Mapping the Topography of Poverty: A Visual Representation of Economic Disparities in the United States
Related Articles: Mapping the Topography of Poverty: A Visual Representation of Economic Disparities in the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Topography of Poverty: A Visual Representation of Economic Disparities in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Topography of Poverty: A Visual Representation of Economic Disparities in the United States

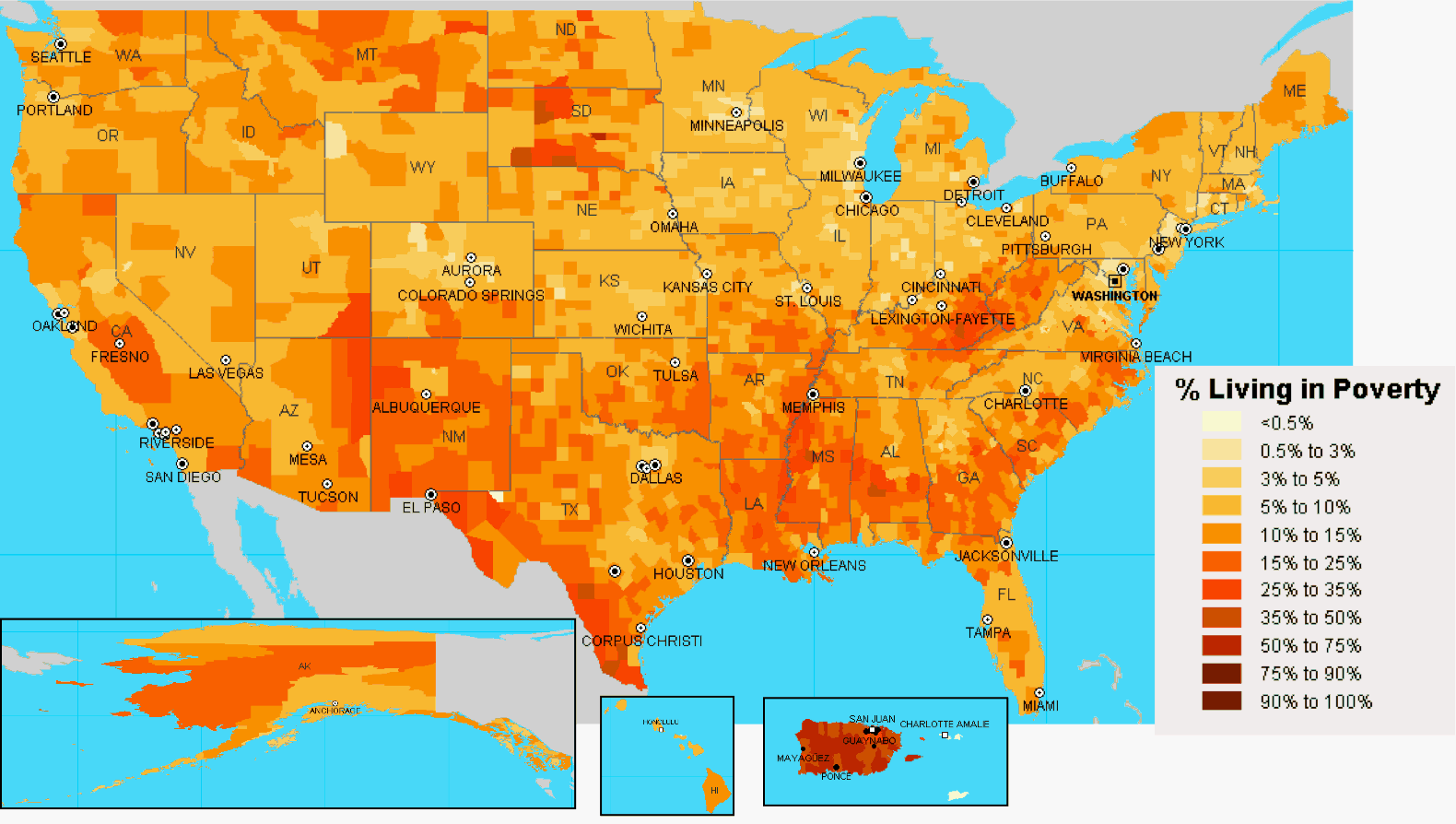
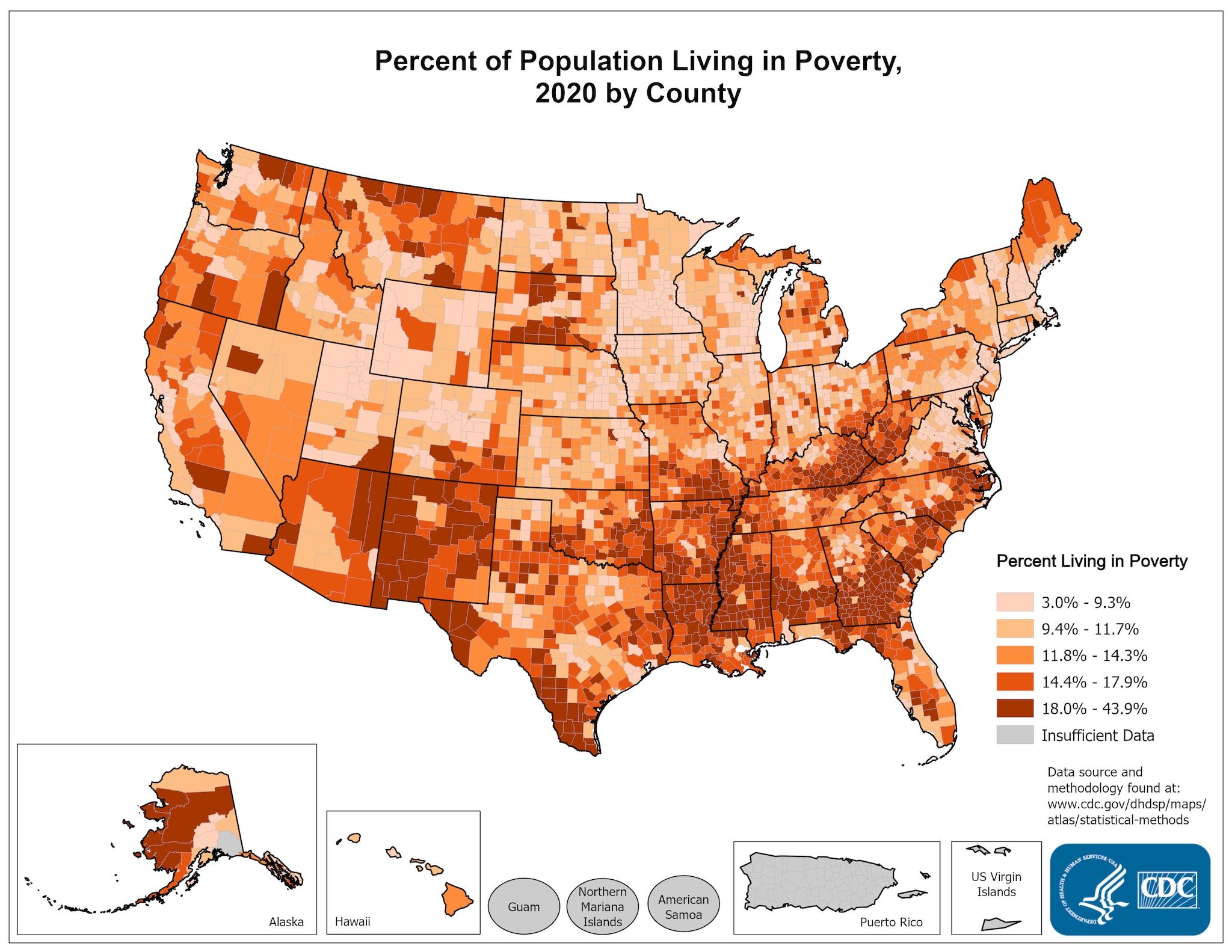
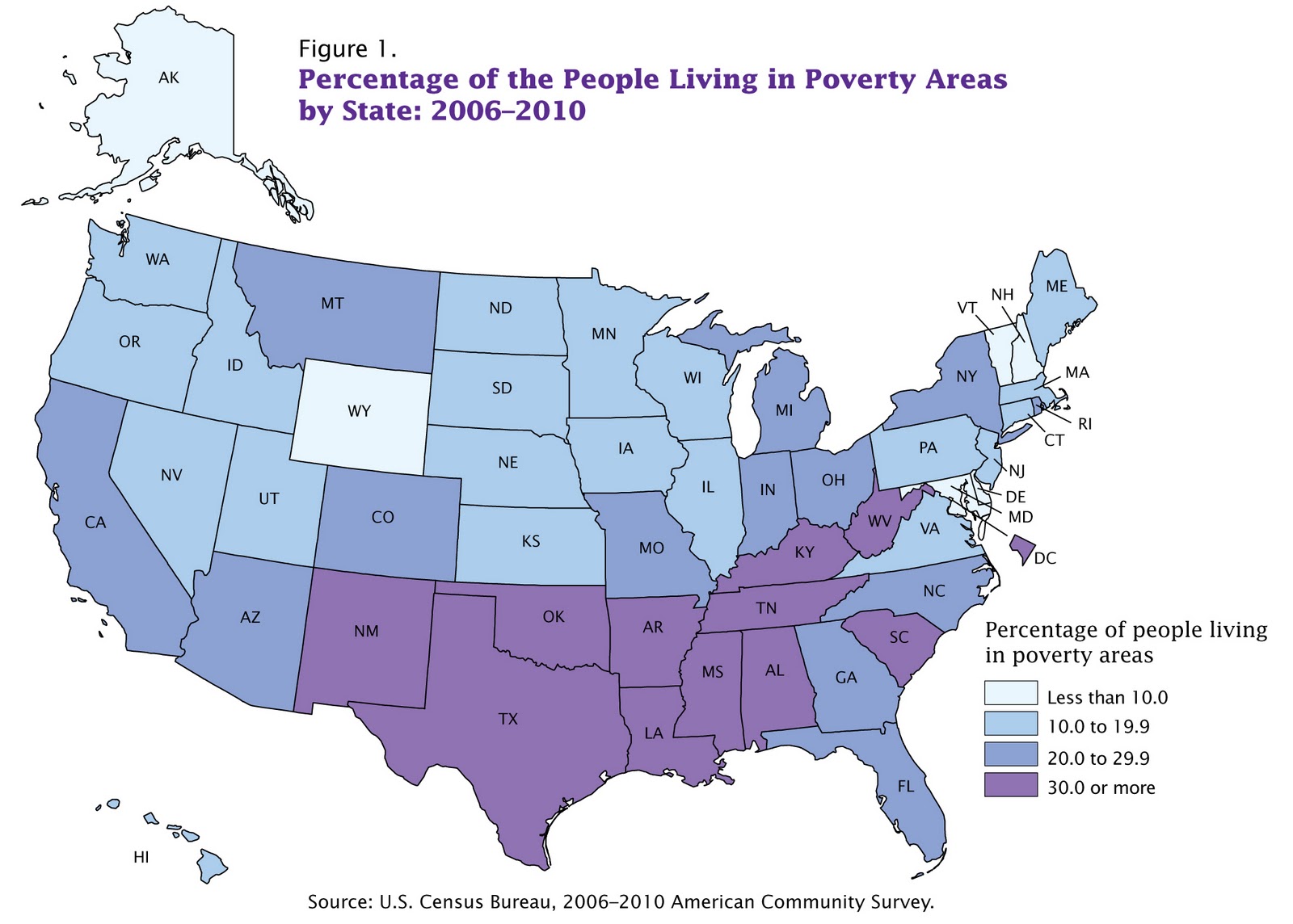
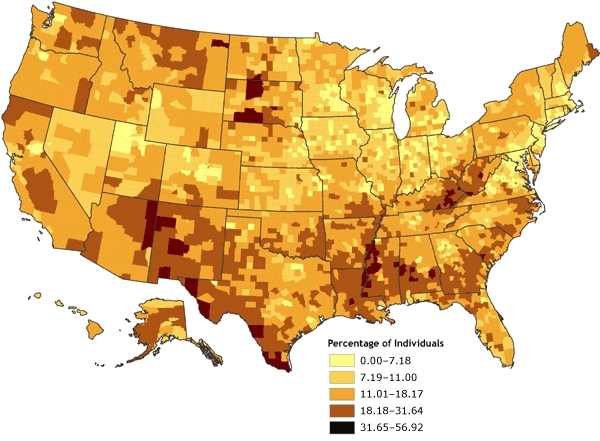
The United States, often lauded for its economic prowess, harbors a complex and multifaceted reality beneath its surface. Poverty, a persistent social issue, affects millions of Americans, creating a stark contrast to the nation’s narrative of prosperity. The United States poverty map, a visual representation of poverty rates across the country, offers a powerful tool for understanding the spatial distribution of this social phenomenon. By illuminating geographic disparities, this map serves as a crucial instrument for policymakers, researchers, and advocates to effectively address the root causes of poverty and implement targeted interventions.
Understanding the Data: A Glimpse into Poverty’s Landscape
The United States poverty map is constructed using data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey (ACS). This comprehensive survey collects information on a wide range of socioeconomic indicators, including income, poverty status, and housing conditions. The ACS data is then aggregated and analyzed to generate poverty rates at various geographic levels, ranging from counties and census tracts to states and the national level.
The resulting map typically depicts poverty rates using color gradients, with darker shades representing higher poverty rates and lighter shades representing lower poverty rates. This visual representation allows for immediate identification of areas with concentrated poverty, enabling a deeper understanding of the spatial distribution of poverty across the country.
Uneven Distribution: Geographic Disparities in Poverty Rates
The United States poverty map reveals a striking pattern of uneven distribution, with certain regions exhibiting significantly higher poverty rates than others. This unevenness is a result of a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Rural vs. Urban Divide: Poverty rates tend to be higher in rural areas compared to urban areas. This disparity is often attributed to limited job opportunities, lower wages, and a lack of access to essential services, including healthcare, education, and transportation.
- Regional Variations: Certain regions, particularly the South and the Appalachian region, consistently experience higher poverty rates than other parts of the country. This is influenced by factors such as historical economic disparities, limited industrialization, and a higher concentration of low-wage jobs.
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Poverty rates are disproportionately higher among minority groups, particularly African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans. This disparity reflects systemic racism and discrimination, which have historically disadvantaged these communities, limiting access to opportunities and resources.
- Geographic Isolation: Areas with limited access to major transportation networks, such as remote rural communities, often experience higher poverty rates due to reduced economic opportunities and limited access to essential services.
The Significance of Mapping Poverty: A Call to Action
The United States poverty map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the complexities of poverty in the United States. Its significance extends beyond mere visualization, as it facilitates:
- Targeted Intervention: By identifying areas with concentrated poverty, the map allows policymakers and social service agencies to prioritize resources and implement targeted programs that address the specific needs of these communities.
- Community-Based Solutions: The map can be used to empower local communities to identify and address the root causes of poverty within their own areas. This localized approach encourages community ownership and fosters sustainable solutions.
- Research and Analysis: The map provides a valuable dataset for researchers and academics to study the dynamics of poverty, analyze the effectiveness of interventions, and develop evidence-based policy recommendations.
- Public Awareness and Advocacy: The map serves as a powerful visual tool for raising public awareness about the extent and distribution of poverty, fostering empathy and promoting advocacy efforts to address this critical social issue.
FAQs: Demystifying the United States Poverty Map
Q: What is the official poverty threshold used to define poverty in the United States?
A: The official poverty threshold is determined annually by the U.S. Census Bureau. It is based on a family’s income relative to its size and composition. Families whose total income falls below the poverty threshold are considered to be living in poverty.
Q: How often is the United States poverty map updated?
A: The poverty map is typically updated annually, based on the latest data from the American Community Survey. This ensures that the map reflects the most recent trends in poverty rates across the country.
Q: What are some of the limitations of the United States poverty map?
A: While the poverty map provides a valuable snapshot of poverty, it is important to recognize its limitations:
- The poverty threshold is a static measure: It does not fully account for the cost of living variations across different geographic areas.
- The map relies on self-reported data: This can introduce inaccuracies due to potential underreporting or misreporting of income.
- The map does not capture the full complexity of poverty: It focuses primarily on income poverty, but does not account for other forms of deprivation, such as food insecurity, housing instability, and lack of access to healthcare.
Tips for Interpreting and Utilizing the United States Poverty Map
- Consider the context: When interpreting the map, it is essential to consider the specific geographic context of each area, including its economic structure, social demographics, and historical factors.
- Look beyond the overall poverty rate: Explore the map’s data to understand the distribution of poverty across different demographic groups, such as race, ethnicity, and age.
- Connect the map with other data sources: Integrate the poverty map with other data sources, such as unemployment rates, education levels, and health outcomes, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to poverty.
- Use the map to inform action: The map should not be viewed as a static representation, but rather as a tool for guiding action and implementing effective interventions to address poverty.
Conclusion: A Journey Towards Equitable Prosperity
The United States poverty map serves as a visual reminder of the persistent challenges of poverty in the United States. It underscores the importance of understanding the spatial distribution of poverty and the need for targeted interventions to address the root causes of this complex social issue. By utilizing this powerful tool, policymakers, researchers, and advocates can work collaboratively to create a more equitable and prosperous future for all Americans.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Topography of Poverty: A Visual Representation of Economic Disparities in the United States. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!