Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
Related Articles: Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads
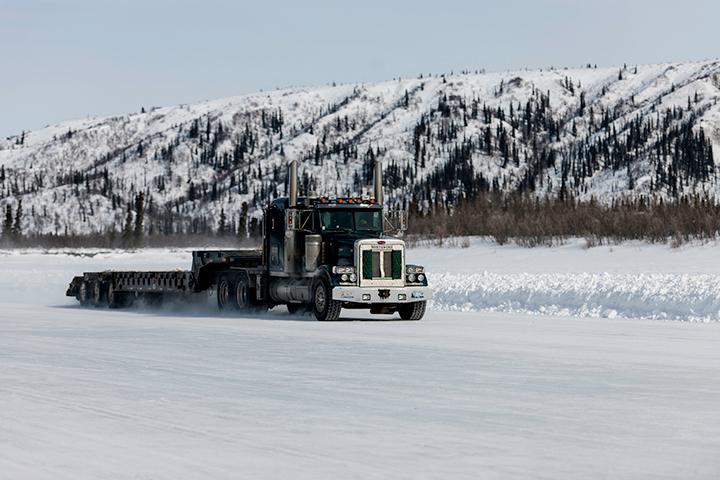

Canada, a nation renowned for its vast landscapes and harsh winters, boasts a unique infrastructure that emerges annually from the frozen depths: the ice roads. These temporary arteries, constructed on frozen lakes and rivers, provide vital access to remote communities and resource extraction sites during the frigid months. This article delves into the intricacies of these remarkable roads, exploring their construction, operation, and the critical role they play in Canadian life.
The Genesis of Ice Roads:
The concept of utilizing frozen water bodies for transportation dates back centuries, with indigenous communities in Canada and other northern regions relying on ice bridges and paths for travel. However, the modern-day ice road, as we know it, evolved in the mid-20th century, driven by the burgeoning resource extraction industry in Canada’s north.
The construction of an ice road begins with meticulous planning and surveying. Engineers assess the thickness and stability of the ice, taking into account factors such as water depth, current flow, and anticipated weather conditions. Once a suitable location is identified, heavy machinery is employed to clear snow and prepare the surface. Water is often sprayed onto the ice to create a smooth and durable surface, further enhancing its load-bearing capacity.
The Lifeline of the North:
Ice roads serve as vital lifelines for communities and industries situated in remote regions of Canada, particularly in the territories of Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Their significance is multifaceted:
- Access to Essential Supplies: For isolated communities, ice roads provide a crucial link to the outside world, enabling the transportation of essential goods, including food, fuel, building materials, and medical supplies. Without these temporary roadways, these communities would face severe logistical challenges and potential shortages during the winter months.
- Resource Extraction: Canada’s north is rich in natural resources, including diamonds, gold, and oil. Ice roads facilitate the transportation of heavy equipment, supplies, and extracted resources to and from mining sites, oil fields, and other industrial operations. This access is essential for the development and economic viability of these industries.
- Community Connectivity: Ice roads connect remote communities to larger centers, enabling residents to access healthcare, education, and social services. They also facilitate cultural exchange and recreational activities, fostering a sense of connection between communities.
Navigating the Frozen Terrain:
Traveling on an ice road presents unique challenges and requires careful planning and adherence to safety protocols. Some key considerations include:
- Weather Conditions: Ice roads are inherently susceptible to weather changes. Thawing temperatures, heavy snowfall, and high winds can compromise the integrity of the ice, leading to road closures and potential hazards.
- Vehicle Limitations: Only specially equipped vehicles with heavy-duty tires and reinforced chassis are permitted on ice roads. Load limits are strictly enforced to prevent damage to the ice.
- Safety Precautions: Drivers must be highly skilled and experienced in navigating icy conditions. Strict speed limits and adherence to designated routes are crucial for ensuring safety.
A Seasonal Phenomenon:
Ice roads are inherently temporary structures, their existence dictated by the harsh Canadian winter. Construction typically commences in late autumn or early winter, as temperatures plummet and ice forms. The roads remain operational until spring, when rising temperatures and melting ice render them unsafe for travel.
The seasonal nature of ice roads presents logistical challenges for communities and industries relying on them. Advance planning is essential to ensure the timely delivery of goods and services before the roads close for the season. Additionally, the seasonal closure necessitates the development of alternative transportation methods, such as air transport, for the remaining months of the year.
The Future of Ice Roads:
While ice roads have played a critical role in Canada’s development, their future is subject to evolving factors, including climate change and technological advancements.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns pose significant challenges to the stability and longevity of ice roads. As winters become shorter and less severe, the construction and operational windows for these temporary arteries may shrink, impacting their effectiveness.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in alternative transportation methods, such as all-terrain vehicles, snowmobiles, and air transport, may offer viable alternatives to ice roads in certain situations. However, the cost and accessibility of these alternatives may limit their widespread adoption.
FAQs about Ice Roads:
- How thick does the ice need to be for an ice road? The minimum ice thickness required for an ice road varies depending on the load capacity and traffic volume. Typically, a minimum thickness of 30-40 centimeters is considered safe for light vehicles, while heavier loads require thicker ice.
- Are ice roads safe? Ice roads are generally safe when properly constructed and maintained, and when drivers adhere to safety regulations. However, they are inherently susceptible to weather conditions and require careful navigation.
- How long are ice roads? Ice roads can range in length from a few kilometers to hundreds of kilometers, depending on the location and the need they serve.
- Who maintains ice roads? Ice roads are typically maintained by government agencies, resource extraction companies, or local communities. Maintenance involves regular inspections, snow removal, and ice resurfacing.
- What happens when an ice road breaks? If an ice road breaks, it can be dangerous for vehicles and drivers. Vehicles may fall through the ice, and drivers may be injured or even drown. If an ice road breaks, it is important to stay calm and call for help immediately.
Tips for Traveling on Ice Roads:
- Plan your trip carefully: Check the weather forecast and road conditions before setting out.
- Drive slowly and cautiously: Ice roads are slippery and can be unpredictable.
- Maintain a safe distance from other vehicles: This will give you time to react if something unexpected happens.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to the ice conditions and any warning signs.
- Carry emergency supplies: This includes food, water, blankets, a first-aid kit, and a cell phone.
Conclusion:
Canada’s ice roads stand as testament to the resilience and ingenuity of its people, showcasing their ability to adapt to challenging environments. These temporary arteries play a vital role in connecting remote communities, facilitating resource extraction, and supporting the economic development of the north. While their future is subject to evolving factors, their legacy as a unique and essential part of Canadian infrastructure is firmly established. As technology advances and the climate changes, the ingenuity and resourcefulness of Canadians will continue to shape the future of these remarkable roads.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Frozen Frontier: A Guide to Canada’s Ice Roads. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!