Mapping the Red and Blue: Understanding the Electoral Landscape of the 2016 and 2020 Presidential Elections
Related Articles: Mapping the Red and Blue: Understanding the Electoral Landscape of the 2016 and 2020 Presidential Elections
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Red and Blue: Understanding the Electoral Landscape of the 2016 and 2020 Presidential Elections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Red and Blue: Understanding the Electoral Landscape of the 2016 and 2020 Presidential Elections

The 2016 and 2020 presidential elections in the United States were marked by intense political polarization and a dramatic shift in the electoral landscape. These shifts are vividly illustrated by the visual representation of election results: the electoral vote maps. These maps, often depicted in red and blue, offer a powerful tool for understanding the geographic distribution of support for each candidate, revealing underlying demographic, economic, and social factors that influence voting patterns.
Understanding the Electoral College:
The United States does not elect its president through a direct popular vote. Instead, the Electoral College system assigns electoral votes to each state based on its congressional representation, with a minimum of three votes per state. The candidate who wins the majority of electoral votes, currently 270 out of 538, becomes the president. This system, while designed to balance the influence of smaller states, often results in a candidate winning the presidency despite losing the popular vote, as seen in the 2016 election.
Visualizing the Shift: The 2016 and 2020 Election Maps
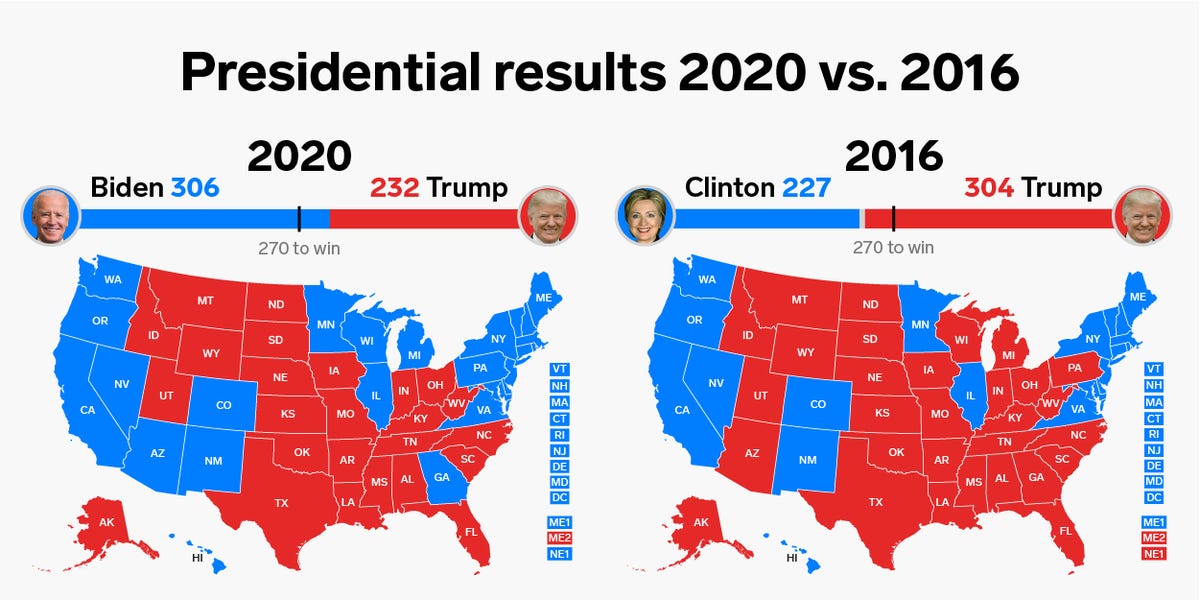
The 2016 election map, with its stark red-dominated landscape, signified a significant shift in the political landscape. Donald Trump, the Republican candidate, won 306 electoral votes, securing victory despite losing the popular vote by nearly 3 million. The map highlighted the strength of his support in rural areas, particularly in the Midwest and South, while Democratic candidate Hillary Clinton won urban areas and coastal states.
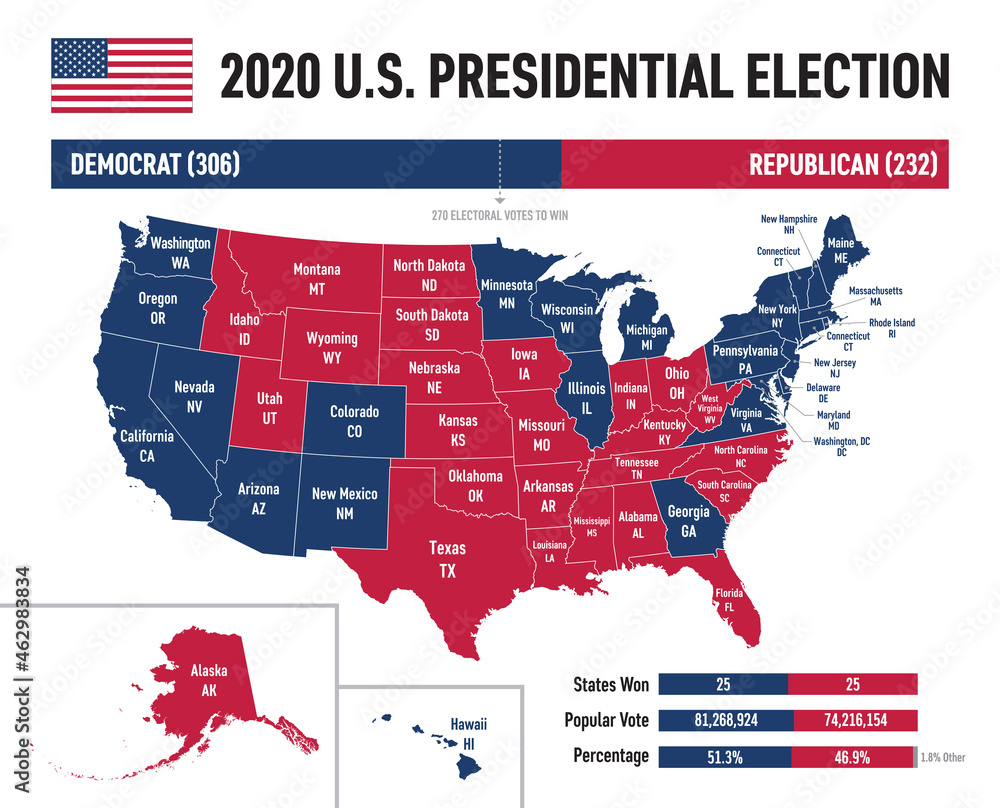
The 2020 election, while resulting in a victory for Joe Biden, the Democratic candidate, revealed a more nuanced picture. While Biden won the popular vote by a larger margin than Clinton, the map remained largely divided along the same lines, with Trump retaining strong support in the same regions. The outcome, however, highlighted the importance of key swing states like Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Wisconsin, which flipped from red to blue, ultimately deciding the election.
Beyond the Colors: Analyzing the Geographic Patterns
The red and blue maps, while visually striking, are only the starting point for understanding the complexities of the American electorate. A deeper analysis reveals underlying factors influencing voting patterns:
-
Rural vs. Urban Divide: The maps illustrate the persistent divide between rural and urban areas, with Trump garnering significant support in rural communities, while Biden dominated urban centers. This divide is often attributed to differing economic priorities, cultural values, and perceptions of social change.
-
Economic Factors: Economic anxieties and concerns about job security played a significant role in both elections. Trump’s promises to "Make America Great Again" resonated with voters in regions experiencing economic hardship, while Biden focused on policies aimed at addressing income inequality and creating economic opportunities.
-
Demographic Shifts: The maps reflect ongoing demographic shifts in the United States, particularly the growing Hispanic population, which largely supported Biden in 2020. These shifts are likely to continue influencing future elections, potentially altering the political landscape in the coming years.
-
Social and Cultural Issues: Social and cultural issues, including immigration, abortion, and gun control, played a significant role in mobilizing voters. These issues often cut across geographic boundaries, influencing voting patterns in both rural and urban areas.
The Importance of Understanding the Electoral Landscape
Analyzing the electoral maps is crucial for understanding the dynamics of American politics. It allows for:
-
Identifying Key Voting Blocs: By identifying regions with strong support for specific candidates, campaigns can tailor their messaging and outreach efforts to target specific groups of voters.
-
Understanding Political Trends: Examining the evolution of electoral maps over time reveals shifts in voter sentiment and provides insights into emerging political trends.
-
Predicting Future Elections: While not a perfect predictor, the analysis of past electoral maps can help forecast potential outcomes of future elections, informing strategic planning and resource allocation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the limitations of electoral maps?
A: Electoral maps provide a snapshot of voting patterns but cannot fully capture the complexities of the American electorate. They do not reflect the nuances of individual voter preferences or the influence of factors like voter turnout and campaign spending.
Q: How can electoral maps be used to improve voter participation?
A: By identifying areas with low voter turnout, organizations can focus their efforts on voter registration drives and outreach programs, encouraging greater participation in the democratic process.
Q: Are electoral maps always accurate predictors of future elections?
A: Electoral maps are not always accurate predictors of future elections. They can be influenced by external factors like economic conditions, social movements, and unexpected events.
Tips for Using Electoral Maps:
- Consider the context: When analyzing electoral maps, it is essential to consider the historical, social, and economic context surrounding each election.
- Look beyond the colors: Focus on the underlying factors influencing voting patterns, such as demographics, economic conditions, and social issues.
- Compare maps over time: Analyze the evolution of electoral maps to identify trends and shifts in voting behavior.
- Use maps as a starting point: Electoral maps should be used in conjunction with other data sources and analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of the electorate.
Conclusion:
The red and blue electoral maps, while often simplified representations of complex political realities, offer a powerful tool for understanding the geographic distribution of support for different candidates. By analyzing these maps in conjunction with other data sources, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of American politics, identify key voting blocs, and understand the underlying factors influencing voting patterns. This knowledge is crucial for informing campaign strategies, understanding political trends, and ultimately strengthening the democratic process.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Red and Blue: Understanding the Electoral Landscape of the 2016 and 2020 Presidential Elections. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!