Mapping the Meal Gap: Addressing Food Insecurity with Data-Driven Solutions
Related Articles: Mapping the Meal Gap: Addressing Food Insecurity with Data-Driven Solutions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Meal Gap: Addressing Food Insecurity with Data-Driven Solutions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Meal Gap: Addressing Food Insecurity with Data-Driven Solutions

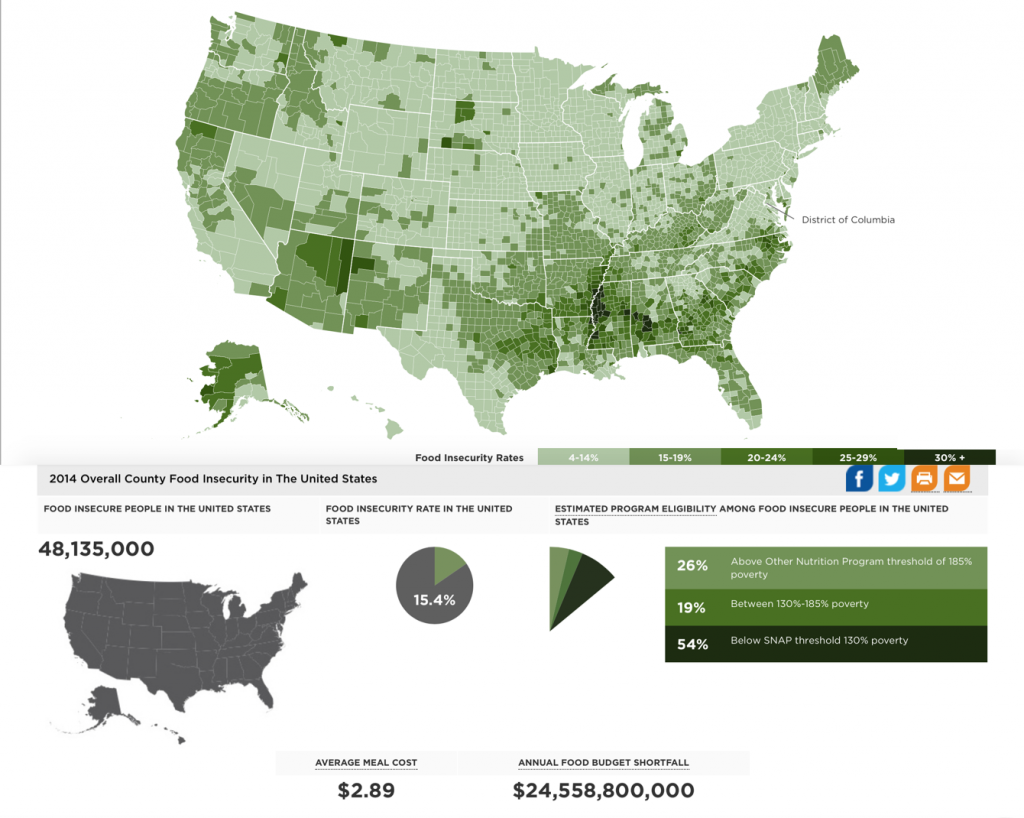
Food insecurity, the state of not having consistent access to enough food for an active, healthy life, is a global challenge with profound consequences for individuals, communities, and societies. While traditional approaches to tackling food insecurity often rely on anecdotal evidence and limited data, a new wave of innovative solutions is emerging, leveraging the power of data and technology to create a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the problem. One such solution is "Mapping the Meal Gap," a data-driven initiative that aims to pinpoint the precise locations and populations most vulnerable to food insecurity.
Understanding the Meal Gap:
The "meal gap" refers to the difference between the food needed for a healthy diet and the food actually consumed. It represents the shortfall in food access experienced by individuals and households, often due to factors like poverty, lack of access to affordable food, and limited transportation options. Mapping the Meal Gap goes beyond simply identifying the existence of food insecurity; it seeks to quantify and visualize the extent of the problem, providing a detailed picture of where and how food insecurity manifests itself.
The Power of Data Visualization:
The key to effectively addressing food insecurity lies in understanding its nuances and geographical distribution. Mapping the Meal Gap utilizes various data sources, including census data, food assistance program enrollment figures, and surveys on food insecurity, to create interactive maps and visualizations. These maps offer a powerful tool for:
- Identifying High-Risk Areas: By overlaying different data layers, the maps can pinpoint neighborhoods, communities, and even specific addresses where food insecurity is most prevalent. This allows for targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Understanding Vulnerability Factors: The maps can reveal correlations between food insecurity and factors like income levels, household size, and proximity to grocery stores. This information helps policymakers and community organizations tailor their strategies to address the underlying causes of food insecurity.
- Measuring Impact: By tracking changes in food insecurity indicators over time, the maps can measure the effectiveness of interventions and programs, allowing for adjustments and optimization.
Beyond the Map: Empowering Action:
Mapping the Meal Gap is not merely a data visualization project; it serves as a catalyst for action. The insights gleaned from the maps empower stakeholders to:
- Direct Resources Effectively: By understanding the precise locations and populations most affected by food insecurity, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that food assistance reaches those who need it most.
- Develop Targeted Interventions: The data can inform the development of tailored programs and initiatives, addressing specific needs and challenges within different communities. For example, maps might reveal a lack of access to fresh produce in certain areas, prompting the creation of mobile farmers markets or community gardens.
- Promote Collaboration: The maps can facilitate collaboration between different organizations working on food insecurity, fostering a coordinated approach to addressing the problem.
FAQs:
Q: How are the maps created?
A: The maps are created using a combination of publicly available data sources, including:
- Census data: Provides demographic information, including income levels, household size, and population density.
- Food assistance program enrollment data: Tracks the number of individuals and families enrolled in programs like SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program).
- Food insecurity surveys: Gather data on the prevalence of food insecurity, the types of food insecurity experienced, and the factors contributing to it.
Q: What kind of data is used to create the maps?
A: The data used to create the maps can vary depending on the specific project and location. However, common data points include:
- Geographic location: Coordinates of households, communities, or neighborhoods.
- Socioeconomic indicators: Income levels, poverty rates, and household size.
- Access to food: Proximity to grocery stores, farmers markets, and food banks.
- Food insecurity indicators: Prevalence of food insecurity, frequency of food insecurity, and types of food insecurity experienced.
Q: How can I use the maps?
A: The maps can be used by a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Policymakers: To inform the development and implementation of food security policies.
- Community organizations: To identify areas of need and target their services.
- Researchers: To study the prevalence and factors contributing to food insecurity.
- Individuals: To learn about food insecurity in their communities and find resources.
Tips for Using the Maps:
- Consider the scale: The maps can be viewed at different levels of detail, from national to local. Choose the appropriate scale for your needs.
- Focus on specific indicators: The maps often contain multiple data layers. Focus on the indicators most relevant to your goals.
- Use the maps to inform action: The maps should not be used as a passive tool for data visualization. Use them to drive action and improve food security.
Conclusion:
Mapping the Meal Gap represents a significant advancement in our understanding and response to food insecurity. By harnessing the power of data and technology, we can create a more accurate and nuanced picture of the problem, enabling us to develop targeted interventions and resource allocation strategies that effectively address the root causes of food insecurity. As we continue to refine and expand these data-driven approaches, we move closer to a future where food security is a reality for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Meal Gap: Addressing Food Insecurity with Data-Driven Solutions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!