Unraveling Humanity’s Journey: A Map of Early Human Migrations
Related Articles: Unraveling Humanity’s Journey: A Map of Early Human Migrations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Humanity’s Journey: A Map of Early Human Migrations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling Humanity’s Journey: A Map of Early Human Migrations

The Earth, a vast and diverse tapestry, is a testament to the remarkable journey of humankind. Our species, Homo sapiens, has traversed continents, adapted to diverse environments, and shaped the planet in ways unimaginable to our ancestors. Understanding the paths of these early migrations is crucial to understanding our shared history, cultural diversity, and the very essence of what it means to be human.
A Mosaic of Movement: Tracing the Paths of Our Ancestors
Maps of early human migrations, like intricate mosaics, piece together the story of our species’ dispersal from its African birthplace. These maps, meticulously crafted by researchers using genetic, archaeological, and linguistic evidence, reveal a complex tapestry of movement, adaptation, and interaction.
The African Cradle: Our Evolutionary Roots
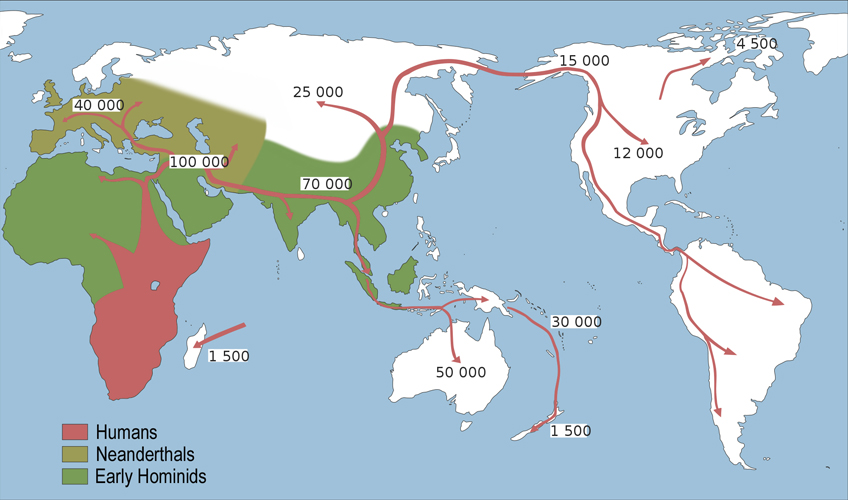
The story begins in Africa, the cradle of humankind. Archaeological evidence suggests that Homo sapiens first emerged in eastern Africa, approximately 300,000 years ago. These early humans, equipped with advanced cognitive abilities and tools, began to spread across the continent, adapting to diverse environments and evolving into distinct populations.
Out of Africa: The First Migrations
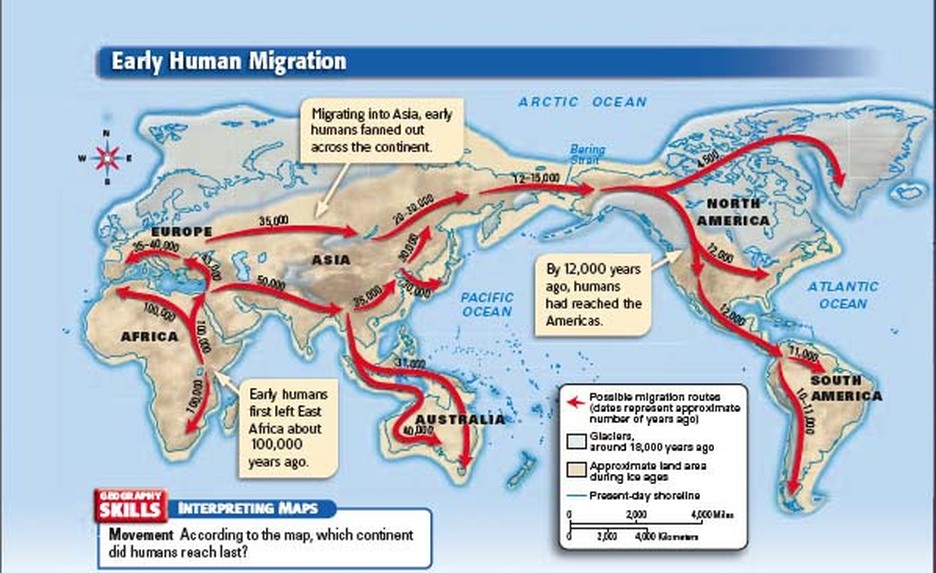
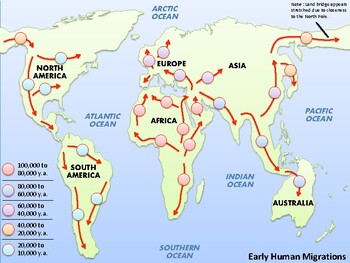
Around 70,000 years ago, a significant event occurred: a small group of Homo sapiens ventured out of Africa, embarking on a journey that would forever change the course of human history. This "Out of Africa" migration, driven by factors such as climate change, resource scarcity, and perhaps even simple curiosity, led these early humans across the Red Sea and into the Arabian Peninsula.
A Global Odyssey: The Spread of Modern Humans
From the Arabian Peninsula, these intrepid pioneers spread eastward into Asia, reaching Australia by 50,000 years ago. Simultaneously, other groups ventured northward, crossing into Europe around 45,000 years ago. These migrations were not linear or unidirectional; they were characterized by branching routes, periods of stagnation, and even backflows, resulting in a complex pattern of human dispersal across the globe.
The Legacy of Migration: Shaping Cultures and Landscapes
These early migrations left an indelible mark on the world. They led to the establishment of diverse human populations, each with unique cultural practices, languages, and genetic profiles. The interaction between these populations, often marked by both conflict and collaboration, has shaped the course of human history, fostering innovation, cultural exchange, and the development of complex societies.
The Power of Maps: Illuminating the Past, Guiding the Future
Maps of early human migrations are not merely static representations of past events. They are powerful tools for understanding our shared history, appreciating the diversity of human experience, and fostering a sense of global interconnectedness. They remind us that we are all part of a larger human story, one that began in Africa and continues to unfold across the globe.
FAQs on Early Human Migrations
1. What evidence is used to reconstruct early human migrations?
Researchers utilize a multidisciplinary approach, combining genetic evidence from ancient DNA and modern populations, archaeological findings like tools and settlements, and linguistic analysis to reconstruct the paths of early human migrations.
2. Why did early humans migrate?
While the exact motivations are complex and multifaceted, the primary drivers of early human migrations are believed to be:
- Climate Change: Shifts in climate and environmental conditions, such as the drying of Africa, might have forced early humans to seek new resources and more favorable habitats.
- Resource Availability: The pursuit of food, water, and other resources could have prompted migrations to areas with greater abundance.
- Population Pressure: As human populations grew, competition for resources and territory might have driven groups to explore new territories.
- Curiosity and Exploration: A natural human instinct for exploration and discovery may have motivated some groups to venture into unknown lands.
3. What impact did these migrations have on the world?
The impact of early human migrations was profound and far-reaching:
- Cultural Diversity: Migrations led to the establishment of diverse human populations, each with unique cultural practices, languages, and traditions.
- Genetic Diversity: The movement of people across continents resulted in the mixing of gene pools, contributing to the remarkable genetic diversity observed in modern humans.
- Technological Advancements: The interaction between different groups fostered the exchange of knowledge and technology, driving innovation and the development of new tools and techniques.
- Environmental Change: Human activities, including the introduction of new species and land use practices, have had a significant impact on the environment, shaping ecosystems and influencing the course of evolution.
4. Are there any ongoing migrations today?
Yes, human migration continues to be a significant phenomenon in the modern world. Driven by factors such as economic opportunity, political instability, conflict, and climate change, millions of people migrate each year, seeking a better life or escaping hardship.
Tips for Studying Early Human Migrations
- Explore Interactive Maps: Numerous online resources offer interactive maps that visualize early human migrations, providing a dynamic and engaging way to learn about these journeys.
- Engage with Primary Sources: Explore archaeological reports, genetic studies, and linguistic analyses to gain a deeper understanding of the evidence used to reconstruct these migrations.
- Connect with History: Learn about the cultures, languages, and traditions of different human populations to appreciate the rich tapestry of human diversity that emerged from these migrations.
- Consider the Ethical Implications: Reflect on the ethical considerations surrounding the study of human migrations, recognizing the potential for misinterpretation and the importance of respecting diverse cultural perspectives.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Movement and Adaptation
Maps of early human migrations are not merely historical artifacts; they are windows into the dynamic story of our species. They reveal the remarkable resilience, adaptability, and interconnectedness of humankind, highlighting the shared journey that has brought us to where we are today. As we continue to explore the world and its history, these maps serve as a powerful reminder of our common origins and the enduring legacy of human migration.
![Timeline-Map of Human Migrations Across Continents.[1911x1100] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/huwc6oqutnfy.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Humanity’s Journey: A Map of Early Human Migrations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!