The Nile River: Lifeline of Ancient Egypt
Related Articles: The Nile River: Lifeline of Ancient Egypt
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Nile River: Lifeline of Ancient Egypt. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Nile River: Lifeline of Ancient Egypt

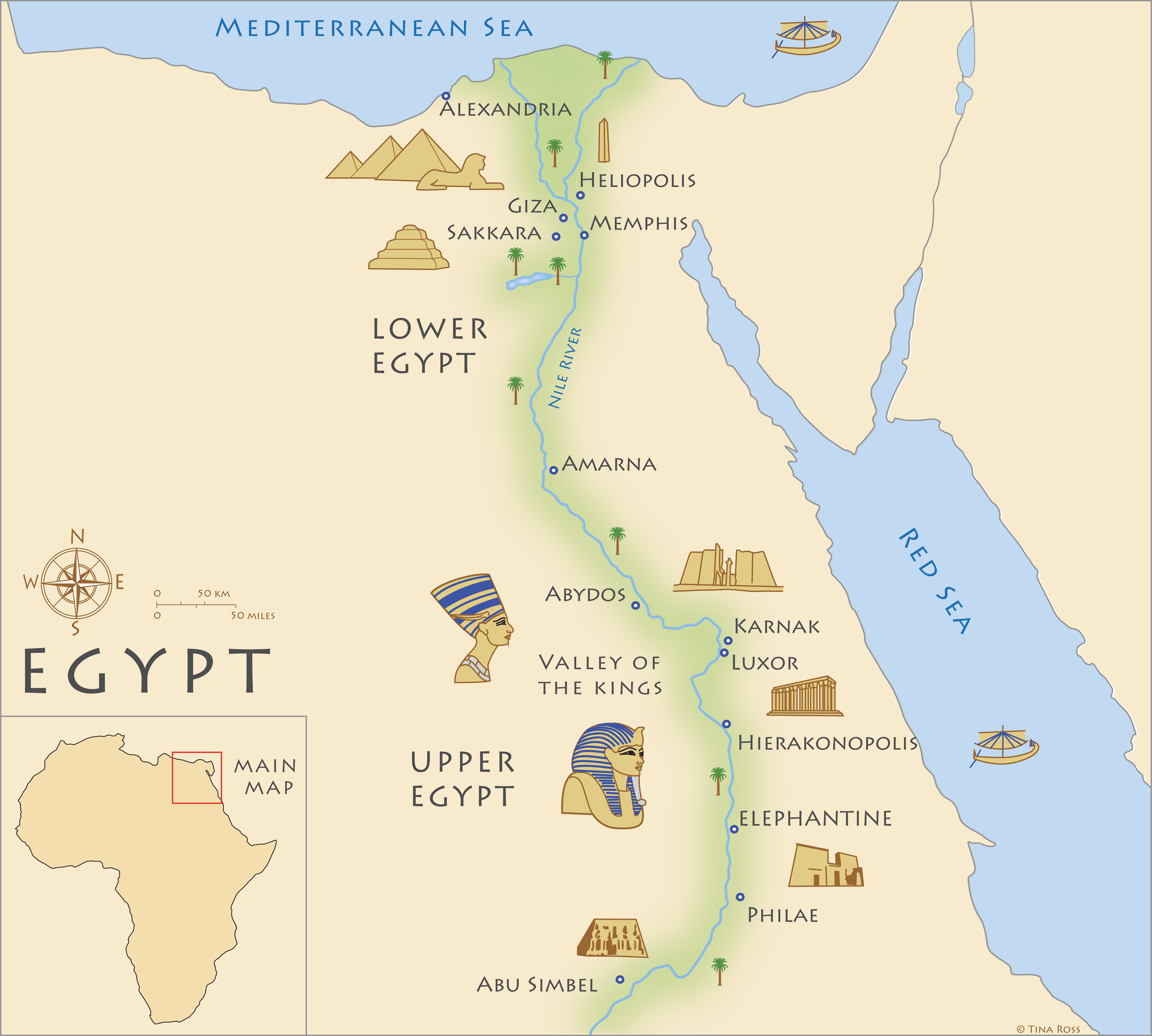
The Nile River, a ribbon of life coursing through the parched landscape of northeastern Africa, holds a pivotal place in the history of civilization. For the ancient Egyptians, it was more than just a waterway; it was the very essence of their existence. The Nile’s annual floods, a predictable rhythm of life and death, provided the fertile soil that sustained their agriculture, nurtured their culture, and shaped their beliefs. This article delves into the intricate relationship between the Nile River and ancient Egypt, exploring its map, its influence on their civilization, and its enduring legacy.
A River’s Embrace: The Nile’s Geography
The Nile River, the longest river in the world, originates in the highlands of central Africa and flows northward for over 6,650 kilometers, traversing eleven countries before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. Its journey through Egypt, a stretch of approximately 1,500 kilometers, is where its impact on ancient civilization is most profound. The river’s course through Egypt can be divided into three distinct sections:
-
The Upper Nile: This section begins at the First Cataract, a series of rapids near the modern city of Aswan. It flows north through a narrow valley, characterized by steep cliffs and rocky terrain. The Upper Nile was a challenging stretch for navigation, but it was also rich in resources, particularly gold and precious stones.
-
The Middle Nile: This section stretches from the First Cataract to Cairo, traversing a fertile valley that widens considerably. The Middle Nile was the heartland of ancient Egypt, where the majority of the population lived and where the most important cities, such as Thebes and Memphis, were established. The annual inundation of the Nile, a phenomenon caused by the summer rains in Ethiopia, deposited rich silt along the banks, making this region a fertile agricultural paradise.
-
The Lower Nile: This final section flows through the Nile Delta, a vast expanse of fertile land formed by the river’s sediment. The Lower Nile was a region of intense agricultural activity, supporting a large population and a complex network of canals and irrigation systems. The delta was also a vital trade route, connecting Egypt to the Mediterranean world.
Mapping the Lifeblood: The Nile River’s Influence on Ancient Egypt
The Nile River’s influence on ancient Egypt is evident in every aspect of their civilization, from their daily lives to their religious beliefs. The map of the Nile, with its distinct sections, provides a framework for understanding the development and evolution of ancient Egyptian society.
Agriculture: The Backbone of Civilization: The annual floods of the Nile, a predictable event that occurred between June and October, deposited fertile silt along the riverbanks, transforming the otherwise barren landscape into a thriving agricultural region. This fertile land allowed the ancient Egyptians to cultivate a variety of crops, including wheat, barley, emmer, and flax, providing a reliable source of food and resources. The Nile’s predictable flooding also facilitated the development of a sophisticated irrigation system, enabling the Egyptians to control the flow of water and maximize agricultural yields.
Urbanization: The Rise of Cities: The Nile’s fertile land and reliable water supply fostered the growth of large urban centers. The river served as a vital transportation artery, connecting cities and facilitating trade. The most important cities of ancient Egypt, such as Memphis, Thebes, and Heliopolis, were strategically located along the Nile, benefiting from its resources and its strategic position.
Religion: The River as a Deity: The Nile River held a profound religious significance for the ancient Egyptians. They worshipped the river as a deity, Hapy, who was responsible for the annual floods and the prosperity they brought. The Nile’s life-giving power was deeply ingrained in their mythology and religious practices. Temples were built along the riverbanks, and festivals were held to honor Hapy and ensure his continued favor.
Trade and Transportation: The Nile as a Lifeline: The Nile River served as a vital trade route, connecting Egypt to the Mediterranean world and to other parts of Africa. The river’s navigability allowed for the transportation of goods, people, and ideas, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth. Boats, powered by sails and oars, were a common sight on the Nile, transporting agricultural products, building materials, and other goods.
The Nile’s Legacy: A Lasting Impact
The Nile River’s influence on ancient Egypt extended far beyond its physical presence. It shaped their art, their literature, their architecture, and their very way of life. The river’s cyclical rhythm, its life-giving power, and its role in their religious beliefs, all contributed to the unique and enduring legacy of ancient Egyptian civilization.
The Nile River: A Source of Wonder and Inspiration
The Nile River continues to be a source of wonder and inspiration for people around the world. Its ancient history, its cultural significance, and its enduring beauty make it a destination for travelers and a subject of fascination for historians, archaeologists, and artists alike. The Nile River’s legacy is a testament to the power of nature and the ingenuity of human civilization.
FAQs about the Nile River Map of Ancient Egypt:
Q: What is the significance of the Nile River in ancient Egyptian civilization?
A: The Nile River was the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, providing the fertile land for agriculture, facilitating transportation and trade, and shaping their religious beliefs and cultural practices.
Q: How did the Nile River influence the development of agriculture in ancient Egypt?
A: The annual floods of the Nile deposited rich silt along the riverbanks, creating fertile land that allowed the ancient Egyptians to cultivate a variety of crops. The predictable flooding also enabled the development of a sophisticated irrigation system.
Q: What role did the Nile River play in the development of cities in ancient Egypt?
A: The Nile’s fertile land and reliable water supply fostered the growth of large urban centers. The river served as a vital transportation artery, connecting cities and facilitating trade.
Q: What is the religious significance of the Nile River in ancient Egyptian mythology?
A: The ancient Egyptians worshipped the Nile as a deity, Hapy, who was responsible for the annual floods and the prosperity they brought. The river’s life-giving power was deeply ingrained in their mythology and religious practices.
Q: How did the Nile River contribute to trade and transportation in ancient Egypt?
A: The Nile River served as a vital trade route, connecting Egypt to the Mediterranean world and to other parts of Africa. The river’s navigability allowed for the transportation of goods, people, and ideas, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth.
Tips for Exploring the Nile River’s Legacy:
-
Visit the ancient cities of Memphis, Thebes, and Heliopolis: These cities were strategically located along the Nile and provide insights into the ancient Egyptian civilization.
-
Explore the temples and monuments built along the riverbanks: These structures, such as the Karnak Temple Complex and the Valley of the Kings, offer a glimpse into the religious beliefs and artistic achievements of the ancient Egyptians.
-
Take a cruise along the Nile River: This is a unique way to experience the beauty and tranquility of the river and to visit some of the most iconic landmarks of ancient Egypt.
-
Learn about the ancient Egyptian mythology and their relationship with the Nile River: Understanding their beliefs and practices provides a deeper appreciation for the river’s significance in their civilization.
Conclusion:
The Nile River, a majestic ribbon of life flowing through the heart of ancient Egypt, played a pivotal role in shaping their civilization. It provided the fertile land for agriculture, facilitated transportation and trade, and influenced their religious beliefs and cultural practices. The Nile’s legacy continues to inspire and fascinate, reminding us of the profound relationship between nature and human civilization. As we explore the map of the Nile and the history of ancient Egypt, we gain a deeper understanding of the enduring power of this remarkable river.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nile River: Lifeline of Ancient Egypt. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!