Decoding the Taste Buds: A Journey Through the Tongue Map
Related Articles: Decoding the Taste Buds: A Journey Through the Tongue Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Taste Buds: A Journey Through the Tongue Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding the Taste Buds: A Journey Through the Tongue Map
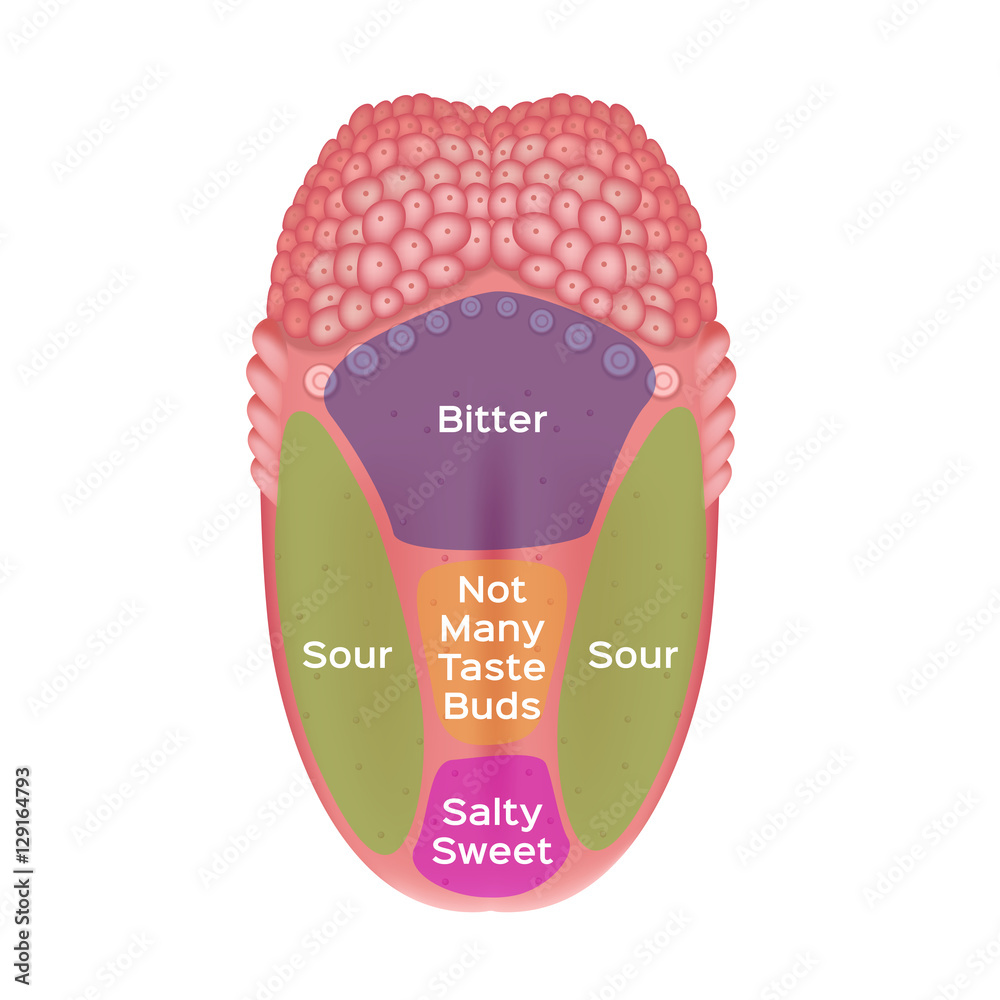
The human tongue, a marvel of evolution, is not just a muscle for speech and swallowing. It plays a vital role in our perception of taste, a complex process involving a delicate interplay of taste receptors, sensory neurons, and the brain. This intricate mechanism is often depicted by a simplified diagram known as the "tongue map," which purports to show distinct regions on the tongue responsible for specific tastes.
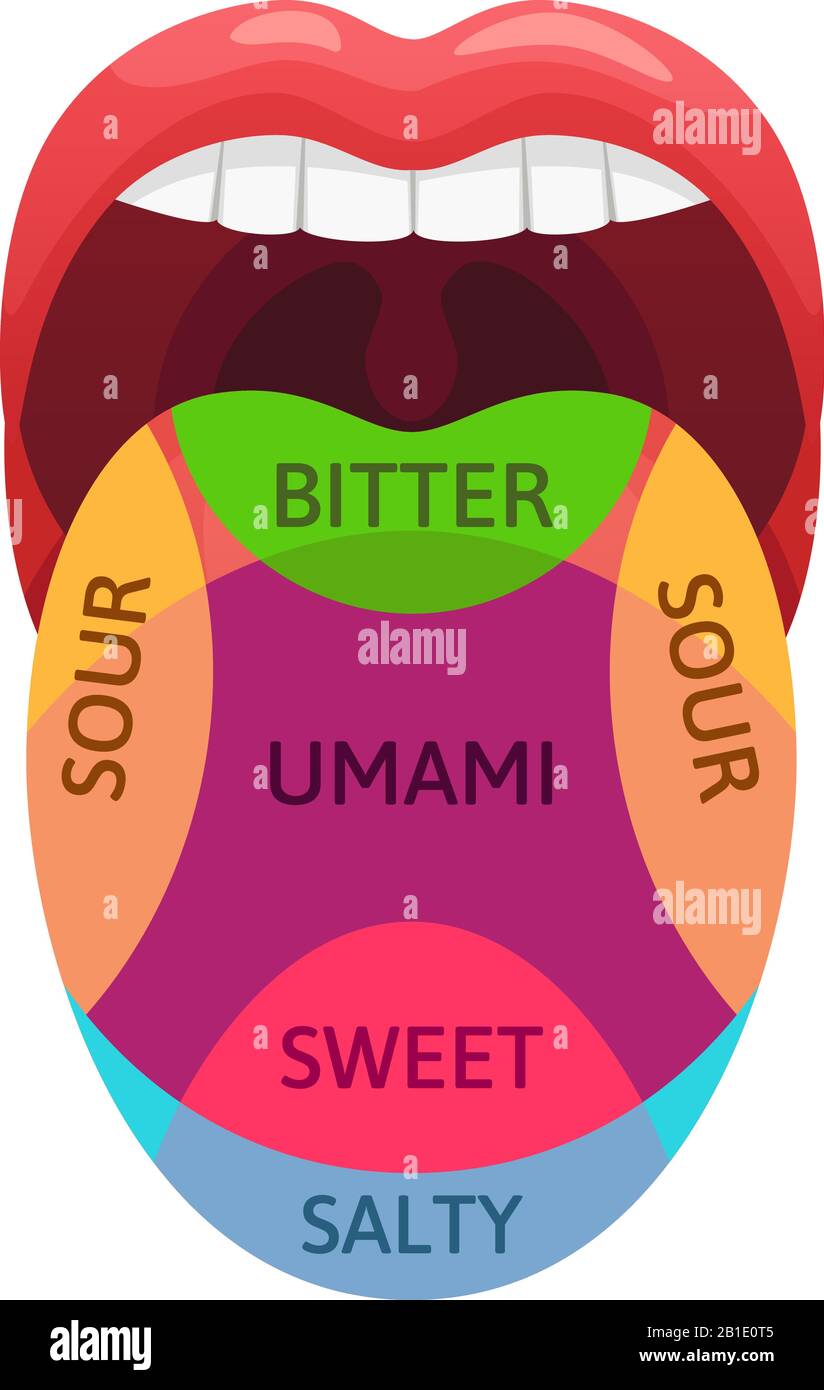
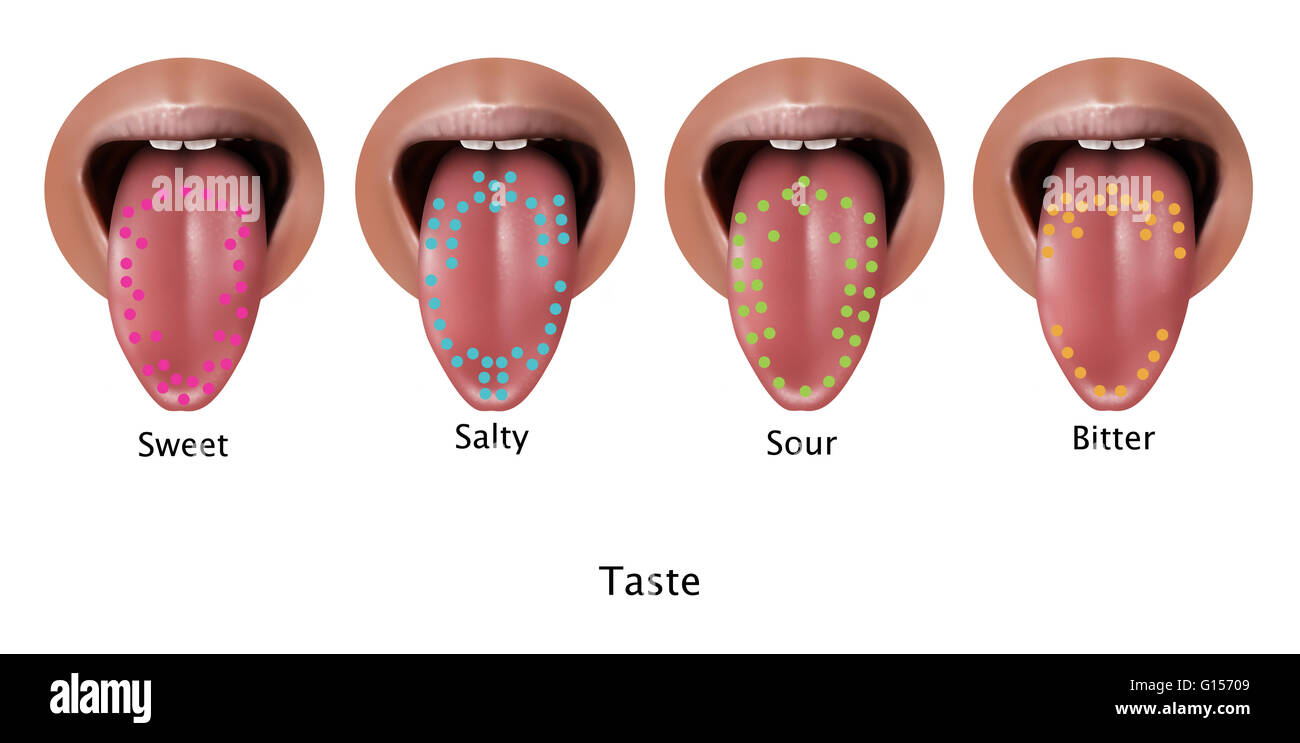
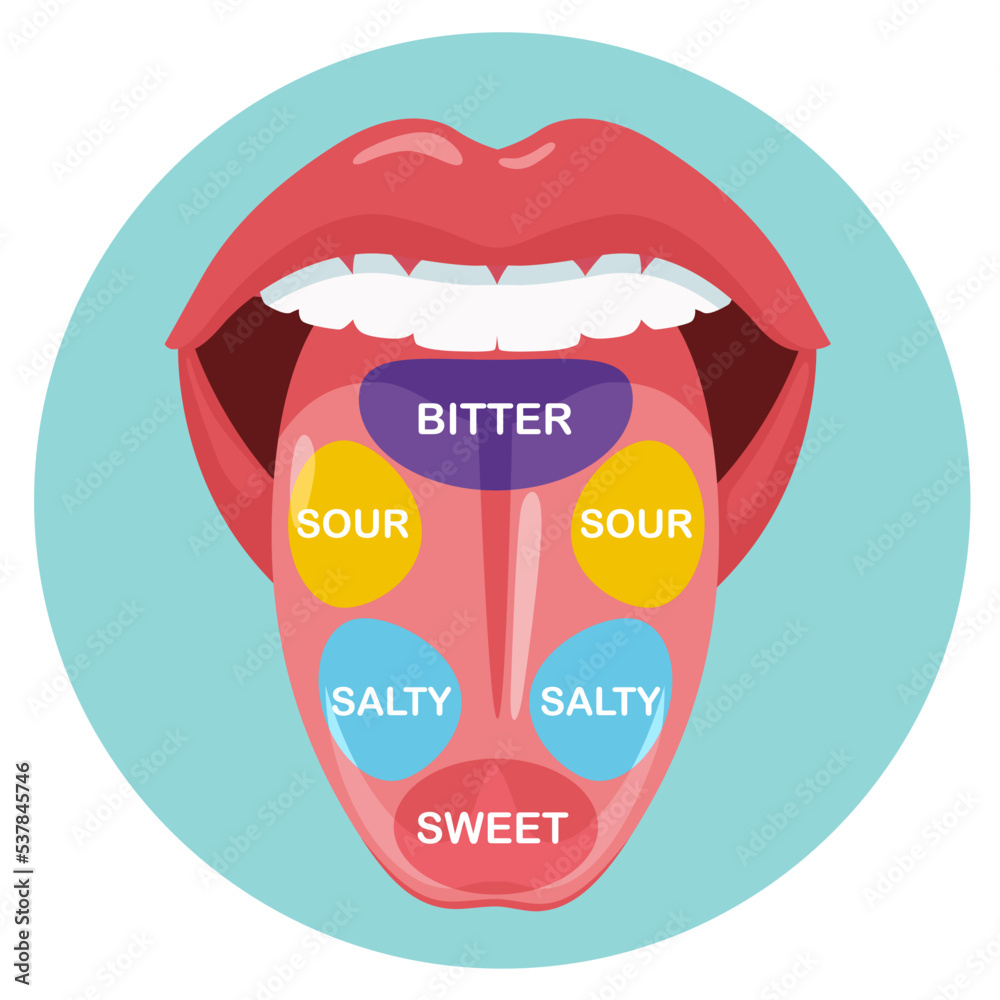
While the tongue map has become ingrained in popular culture, its accuracy has been a subject of debate among scientists. The concept originated in the 19th century, based on the work of German physiologist David Hänig, who suggested that different regions of the tongue were more sensitive to specific tastes. This led to the popularized image of the tongue map, dividing it into zones for sweet (tip), sour (sides), salty (front), and bitter (back).
However, research has revealed a more nuanced reality. While the tongue map may be a helpful visual aid for understanding basic taste perception, it significantly oversimplifies the actual process.
Beyond the Tongue Map: A Complex System of Taste Perception
The truth is, taste buds, the sensory organs responsible for taste, are distributed throughout the tongue’s surface, not confined to specific areas. Each taste bud contains approximately 50 to 100 taste receptor cells, each sensitive to a particular taste quality. These taste receptor cells are constantly replaced, ensuring a continuous sensory experience.
While the tongue map suggests distinct zones for each taste, all taste buds are capable of detecting all five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. These tastes are perceived by the brain as a result of signals transmitted from taste receptor cells through sensory neurons. The intensity of each taste perception depends on the concentration of the taste molecule and the number of activated taste receptor cells.
The Importance of Taste Bud Distribution
The distribution of taste buds across the tongue is not uniform. The tip and sides of the tongue, containing a higher concentration of taste buds, are more sensitive to sweet, sour, and salty tastes. The back of the tongue, with a lower density of taste buds, is less sensitive to these tastes but more sensitive to bitter tastes. This uneven distribution can be attributed to evolutionary adaptation, with bitter taste receptors being more prevalent in the back of the tongue to protect against potentially harmful substances.
Factors Influencing Taste Perception
Taste perception is not solely determined by the tongue’s structure. It is a dynamic process influenced by various factors, including:
- Genetics: Individual variations in taste receptor genes can influence the sensitivity to different tastes. Some individuals may be more sensitive to bitter tastes due to specific genetic variations.
- Age: Taste sensitivity can decline with age, leading to changes in taste preferences.
- Temperature: Temperature can influence taste perception. For example, warm food can enhance sweetness while cold food can enhance bitterness.
- Texture: The texture of food can influence its taste perception. For instance, a smooth texture can enhance sweetness, while a rough texture can enhance bitterness.
- Smell: Smell plays a crucial role in taste perception. The olfactory system, responsible for smell, interacts with the taste system, enhancing and modifying taste experiences.
- Psychological factors: Psychological factors, such as expectations and mood, can influence taste perception. For example, a positive mood can enhance the perception of sweetness.
The Role of Taste in Health and Wellness
Taste is an essential aspect of our lives, influencing our food choices, enjoyment of meals, and even our overall health. It plays a crucial role in:
- Nutrition: Taste guides our food choices, ensuring we consume a balanced diet with essential nutrients.
- Food safety: Taste helps us identify potentially harmful substances, protecting us from food poisoning.
- Social interaction: Taste is an integral part of social gatherings and cultural traditions, fostering a sense of community and shared experiences.
- Quality of life: Taste contributes to our enjoyment of life, enhancing our experiences with food and beverages.
FAQs about the Tongue Map
1. Is the tongue map accurate?
No, the tongue map is a simplified representation of taste perception and does not accurately reflect the distribution of taste buds. All taste buds can detect all five basic tastes.
2. Why is the tongue map still widely used?
The tongue map has become ingrained in popular culture, and its simplicity makes it a convenient tool for understanding basic taste perception. However, it is important to remember that it is not a scientifically accurate representation of taste.
3. What is the scientific basis for taste perception?
Taste perception involves the activation of taste receptor cells in taste buds, which transmit signals to the brain through sensory neurons. The brain interprets these signals as different tastes.
4. Can the tongue map be used to identify taste disorders?
The tongue map is not a reliable tool for diagnosing taste disorders. Taste disorders can be caused by various factors, including infections, injuries, and certain medications.
5. How can I enhance my taste perception?
To enhance taste perception, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene, avoid smoking, and manage underlying medical conditions that may affect taste.
Tips for Understanding Taste Perception
- Explore different flavors: Experiment with a variety of foods and beverages to broaden your taste palate.
- Pay attention to your senses: Focus on the taste, smell, and texture of food while eating.
- Create a pleasant dining environment: Surround yourself with pleasant aromas and sounds to enhance your dining experience.
- Avoid distractions: Minimize distractions while eating to allow your taste buds to fully experience the flavors.
- Be mindful of your food choices: Choose foods that are fresh, flavorful, and nutritious.
Conclusion
While the tongue map may provide a simplistic visual representation of taste perception, it is crucial to understand that taste is a complex and multifaceted process. The distribution of taste buds across the tongue, along with genetic variations, age, temperature, texture, smell, and psychological factors, all contribute to our perception of taste.
By embracing a nuanced understanding of taste, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern our sensory experiences and make informed choices about our diet and overall well-being.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Taste Buds: A Journey Through the Tongue Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!