forest service region map
Related Articles: forest service region map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to forest service region map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the U.S. Forest Service Region Map
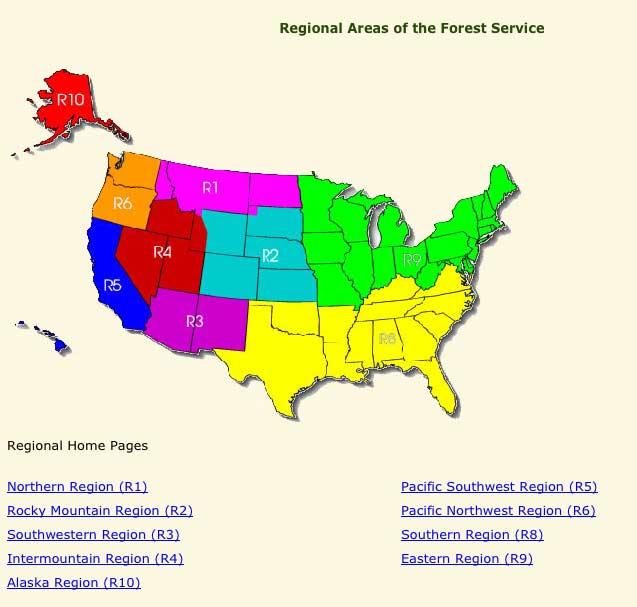
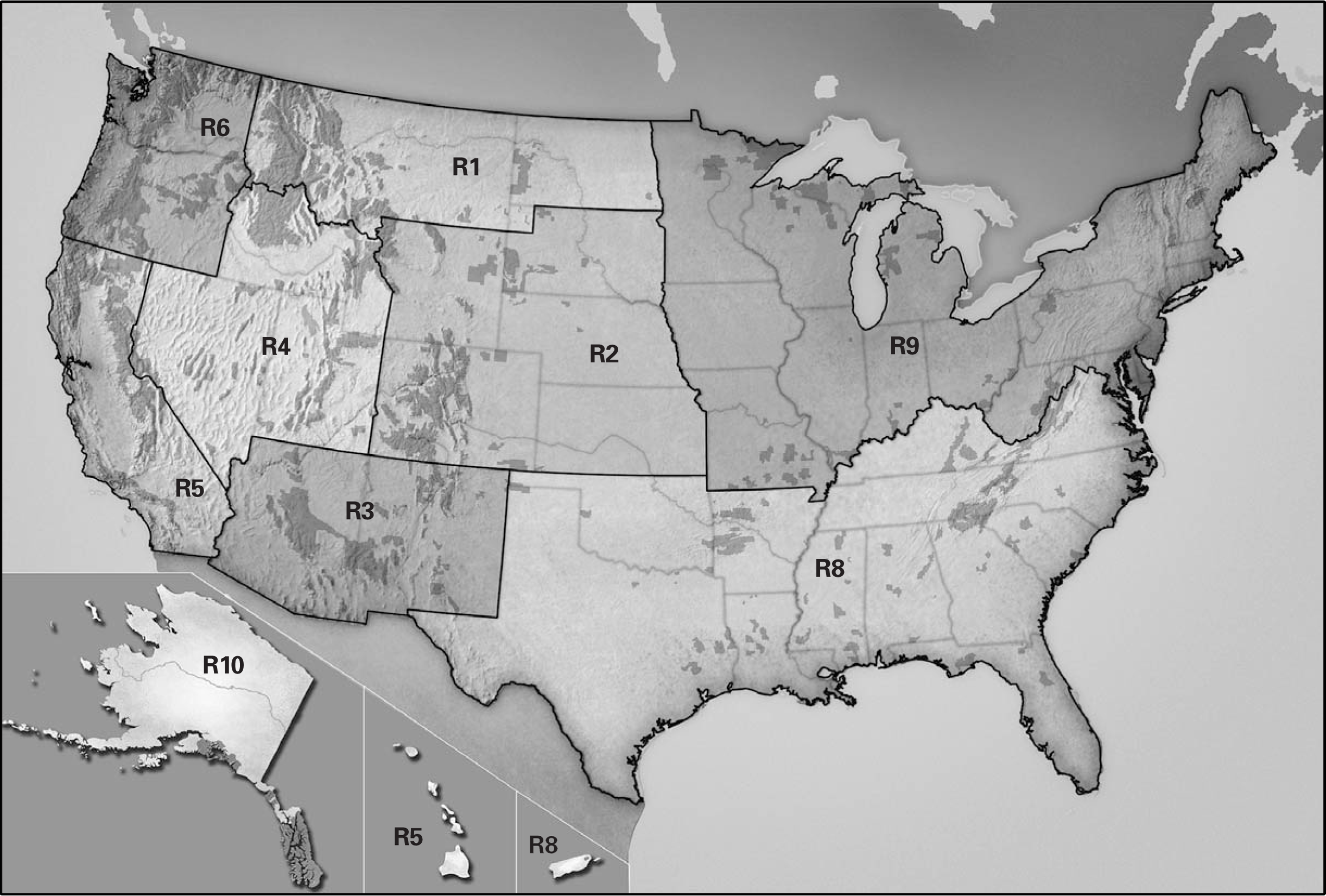
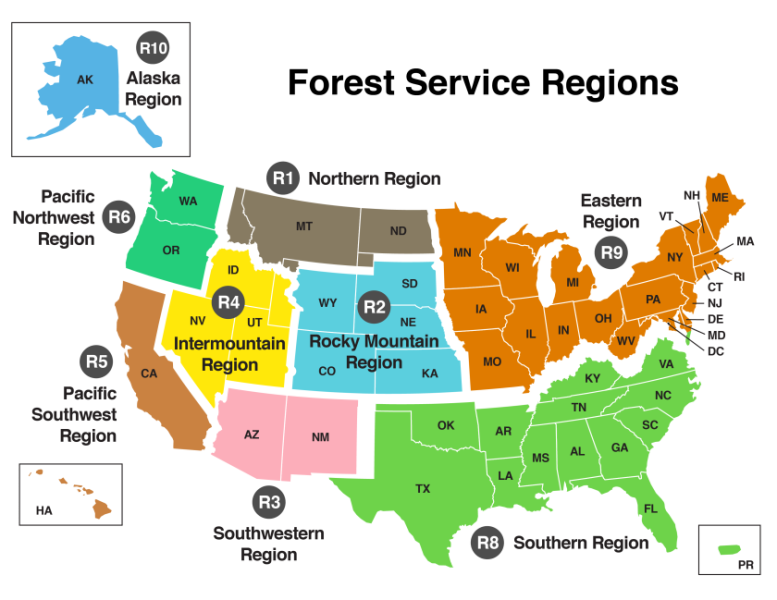
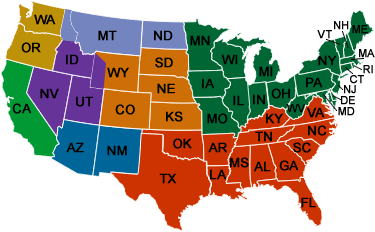
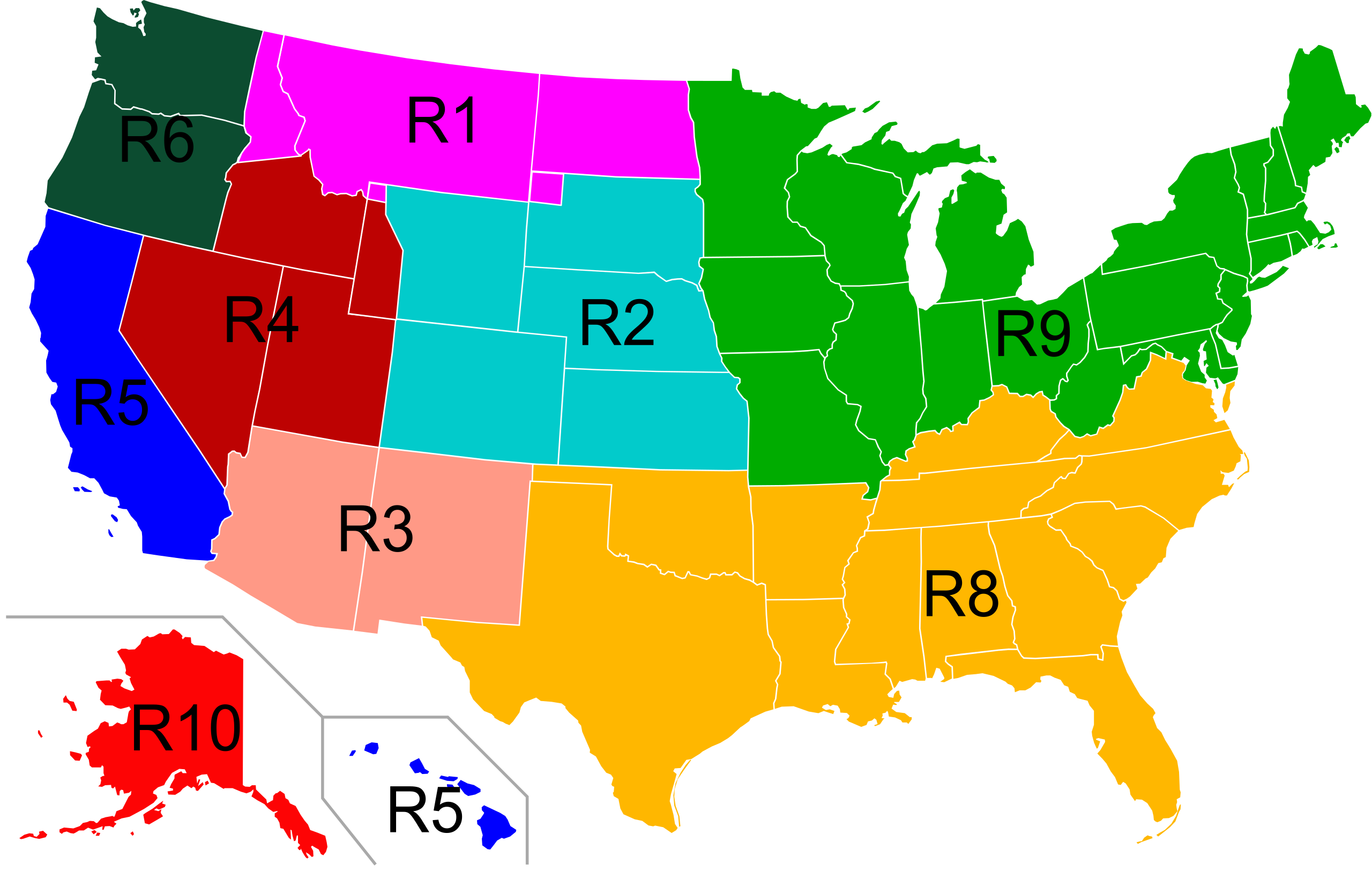
The United States Forest Service (USFS), a branch of the U.S. Department of Agriculture, manages over 193 million acres of public lands, encompassing diverse ecosystems from towering mountains to lush forests and expansive grasslands. To effectively manage this vast portfolio, the USFS has divided the country into nine distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics and priorities. This regional organization, represented by the Forest Service Region Map, is a vital tool for understanding the agency’s structure, responsibilities, and activities across the nation.
Understanding the Regions:
The Forest Service Region Map visually depicts the nine administrative regions, each denoted by a unique color and number. Each region is led by a Regional Forester, who oversees a team of professionals responsible for implementing the agency’s mission within their designated area. These regions are not simply geographical divisions; they reflect the distinct ecological, social, and economic characteristics of the landscapes they encompass.
Region 1: The Northern Region
Stretching across Montana, North Dakota, and parts of Idaho and South Dakota, Region 1 encompasses the northernmost portion of the Rocky Mountains. Known for its rugged terrain, diverse wildlife, and significant timber resources, this region prioritizes fire management, timber harvesting, and recreational opportunities. The region also plays a crucial role in protecting endangered species and managing water resources.
Region 2: The Rocky Mountain Region
Encompassing Colorado, Wyoming, and parts of Kansas, Nebraska, and South Dakota, Region 2 is home to the iconic Rocky Mountains. With a focus on managing the diverse ecosystems of the region, including grasslands, forests, and alpine areas, Region 2 prioritizes watershed protection, wildlife habitat management, and recreational opportunities. The region also plays a key role in addressing the challenges of climate change and wildfire.
Region 3: The Southwestern Region
Spanning Arizona and New Mexico, Region 3 is characterized by its arid climate, diverse landscapes, and unique cultural heritage. The region prioritizes managing water resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. It also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 4: The Intermountain Region
Covering Idaho, Utah, and parts of Nevada and Wyoming, Region 4 is known for its diverse landscapes, ranging from high mountain peaks to sagebrush steppes. The region prioritizes managing water resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 4 also plays a key role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 5: The Pacific Southwest Region
Encompassing California and parts of Nevada and Arizona, Region 5 is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including coastal forests, deserts, and mountains. The region prioritizes managing water resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 5 also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 6: The Pacific Northwest Region
Stretching across Oregon and Washington, Region 6 is known for its vast forests, towering mountains, and abundant wildlife. The region prioritizes managing timber resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 6 also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 8: The Southern Region
Encompassing Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, and Virginia, Region 8 is known for its diverse forests, grasslands, and wetlands. The region prioritizes managing timber resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 8 also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 9: The Alaska Region
Spanning the entire state of Alaska, Region 9 is home to vast forests, mountains, and glaciers. The region prioritizes managing timber resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 9 also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Region 10: The Eastern Region
Covering Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and the District of Columbia, Region 10 is known for its diverse forests, wetlands, and urban areas. The region prioritizes managing timber resources, protecting endangered species, and providing recreational opportunities. Region 10 also plays a crucial role in managing wildfires and restoring degraded ecosystems.
The Importance of Regional Organization:
The Forest Service Region Map is more than just a visual representation of geographical boundaries. It reflects the agency’s commitment to understanding and addressing the unique challenges and opportunities of each region. By organizing its resources and expertise regionally, the USFS can:
- Adapt to Local Conditions: Each region faces distinct ecological challenges, from wildfire risks in the West to invasive species in the East. Regional organization allows the USFS to tailor its management strategies to the specific needs of each area.
- Engage Local Communities: The USFS recognizes the importance of working with local communities to manage public lands. Regional offices provide a point of contact for local residents, businesses, and organizations, facilitating collaboration and ensuring that management decisions reflect local values and priorities.
- Promote Efficient Operations: By decentralizing decision-making and resource allocation, regional organization promotes efficiency and responsiveness. Regional offices can quickly adapt to changing conditions and respond to local needs, ensuring that the agency’s resources are used effectively.
FAQs about the Forest Service Region Map:
1. What are the primary responsibilities of the Forest Service within each region?
Each region has a specific set of priorities based on the unique characteristics of the landscape and the needs of the local communities. However, common responsibilities include:
- Managing timber resources: This includes setting harvest levels, ensuring sustainable forest management practices, and promoting the economic benefits of timber production.
- Protecting endangered species: This involves implementing conservation plans, restoring habitats, and working with partners to ensure the survival of threatened and endangered wildlife.
- Providing recreational opportunities: This includes managing campgrounds, trails, and other recreational facilities, promoting responsible outdoor recreation, and protecting natural resources.
- Managing wildfires: This involves preventing wildfires, responding to incidents, and restoring burned areas.
- Restoring degraded ecosystems: This involves restoring degraded forests, grasslands, and wetlands, and promoting ecosystem health and resilience.
2. How can I access information about specific regions?
Each region has its own website with detailed information about its activities, programs, and contact information. The USFS website also provides a comprehensive overview of each region and its responsibilities.
3. How can I get involved in Forest Service activities in my region?
The USFS encourages public participation in its decision-making processes. You can get involved by:
- Attending public meetings: The USFS holds regular meetings to discuss proposed projects and gather public input.
- Submitting comments: You can provide feedback on proposed projects and management plans through the USFS website.
- Joining advisory groups: The USFS forms advisory groups to provide input on specific issues and projects.
- Volunteering: You can volunteer your time to help with various Forest Service projects, such as trail maintenance or restoration efforts.
Tips for Using the Forest Service Region Map:
- Identify your region: Determine which region encompasses the area you are interested in.
- Explore the region’s website: Learn about the region’s unique characteristics, priorities, and activities.
- Contact your regional office: Reach out to the regional office for specific information or to get involved in local projects.
- Attend public meetings: Stay informed about upcoming meetings and participate in the decision-making process.
- Support the USFS: Volunteer your time, donate to the agency, or advocate for responsible land management.
Conclusion:
The Forest Service Region Map is a valuable tool for understanding the USFS’s structure, responsibilities, and activities across the nation. By dividing the country into nine distinct regions, the agency can effectively manage its vast portfolio of public lands, adapt to local conditions, engage local communities, and promote efficient operations. Whether you are a local resident, a visitor, or simply interested in the management of public lands, the Forest Service Region Map provides a framework for navigating the diverse landscape of the United States Forest Service.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into forest service region map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!