Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to the Oceans and Seas
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to the Oceans and Seas
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to the Oceans and Seas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to the Oceans and Seas

The Earth, our planet, is a mesmerizing tapestry of land and water, with vast oceans and seas covering approximately 71% of its surface. These bodies of water, interconnected and dynamic, play a critical role in shaping the Earth’s climate, supporting diverse ecosystems, and facilitating global trade. Understanding the world’s oceans and seas is essential for comprehending our planet’s intricate workings and appreciating the interconnectedness of life.
The Global Water Canvas: A Journey Through the Oceans and Seas
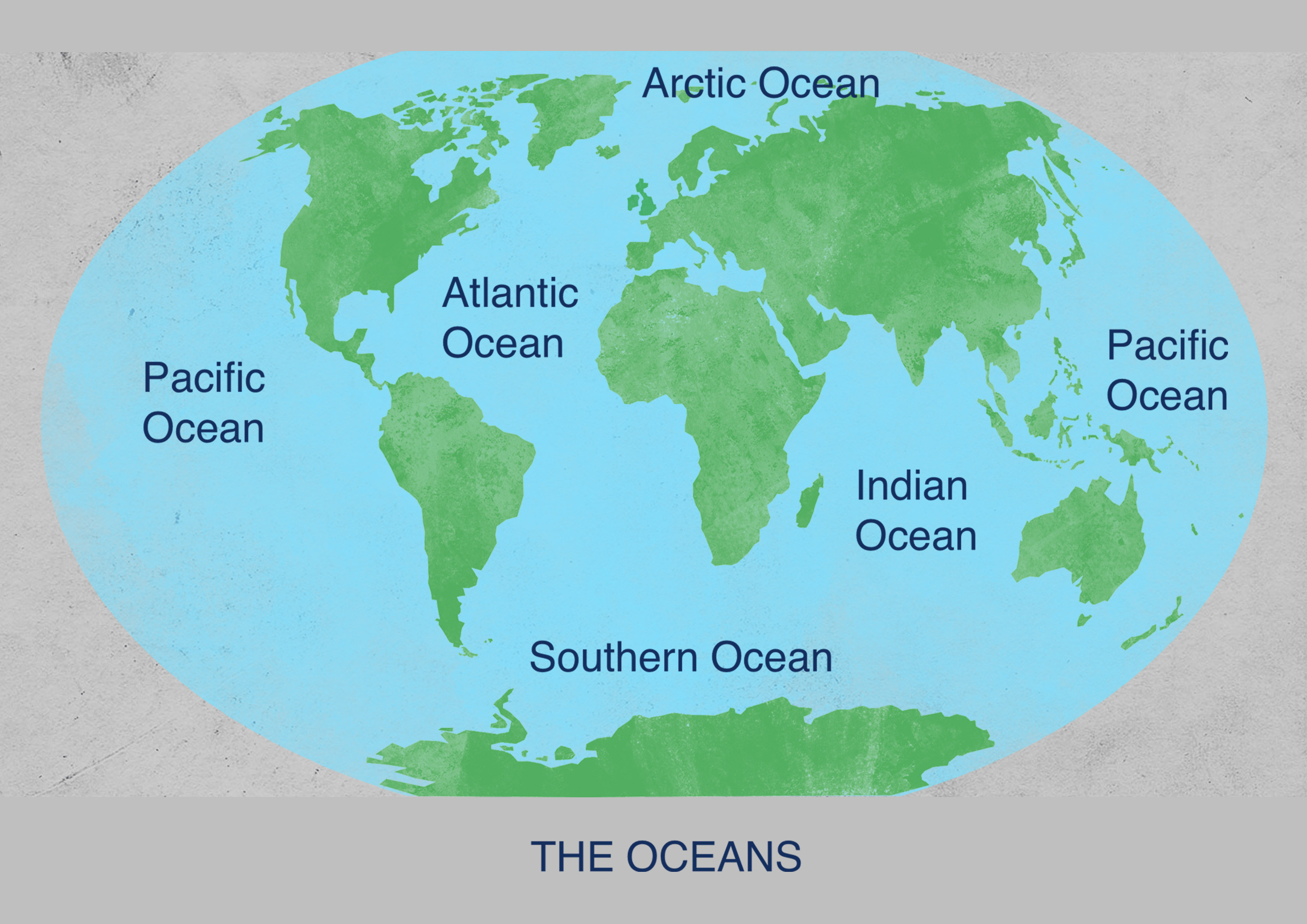
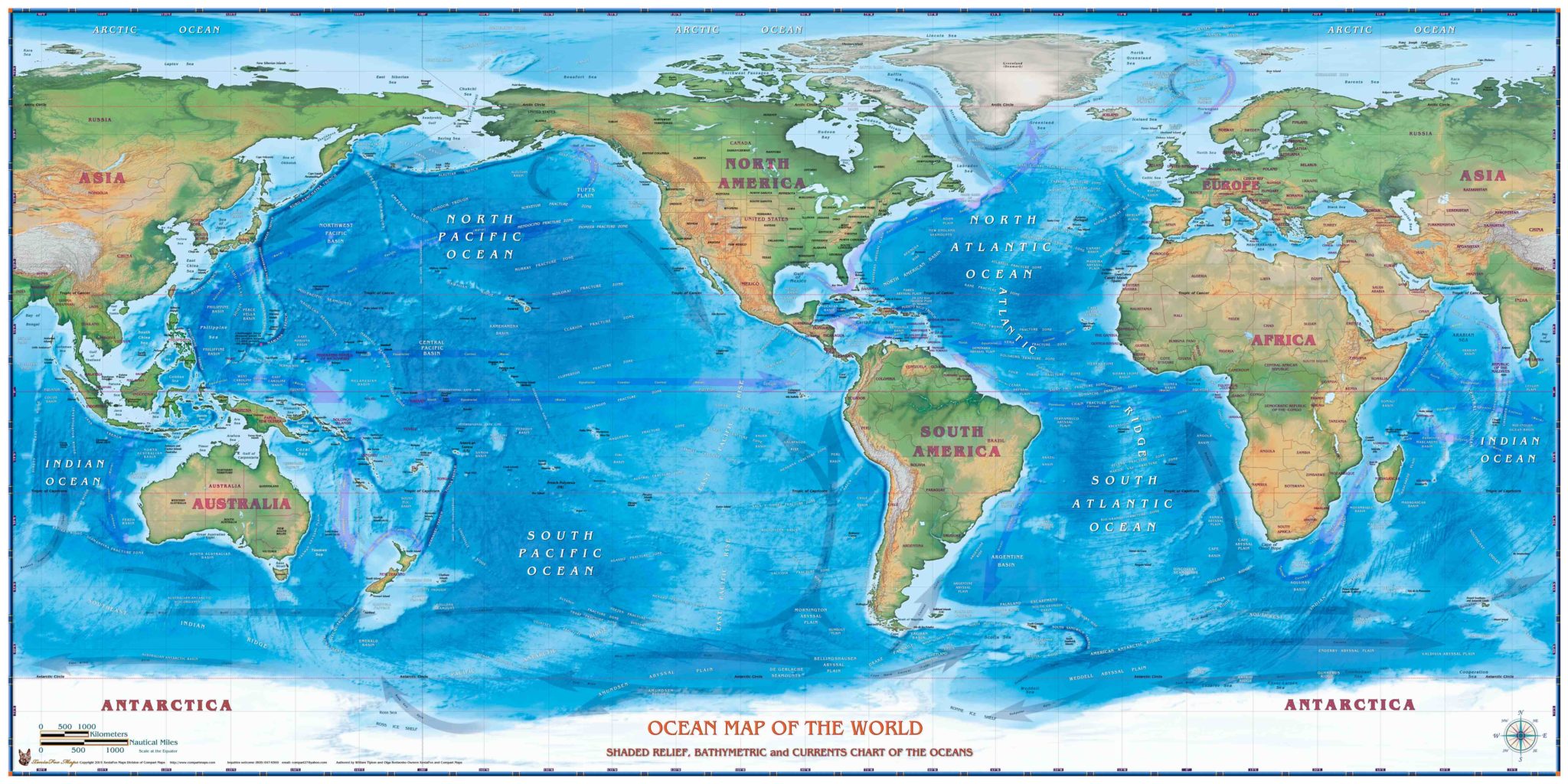
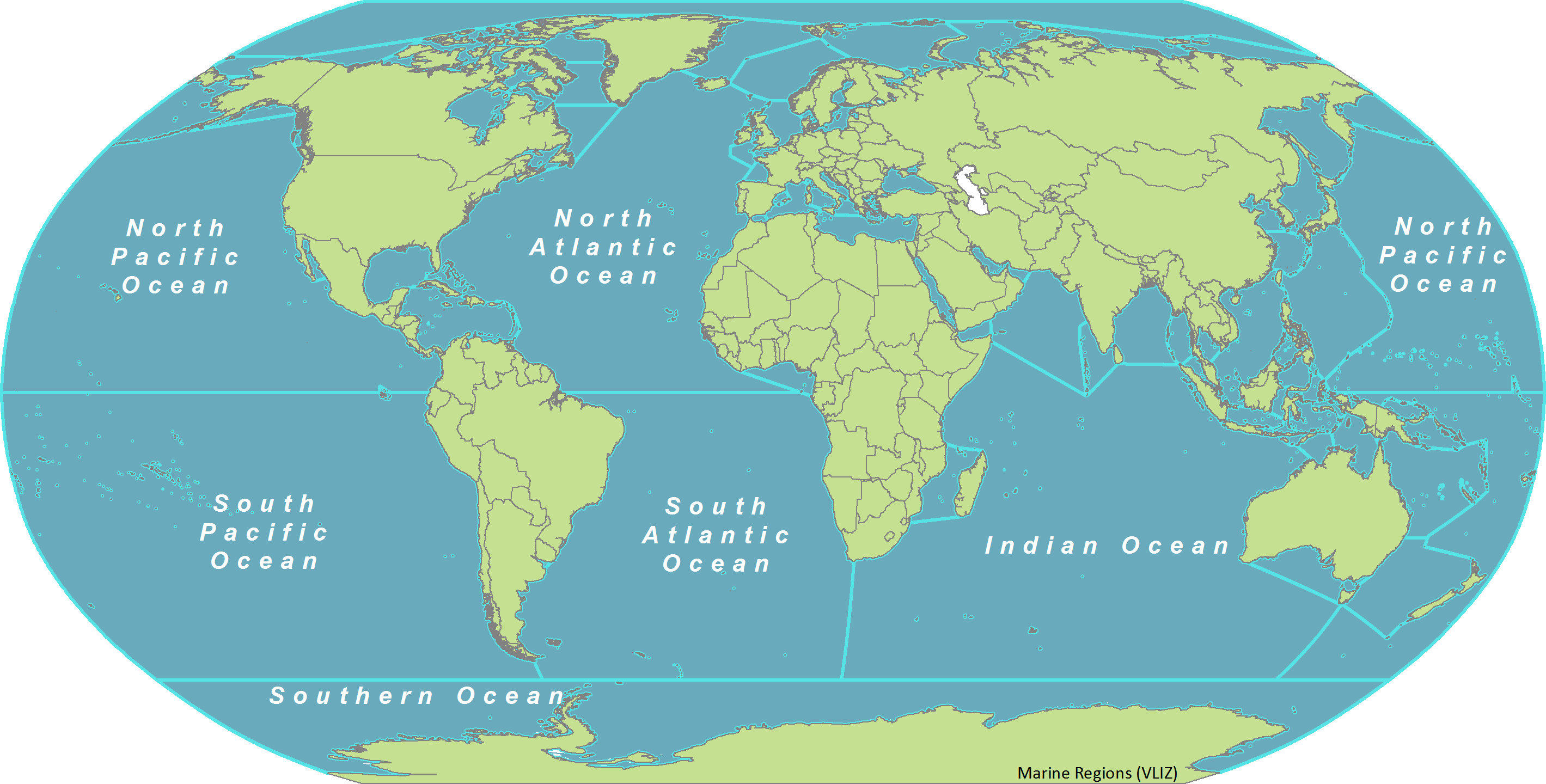
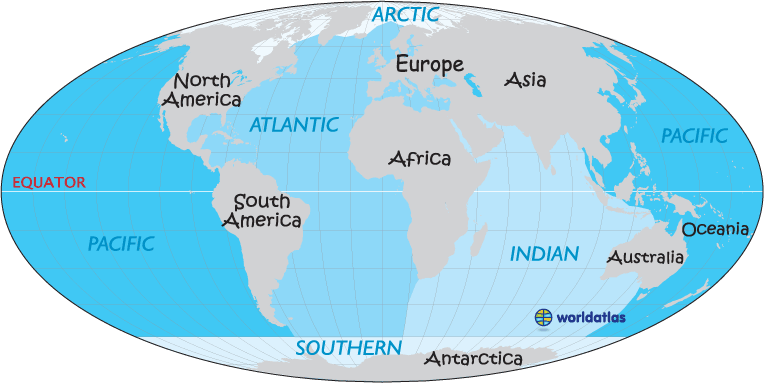
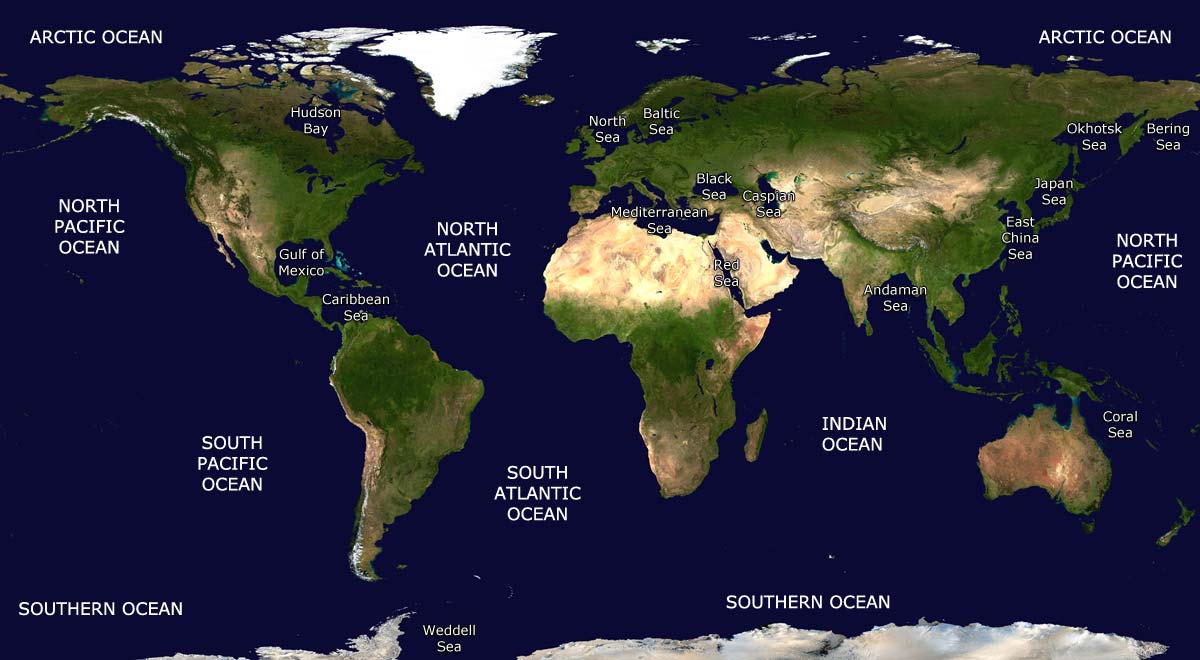
The world’s oceans are vast, interconnected bodies of saline water that cover most of the Earth’s surface. They are typically divided into five major oceans:
- Pacific Ocean: The largest and deepest ocean, covering over 30% of the Earth’s surface. It is home to the Mariana Trench, the deepest point in the world’s oceans.
- Atlantic Ocean: The second largest ocean, characterized by its vast expanse and numerous islands. It is home to the Gulf Stream, a warm current that significantly influences the climate of Western Europe.
- Indian Ocean: Located in the Southern Hemisphere, it is known for its warm waters and monsoon winds. It is home to the world’s largest coral reef system, the Great Barrier Reef.
- Arctic Ocean: The smallest and shallowest of the world’s oceans, located around the North Pole. It is covered in ice for much of the year.
- Southern Ocean: This ocean surrounds Antarctica and is characterized by its strong currents and cold, nutrient-rich waters.
The Interconnectedness of Seas
Smaller bodies of water, known as seas, are often partially enclosed by land and are connected to the oceans. These seas can be classified by their location and characteristics:
- Marginal seas: These seas are located along the edges of continents and are often connected to the oceans through narrow straits. Examples include the Mediterranean Sea, the Caribbean Sea, and the Bering Sea.
- Intercontinental seas: These seas lie between continents and are connected to the oceans by wider passages. Examples include the Red Sea, the Black Sea, and the Baltic Sea.
- Inland seas: These seas are surrounded by land and are not directly connected to the oceans. Examples include the Caspian Sea, the Aral Sea, and the Dead Sea.
The Importance of Oceans and Seas
The oceans and seas are essential for life on Earth, playing a crucial role in regulating the planet’s climate, providing food and resources, and supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Climate regulation: Oceans act as a massive heat sink, absorbing and distributing heat energy from the sun. This process helps moderate global temperatures and influences weather patterns.
- Biodiversity: Oceans are home to a vast array of marine life, including fish, mammals, birds, reptiles, and invertebrates. This biodiversity is essential for the health of the entire planet.
- Food security: Oceans provide a significant source of food for billions of people around the world. Fish, shellfish, and other marine resources are vital for human sustenance.
- Economic activity: Oceans facilitate global trade, transportation, and energy production. Ports and shipping lanes are crucial for international commerce and economic development.
- Recreation and tourism: Oceans and seas offer opportunities for recreation, tourism, and leisure activities, contributing to local economies and promoting well-being.
Challenges Facing Oceans and Seas
Despite their importance, oceans and seas are facing numerous challenges:
- Pollution: Runoff from agriculture, industry, and urban areas is polluting oceans and seas with harmful chemicals, plastics, and other pollutants.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices are depleting fish populations and disrupting marine ecosystems.
- Climate change: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea level rise are altering marine environments and threatening marine life.
- Habitat destruction: Coastal development, oil and gas exploration, and other human activities are destroying marine habitats.
Protecting Our Oceans and Seas
Addressing the challenges facing oceans and seas requires a concerted global effort. Sustainable management practices, international cooperation, and responsible stewardship are essential for protecting these vital resources.
FAQs about Oceans and Seas
1. What is the difference between an ocean and a sea?
Oceans are vast, interconnected bodies of saline water that cover most of the Earth’s surface. Seas are smaller bodies of water, often partially enclosed by land and connected to the oceans.
2. How do oceans influence weather patterns?
Oceans act as a massive heat sink, absorbing and distributing heat energy from the sun. This process helps moderate global temperatures and influences weather patterns.
3. What is the impact of climate change on oceans?
Climate change is causing rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and sea level rise, which are altering marine environments and threatening marine life.
4. What can be done to protect oceans and seas?
Protecting oceans and seas requires sustainable management practices, international cooperation, and responsible stewardship. This includes reducing pollution, managing fisheries sustainably, and addressing climate change.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating Oceans and Seas
- Explore maps and charts: Visualizing the world’s oceans and seas on maps and charts can provide a deeper understanding of their vastness and interconnectedness.
- Learn about marine life: Discover the incredible diversity of marine life through books, documentaries, and online resources.
- Visit coastal areas: Experience the beauty and power of the oceans firsthand by visiting coastal areas and participating in activities like swimming, snorkeling, or diving.
- Support organizations dedicated to ocean conservation: Contribute to efforts to protect oceans and seas by supporting organizations that work to address pollution, overfishing, and climate change.
Conclusion
The world’s oceans and seas are vital for life on Earth, playing a critical role in regulating the planet’s climate, providing food and resources, and supporting diverse ecosystems. Understanding their importance and the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring their long-term health and well-being. By embracing sustainable practices, promoting international cooperation, and fostering responsible stewardship, we can work towards a future where oceans and seas thrive for generations to come.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to the Oceans and Seas. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!