Navigating California’s Seismic Landscape: Understanding Today’s Earthquake Activity
Related Articles: Navigating California’s Seismic Landscape: Understanding Today’s Earthquake Activity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating California’s Seismic Landscape: Understanding Today’s Earthquake Activity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating California’s Seismic Landscape: Understanding Today’s Earthquake Activity
California, renowned for its stunning landscapes and vibrant culture, also sits atop a complex network of fault lines, making it one of the most seismically active regions in the world. Understanding the state’s earthquake activity is crucial for public safety, infrastructure planning, and mitigating potential risks. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of California’s earthquake landscape, focusing on current seismic activity and its implications.
A Dynamic Earth: Understanding California’s Fault Lines
California’s vulnerability to earthquakes stems from its location on the boundary of two major tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. These plates are constantly moving, grinding against each other, and accumulating stress. When this stress is released suddenly, it triggers an earthquake.
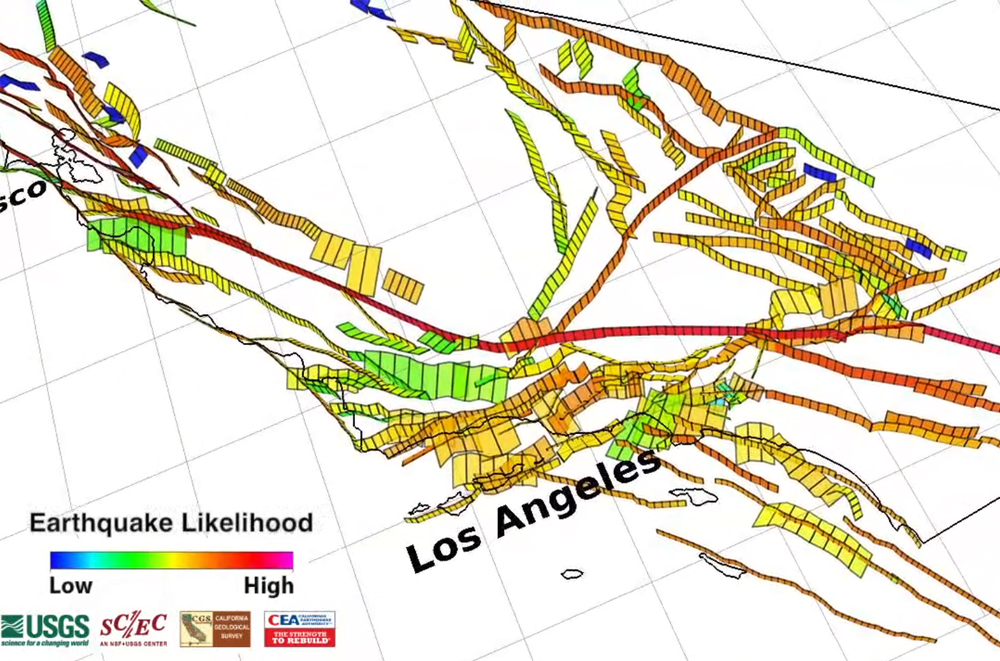
The San Andreas Fault, the most famous fault line in California, is a transform fault, meaning that the plates slide horizontally past each other. This fault runs for over 800 miles, cutting through the state from the Salton Sea in the south to Cape Mendocino in the north. Other significant fault lines include the Hayward Fault, the San Jacinto Fault, and the Calaveras Fault, each contributing to the state’s seismic activity.
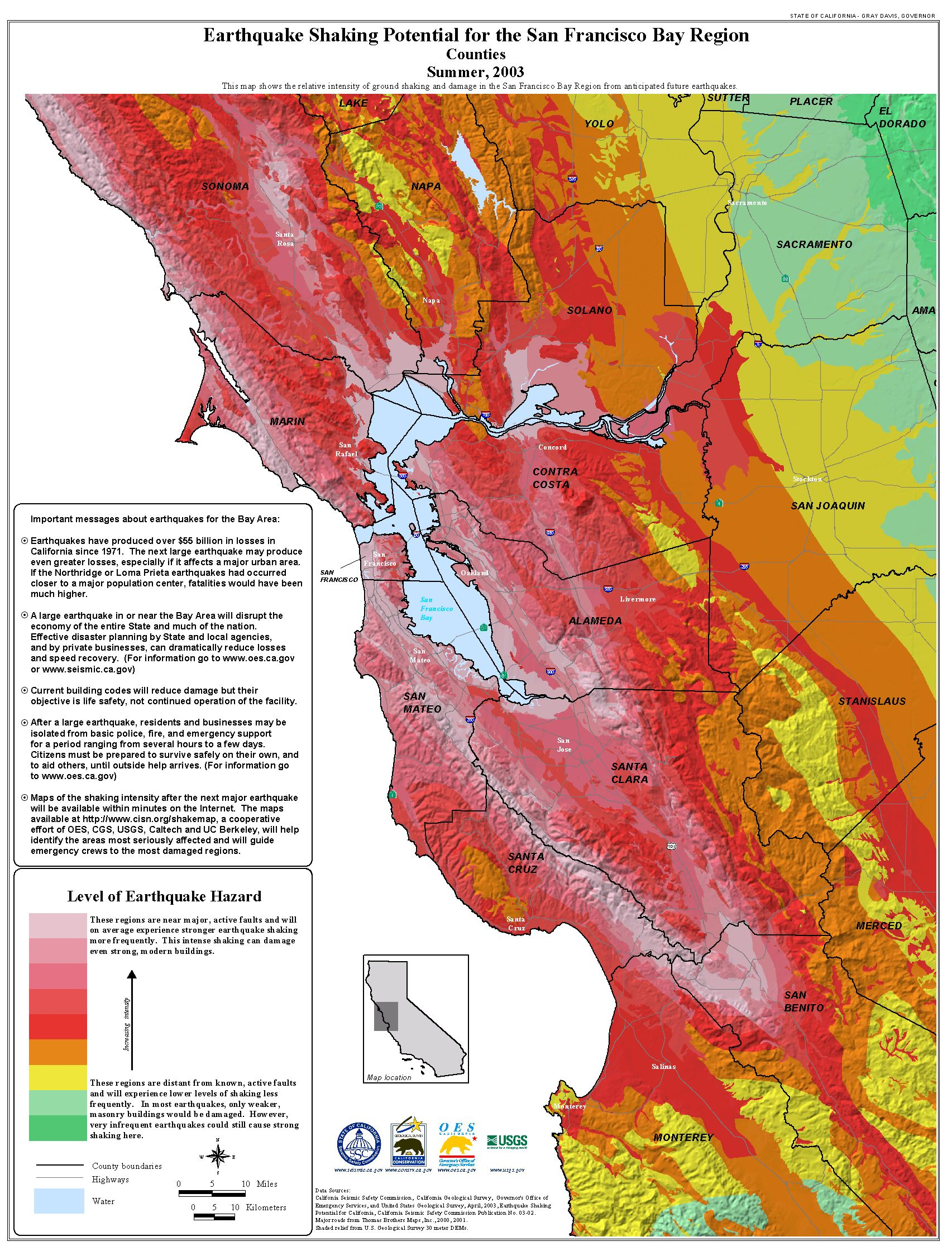
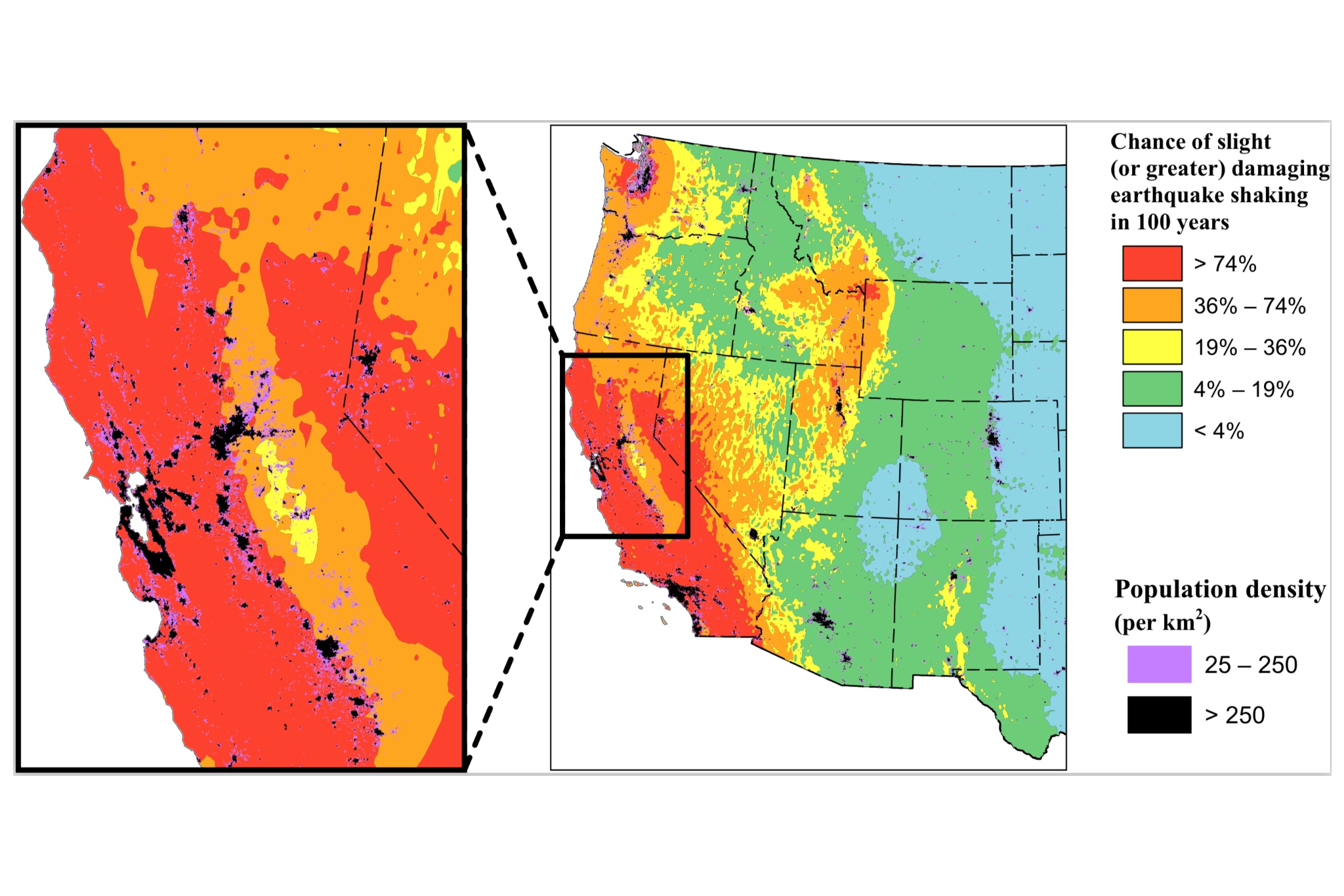
Visualizing Seismic Activity: Maps as Tools for Understanding
Maps play a crucial role in visualizing and understanding earthquake activity in California. They provide a visual representation of the locations, magnitudes, and frequencies of earthquakes, allowing researchers, scientists, and the public to gain valuable insights into the state’s seismic landscape.
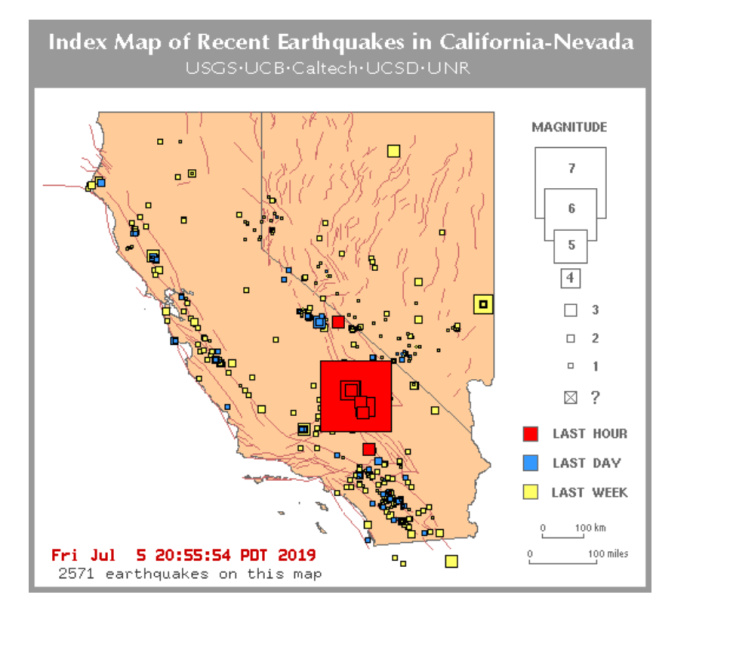
Real-time Earthquake Data: Tracking Seismic Events
Real-time earthquake data is continuously collected by a network of seismographs strategically placed across California. This data is processed and analyzed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and other agencies to provide up-to-the-minute information on earthquake activity.
Today’s Earthquake Activity: A Snapshot of Seismic Events
To provide a detailed account of today’s earthquake activity, we need to consult real-time data sources such as the USGS Earthquake Hazards Program website. This website provides a map displaying recent earthquakes, their locations, magnitudes, and depths.
Analyzing Today’s Earthquake Map: Insights into Seismic Trends
By analyzing the map of today’s earthquake activity, we can glean insights into the current seismic trends in California. For example, we can observe the distribution of earthquakes across different regions, the magnitudes of these events, and whether any specific fault lines are experiencing increased activity.
Understanding the Importance of Earthquake Maps
Earthquake maps are not just visual representations of seismic activity; they are crucial tools for:
- Public Safety: Maps help inform emergency response teams, allowing them to prioritize resources and effectively respond to earthquakes.
- Infrastructure Planning: Engineers and architects use earthquake maps to design buildings and infrastructure that can withstand seismic forces.
- Community Preparedness: Maps raise awareness about earthquake risks, encouraging communities to prepare for potential disasters.
- Scientific Research: Maps provide valuable data for researchers studying earthquake patterns, fault behavior, and the overall dynamics of Earth’s crust.
FAQs Regarding Earthquake Maps
Q: What is the difference between an earthquake map and a fault map?
A: An earthquake map shows the locations and magnitudes of earthquakes that have occurred, while a fault map depicts the locations of known fault lines. Both maps are essential for understanding earthquake hazards.
Q: How often are earthquake maps updated?
A: Real-time earthquake data is constantly updated, so maps reflecting the latest seismic activity are available 24/7.
Q: What are the different colors used on earthquake maps, and what do they represent?
A: Different colors on earthquake maps typically represent the magnitudes of earthquakes, with darker colors indicating stronger events.
Q: Can I use an earthquake map to predict future earthquakes?
A: While earthquake maps provide valuable information about past seismic activity, they cannot predict future earthquakes with certainty.
Tips for Using Earthquake Maps Effectively
- Consult reliable sources: Use maps from reputable organizations like the USGS.
- Understand the map’s scale: Pay attention to the scale to accurately interpret the locations and magnitudes of earthquakes.
- Look for patterns: Analyze the distribution of earthquakes and identify areas with increased activity.
- Stay informed: Regularly check for updates on earthquake maps to stay informed about current seismic events.
Conclusion: A Continuously Evolving Landscape
California’s earthquake landscape is constantly evolving, with seismic activity occurring on a daily basis. Understanding this dynamic environment is crucial for ensuring public safety, mitigating risks, and fostering resilience in the face of potential earthquakes. Earthquake maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and responding to seismic events, providing critical insights into the state’s complex and dynamic geological reality. By embracing the information provided by these maps, we can better prepare for and adapt to the challenges posed by California’s seismic landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating California’s Seismic Landscape: Understanding Today’s Earthquake Activity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!