The Italian Political Landscape: A Complex Tapestry of Regions and Identities
Related Articles: The Italian Political Landscape: A Complex Tapestry of Regions and Identities
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Italian Political Landscape: A Complex Tapestry of Regions and Identities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Italian Political Landscape: A Complex Tapestry of Regions and Identities

Italy, a nation steeped in history and culture, is also a complex political entity. Its political map, a reflection of its unique historical trajectory and diverse regional identities, offers a fascinating insight into the country’s governance and the forces that shape its development. Understanding this intricate tapestry of administrative divisions is crucial for comprehending the nuances of Italian politics, its regional dynamics, and the challenges it faces.
A Mosaic of Regions:
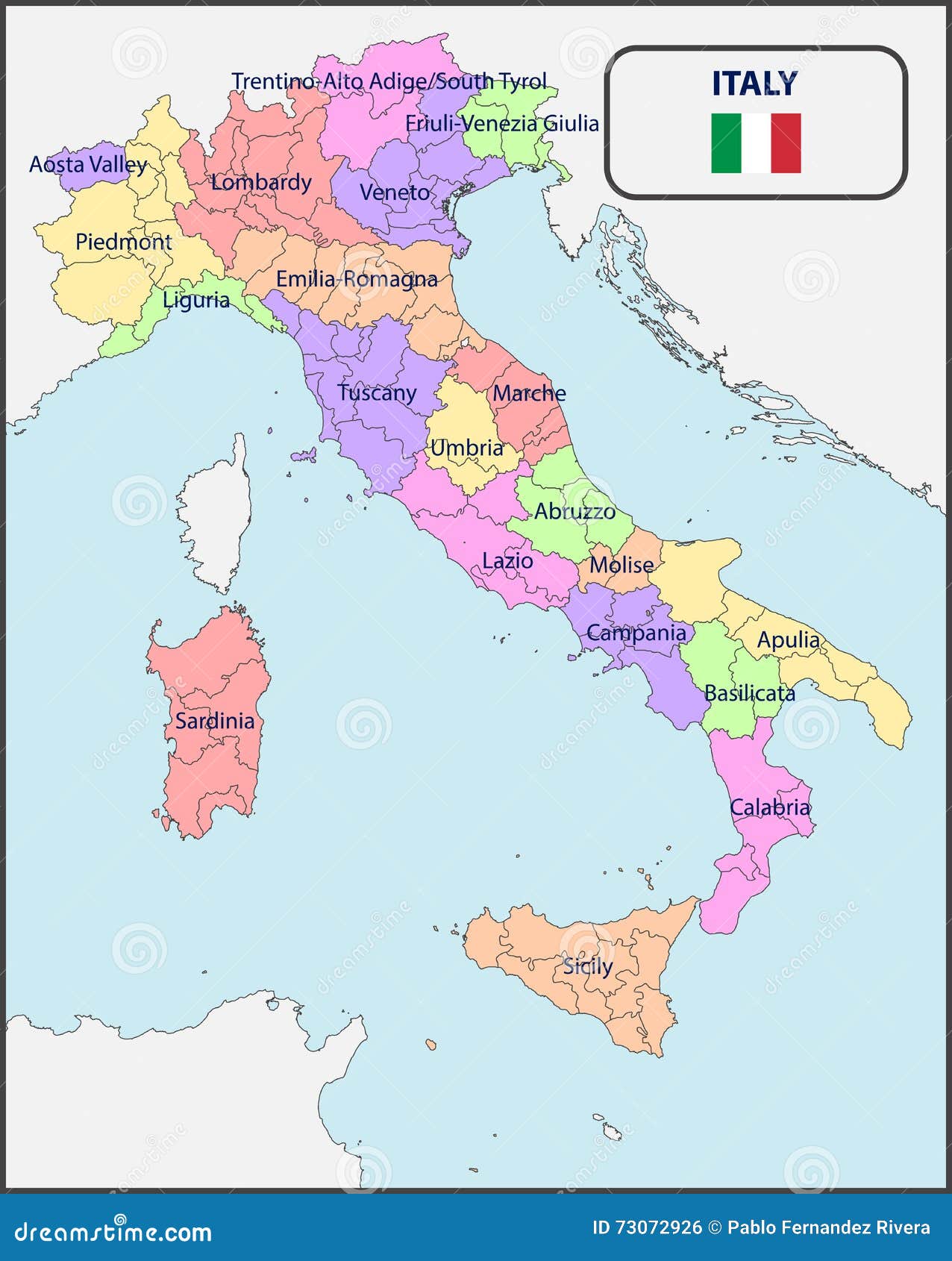
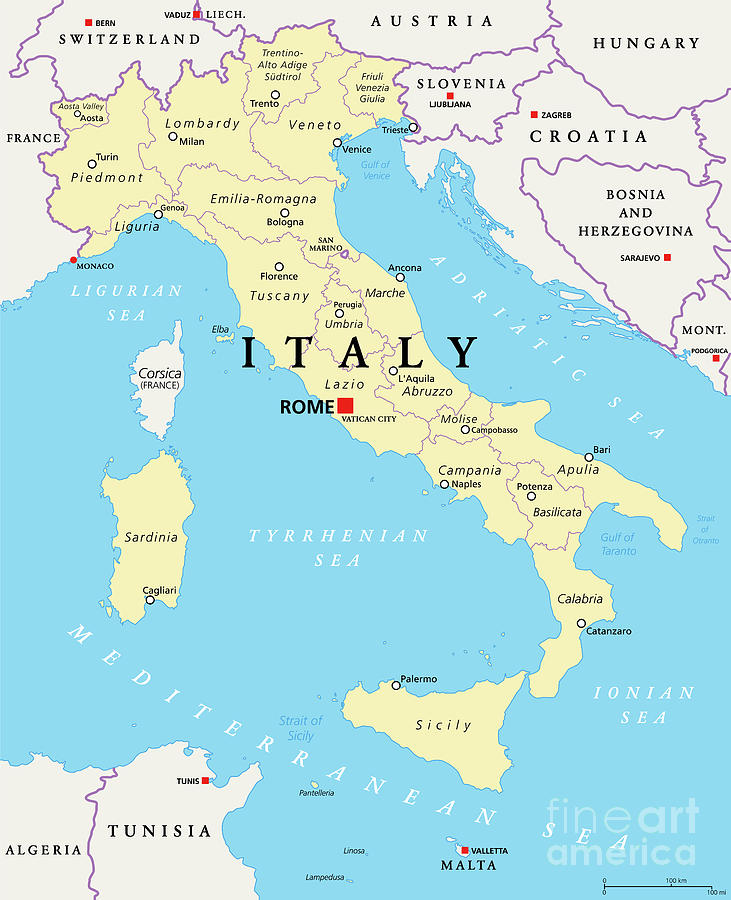
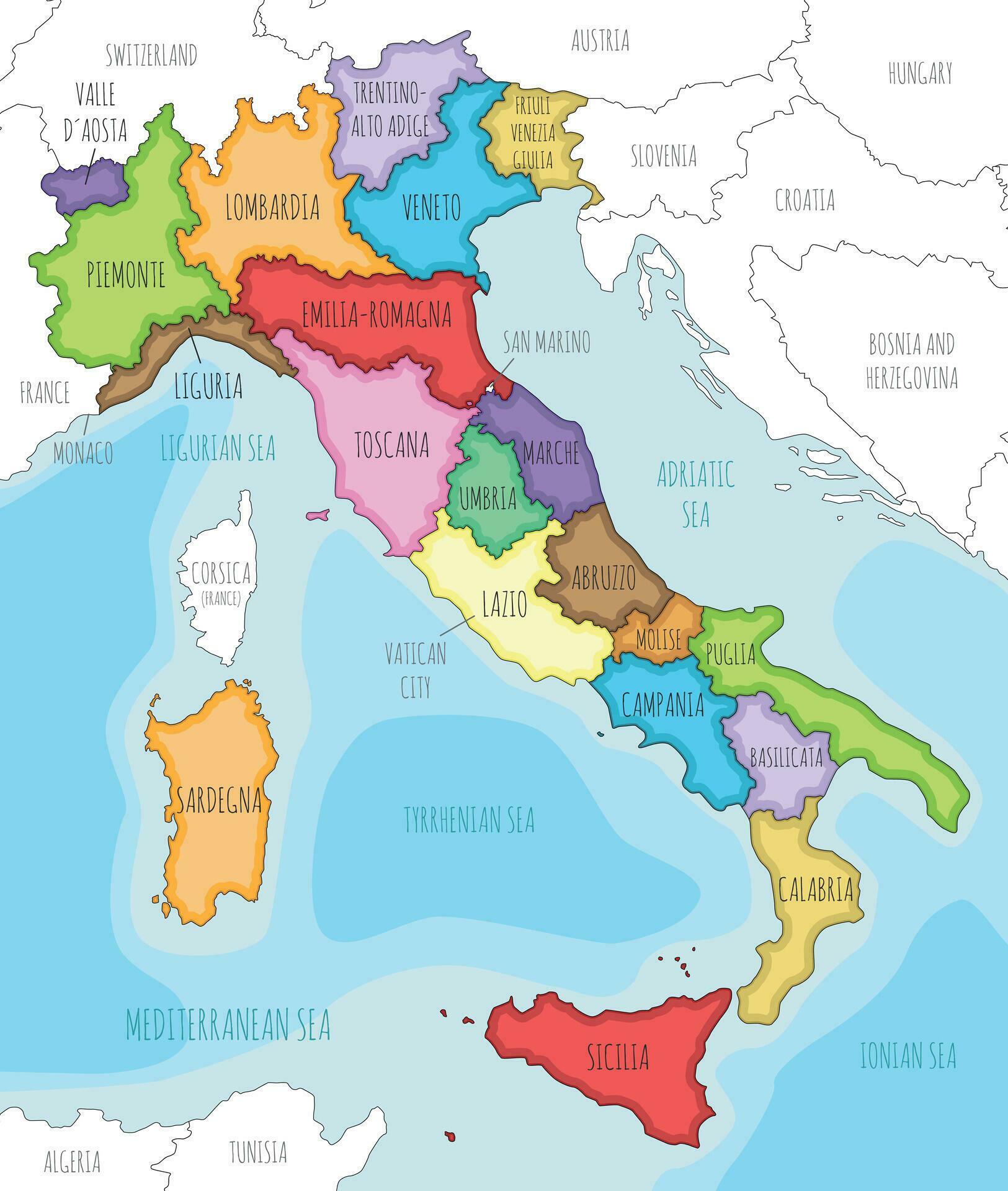
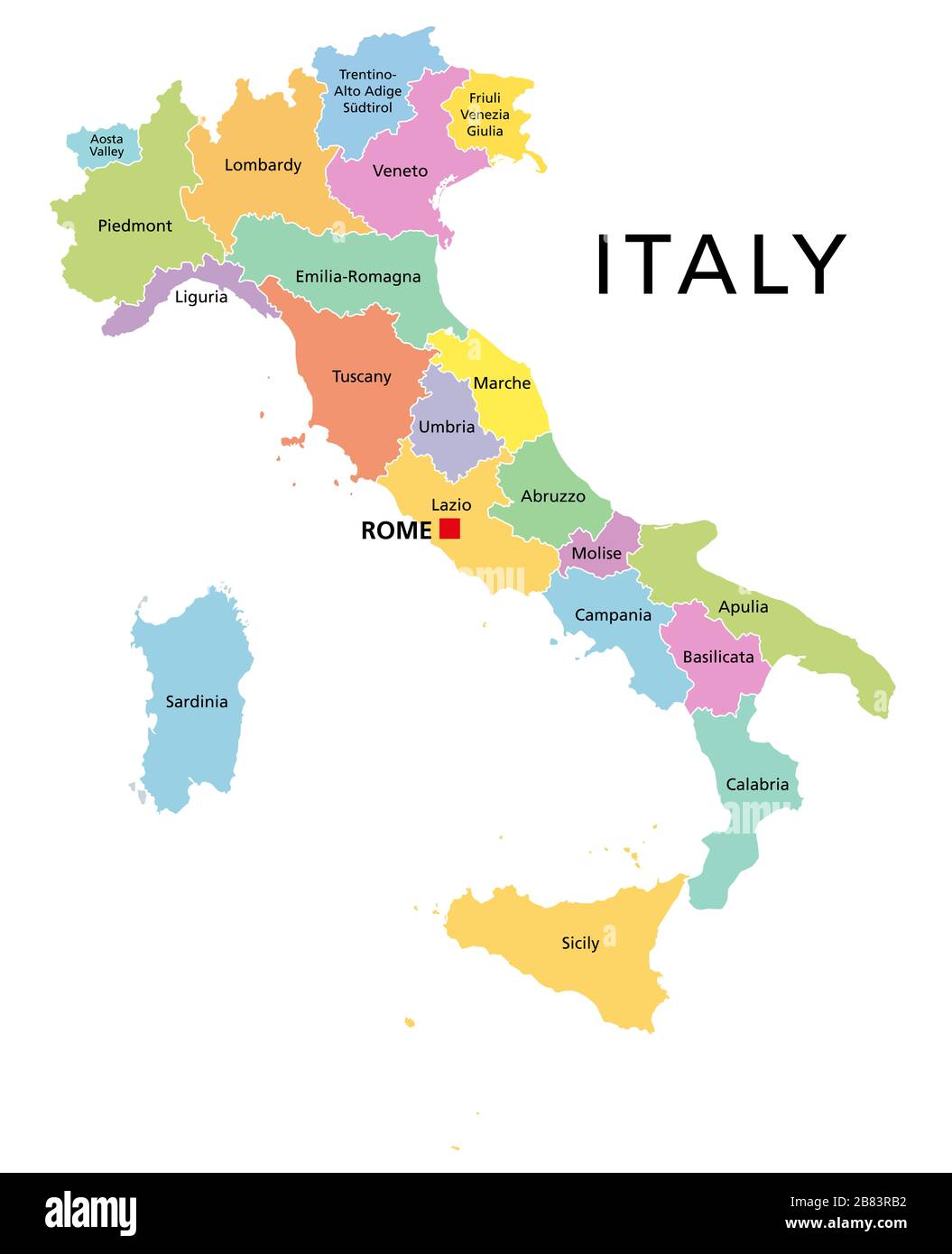
Italy is divided into 20 regions, each possessing a distinct character and a varying degree of autonomy. These regions are further subdivided into 107 provinces, providing an additional layer of administrative organization. The current regional structure, established in 1948, reflects the country’s historical evolution and the desire to balance central authority with regional aspirations.
The Five Autonomous Regions:
Within this regional framework, five regions stand out due to their special status: Valle d’Aosta, Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Sardinia, and Sicily. These regions, known as "autonomous regions," enjoy a higher level of self-governance, with their own legislative assemblies and executive branches. This autonomy stems from their unique linguistic and cultural identities, historical circumstances, and, in some cases, the desire to maintain a degree of independence from the central government.
Regional Politics: A Spectrum of Ideologies:
Each region, with its unique characteristics, has developed its own political landscape. While national political parties play a significant role in regional elections, local parties and movements often emerge, reflecting the specific needs and aspirations of the region. This diversity of political forces can lead to complex coalition governments at the regional level, requiring negotiation and compromise to ensure effective governance.
The Impact of Regionalism on National Politics:
Regional identities and political dynamics have a profound impact on national politics. The Italian Parliament, comprising the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate, reflects this regional diversity through its representation. Each region sends a specific number of deputies and senators to the national legislature, ensuring that regional voices are heard in national policymaking.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Italian political map, while reflecting the country’s rich history and diverse identities, also presents challenges. Regional disparities in economic development, infrastructure, and access to services can create tensions and require targeted policies to address these inequalities. The complex interplay of regional and national interests can also lead to political gridlock and hinder effective governance.
Benefits of the Regional Structure:
Despite these challenges, the Italian regional structure offers significant benefits. It fosters a sense of local identity and empowers citizens to participate in decision-making processes that directly affect their lives. This decentralized system allows for tailored solutions to regional problems and promotes innovation and creativity at the local level.
FAQs about the Italian Political Map:
1. What is the role of the central government in Italian regional governance?
The central government in Italy retains significant authority over regional affairs, including the allocation of resources, the setting of national policies, and the oversight of regional governance. However, regional governments have a significant degree of autonomy in managing their own affairs, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
2. How do regional elections work in Italy?
Regional elections are held every five years, with voters choosing the president and the members of the regional council. These elections are typically characterized by a high degree of local participation and can result in diverse political outcomes, reflecting the unique political landscape of each region.
3. What are the main economic disparities between regions in Italy?
Italy exhibits significant economic disparities between its regions. The northern regions, particularly Lombardy and Veneto, are characterized by a strong industrial base and high levels of economic activity. In contrast, the southern regions, including Campania and Calabria, face higher levels of unemployment, poverty, and economic stagnation.
4. How do regional identities influence national politics in Italy?
Regional identities play a crucial role in shaping national politics in Italy. Political parties often tailor their platforms to address the specific concerns of different regions, and regional issues frequently become central to national debates. This interplay between regional and national interests can create complex political alliances and influence the outcome of national elections.
Tips for Understanding the Italian Political Map:
- Explore the history of each region: Understanding the historical background of each region, including its cultural influences, economic development, and political struggles, provides invaluable context for comprehending its current political landscape.
- Follow regional media and publications: Staying informed about regional news and political developments helps to gain insights into local issues, political trends, and the perspectives of regional stakeholders.
- Engage with regional political figures: Following the speeches and activities of regional politicians provides a valuable window into the priorities and concerns of different regions and their perspectives on national policy.
- Attend regional events and conferences: Participating in regional events and conferences related to politics, culture, and economics allows for direct engagement with regional actors and a deeper understanding of their perspectives.
Conclusion:
The Italian political map is a complex and dynamic system, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse regional identities, and the interplay of national and local interests. Understanding this intricate structure is essential for comprehending the nuances of Italian politics, the challenges it faces, and the opportunities it presents for building a more cohesive and prosperous nation. As Italy continues to navigate the complexities of its political landscape, the regional dimension will remain a key factor in shaping its future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Italian Political Landscape: A Complex Tapestry of Regions and Identities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!