernmost point of the African mainland.
-
Q: What is the largest country in Africa by land area?
- A: Algeria, with a land area of over 2,381,741 square kilometers, is the largest country in Africa.
-
Q: What is the smallest country in Africa by land area?
- A: The Seychelles, with a land area of approximately 455 square kilometers, is the smallest country in Africa.
-
Q: What are the main geographical features that define Africa’s location?
- A: Africa’s location is defined by its surrounding oceans (Atlantic, Indian, and Southern), the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and its position between Europe and Asia.
Tips for Understanding Africa’s Location:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the continent on a globe provides a better understanding of its shape, size, and location relative to other continents.
- Explore online resources: Websites and interactive maps offer detailed information about Africa’s geography, climate, and resources.
- Read about African history and culture: Understanding the continent’s history and cultural diversity provides context for its geographical significance.
- Engage with African perspectives: Seek out resources and perspectives from Africans themselves to gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s complexities.
Conclusion:
Africa’s location on the world map is not merely a geographical fact; it is a defining characteristic that shapes its diverse landscape, rich history, and global significance. Understanding Africa’s location is crucial to appreciating the continent’s unique beauty, cultural richness, and immense potential. As the world increasingly recognizes Africa’s growing role in the global economy and political landscape, understanding its location becomes ever more essential.
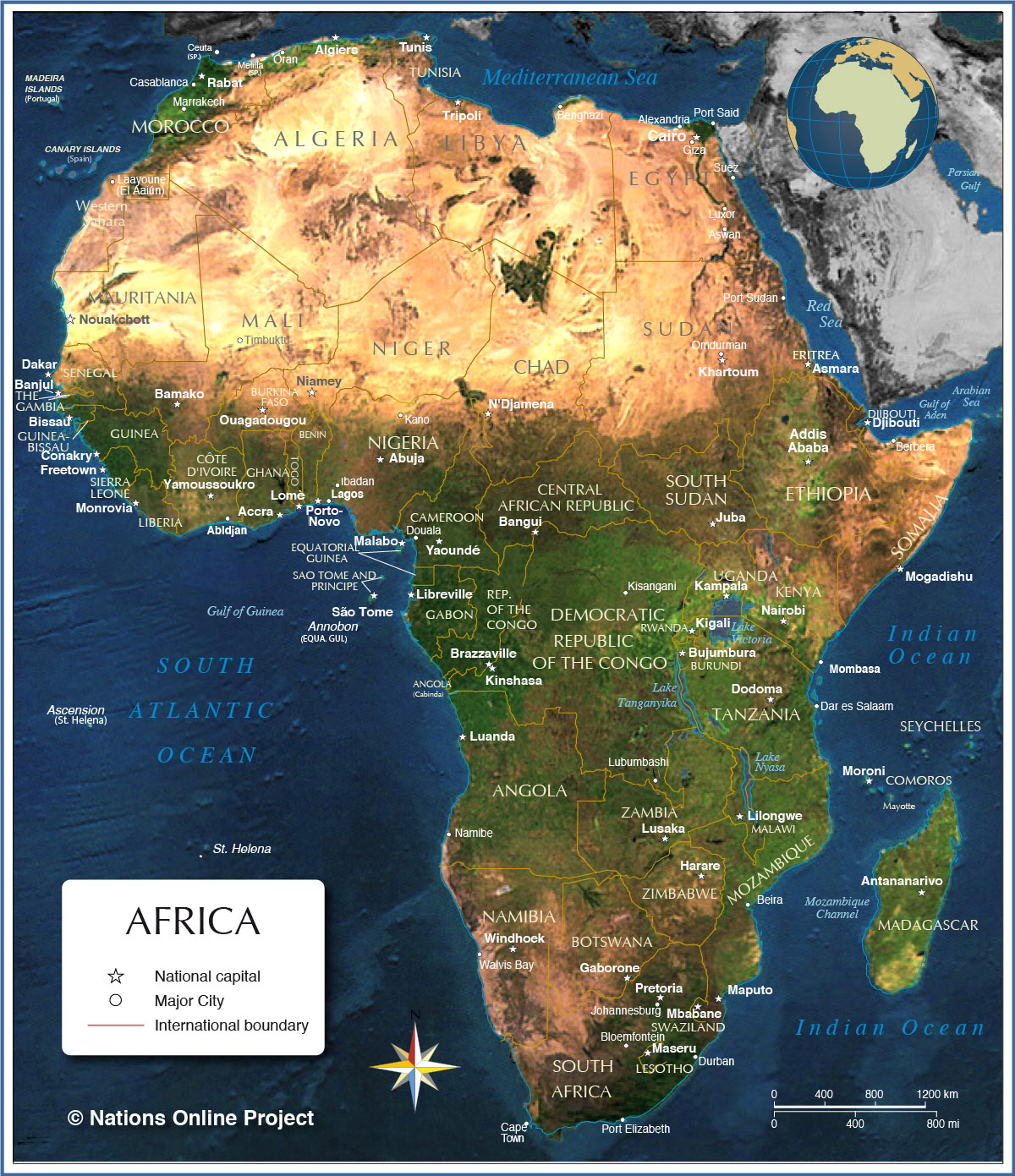


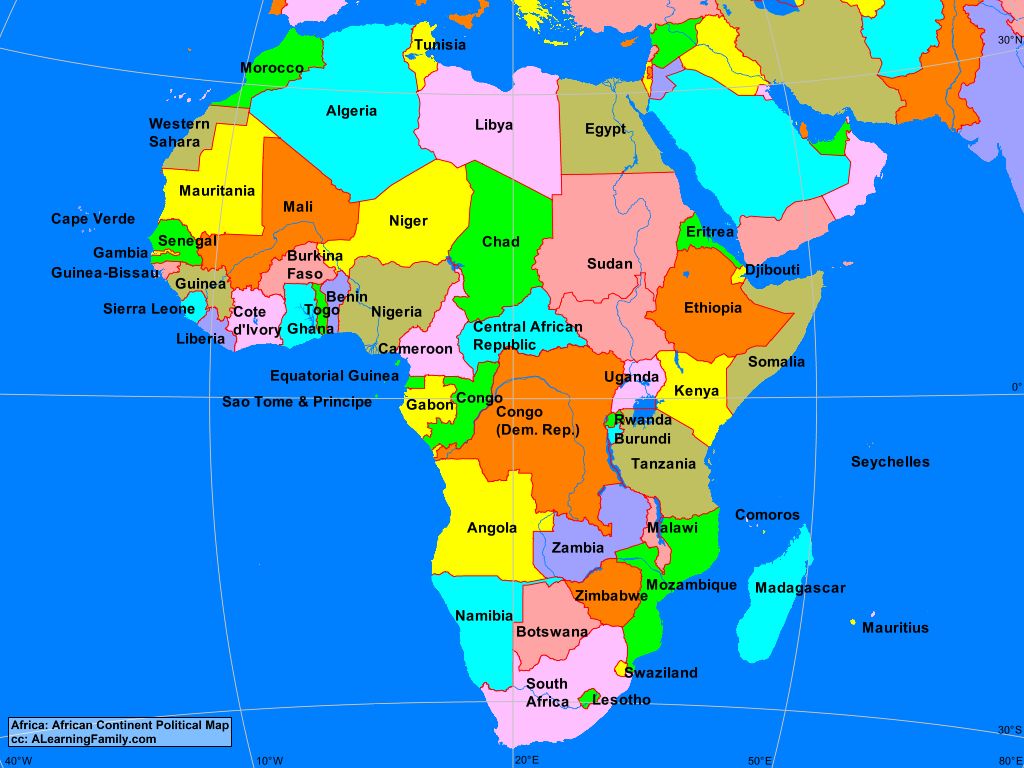
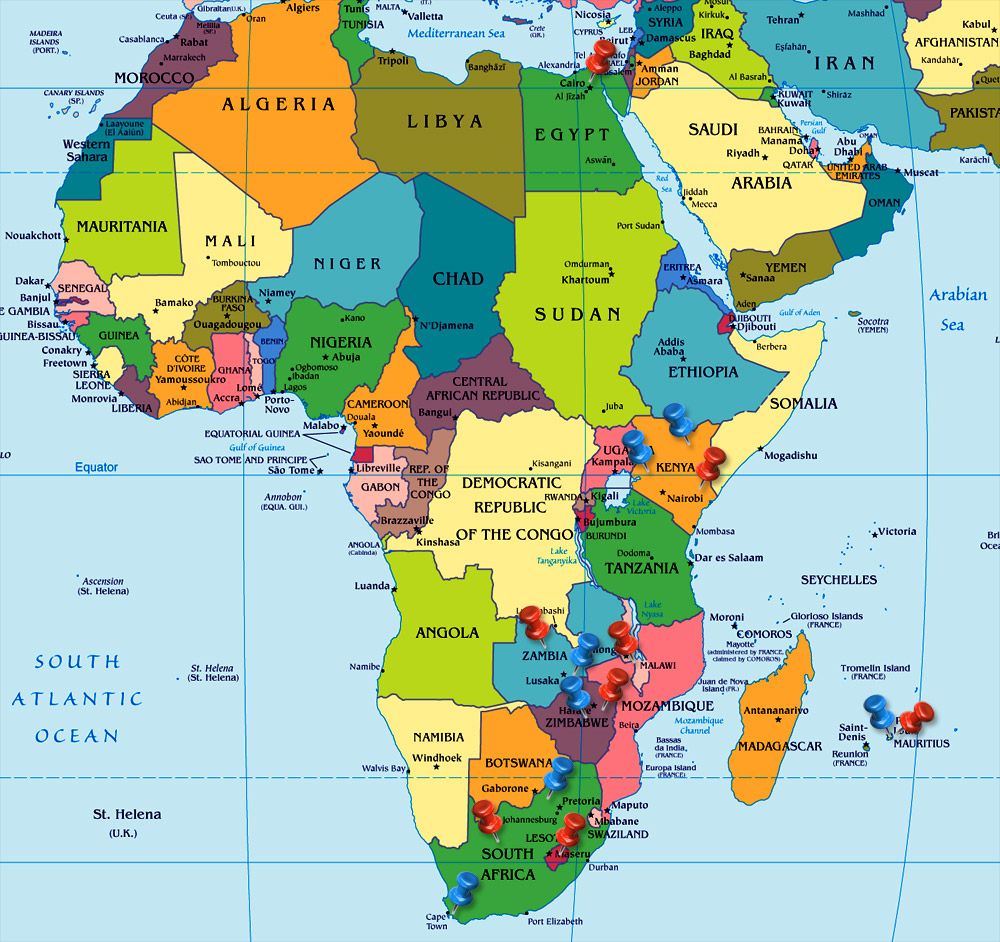



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!