Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping
- 3.1 Unveiling Consumer Perceptions: The Essence of Perceptual Mapping
- 3.2 Constructing a Perceptual Map: A Step-by-Step Approach
- 3.3 Illustrative Examples: Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping
- 3.4 Applications of Perceptual Mapping: Unlocking Business Value
- 3.5 Addressing Common Concerns: FAQs on Perceptual Mapping
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Perceptual Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Landscape with Confidence
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping
![Level Up Your Marketing With A Perceptual Map [Free Template] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/4c6b59e4a10c3c9f/original/inline-business-strategy-perceptual-map-template-3-2x.jpg)
In the competitive landscape of modern business, understanding consumer perceptions is paramount. Consumers make purchasing decisions based on a complex interplay of factors, including brand image, product features, price, and perceived value. Perceptual mapping, a powerful visual tool, helps businesses navigate this complex terrain by offering a clear understanding of how consumers perceive their products or services relative to competitors.
Unveiling Consumer Perceptions: The Essence of Perceptual Mapping
Perceptual mapping, also known as positioning maps or perceptual positioning maps, is a visual representation of consumer perceptions. It plots various brands or products on a two-dimensional graph, with each axis representing a key attribute or dimension that influences consumer preferences. These attributes can range from price and quality to brand image and target audience.
The resulting map provides a visual snapshot of the competitive landscape, revealing:
- Brand Positioning: How consumers perceive a brand relative to its competitors.
- Target Audience: The segment of consumers most attracted to a particular brand or product.
- Competitive Advantages: Strengths and weaknesses of a brand compared to its rivals.
- Market Gaps: Unmet consumer needs and opportunities for new product development.
Constructing a Perceptual Map: A Step-by-Step Approach
Creating a perceptual map involves a systematic process that combines qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Step 1: Identifying Key Attributes: The first step is to identify the key attributes or dimensions that influence consumer preferences within the specific market. This can be achieved through market research, customer surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis.
Step 2: Selecting Attributes for the Axes: From the identified attributes, two key dimensions are selected for the X and Y axes of the map. These dimensions should be chosen based on their relevance to consumer decision-making and their ability to differentiate brands or products.
Step 3: Gathering Consumer Perceptions: Data on consumer perceptions is gathered through surveys or interviews. Respondents are asked to rate brands or products on the chosen attributes, typically using a scale. This data provides the foundation for plotting brands on the map.
Step 4: Plotting Brands: Using the collected data, each brand is plotted on the map based on its perceived position on the chosen attributes. The resulting map visually displays the relative positioning of brands or products within the market.
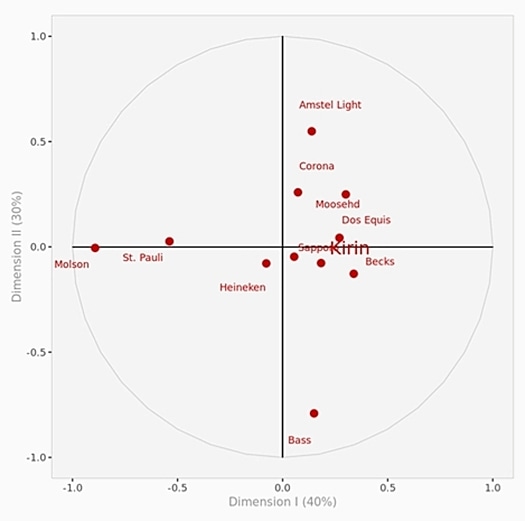
Step 5: Analyzing the Map: Once the map is constructed, it is analyzed to identify key insights:
- Cluster Analysis: Identifying groups of brands that are perceived similarly by consumers.
- Competitive Landscape: Understanding the competitive landscape and identifying direct competitors.
- Brand Positioning: Assessing a brand’s current position and identifying potential opportunities for repositioning.
- Market Gaps: Recognizing unmet consumer needs and identifying opportunities for new product development.
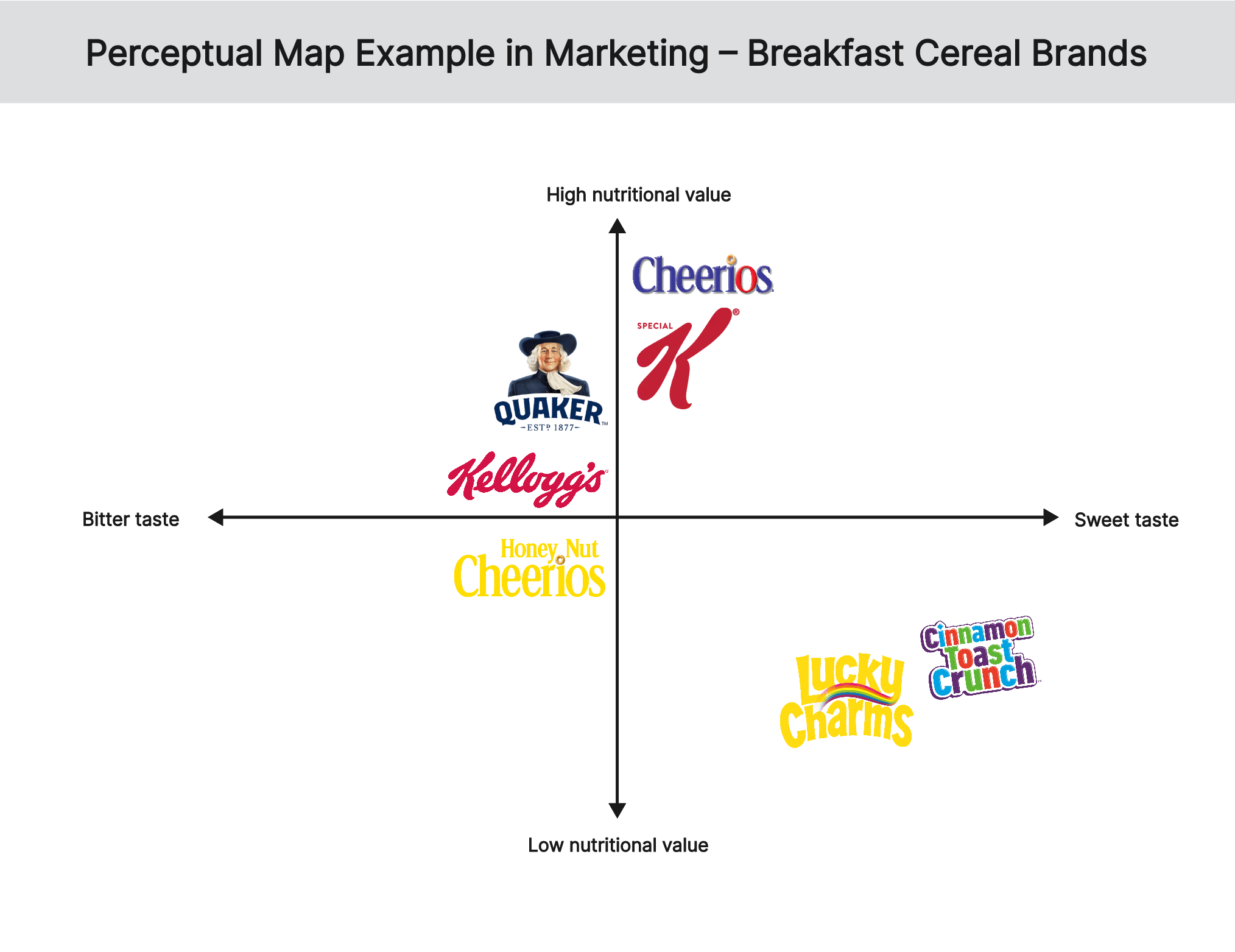
Illustrative Examples: Unveiling the Power of Perceptual Mapping
Example 1: The Automobile Industry:
A perceptual map for the automobile industry could utilize the axes "Price" and "Fuel Efficiency." Luxury brands like Mercedes-Benz and BMW would be positioned in the upper right quadrant, representing high price and high fuel efficiency. In contrast, budget-friendly brands like Hyundai and Kia would be located in the lower left quadrant, representing lower price and lower fuel efficiency.
Example 2: The Smartphone Market:
A perceptual map for smartphones could use the axes "Price" and "Camera Quality." Premium brands like Apple and Samsung would be positioned in the upper right quadrant, representing high price and high camera quality. Budget-friendly brands like Xiaomi and OnePlus would be located in the lower left quadrant, representing lower price and lower camera quality.
Applications of Perceptual Mapping: Unlocking Business Value
Perceptual mapping offers a versatile tool for strategic decision-making across various business functions:
-
Marketing:
- Brand Positioning: Identifying opportunities for repositioning brands to capture new market segments.
- Product Development: Identifying unmet consumer needs and developing new products to fill market gaps.
- Marketing Campaigns: Developing targeted marketing campaigns tailored to specific consumer segments.
-
Product Management:
- Product Differentiation: Identifying unique selling propositions and differentiating products from competitors.
- Product Development: Guiding product development efforts to address specific consumer needs.
-
Sales:
- Sales Strategies: Developing targeted sales strategies based on consumer preferences and competitive landscape.
- Sales Training: Educating sales teams on customer perceptions and competitive advantages.
-
Strategic Planning:
- Market Analysis: Gaining a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape and identifying potential threats and opportunities.
- Strategic Direction: Informing strategic decisions regarding product development, pricing, and marketing.
Addressing Common Concerns: FAQs on Perceptual Mapping
Q1: What are the limitations of perceptual mapping?
While powerful, perceptual mapping has limitations. The accuracy of the map depends on the quality of the data collected, which can be influenced by factors like sample size, survey design, and respondent bias. Moreover, the map only captures two dimensions at a time, potentially overlooking other important attributes.
Q2: How can I ensure the accuracy of my perceptual map?
To ensure accuracy, use a representative sample size, employ rigorous survey design, and consider multiple data sources to mitigate bias. It is also crucial to validate the findings through qualitative research methods like focus groups and interviews.
Q3: Can perceptual mapping be used for new product development?
Absolutely. Perceptual maps can identify gaps in the market, suggesting opportunities for new product development. By understanding consumer preferences and competitive offerings, businesses can develop products that meet specific consumer needs and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Q4: How often should perceptual maps be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on market dynamics. In rapidly evolving markets, frequent updates are essential. However, in stable markets, annual or bi-annual updates may suffice.
Tips for Effective Perceptual Mapping
- Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives for the map before embarking on the process.
- Relevant Attributes: Select attributes that are truly relevant to consumer decision-making.
- Reliable Data: Employ robust data collection methods and ensure data quality.
- Visual Clarity: Create a visually appealing and easy-to-understand map.
- Regular Updates: Update the map periodically to reflect changes in the market.
Conclusion: Navigating the Competitive Landscape with Confidence
Perceptual mapping offers a powerful tool for businesses to navigate the complex landscape of consumer perceptions. By understanding how consumers perceive their products or services relative to competitors, businesses can make informed decisions regarding brand positioning, product development, marketing strategies, and strategic planning. By leveraging the insights provided by perceptual mapping, businesses can gain a competitive advantage, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth.
![Level Up Your Marketing With A Perceptual Map [Free Template] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/ed7a10e837843f7/original/inline-business-strategy-perceptual-map-template-4-2x.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Marketplace: A Deep Dive into Perceptual Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!