Unraveling the Earth’s Midline: A Guide to the Equator
Related Articles: Unraveling the Earth’s Midline: A Guide to the Equator
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Earth’s Midline: A Guide to the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Earth’s Midline: A Guide to the Equator
The Earth, a magnificent sphere suspended in space, is divided by an imaginary line known as the Equator. This invisible circle, equidistant from both the North and South Poles, plays a pivotal role in understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and even culture.
A Circumference of Significance:
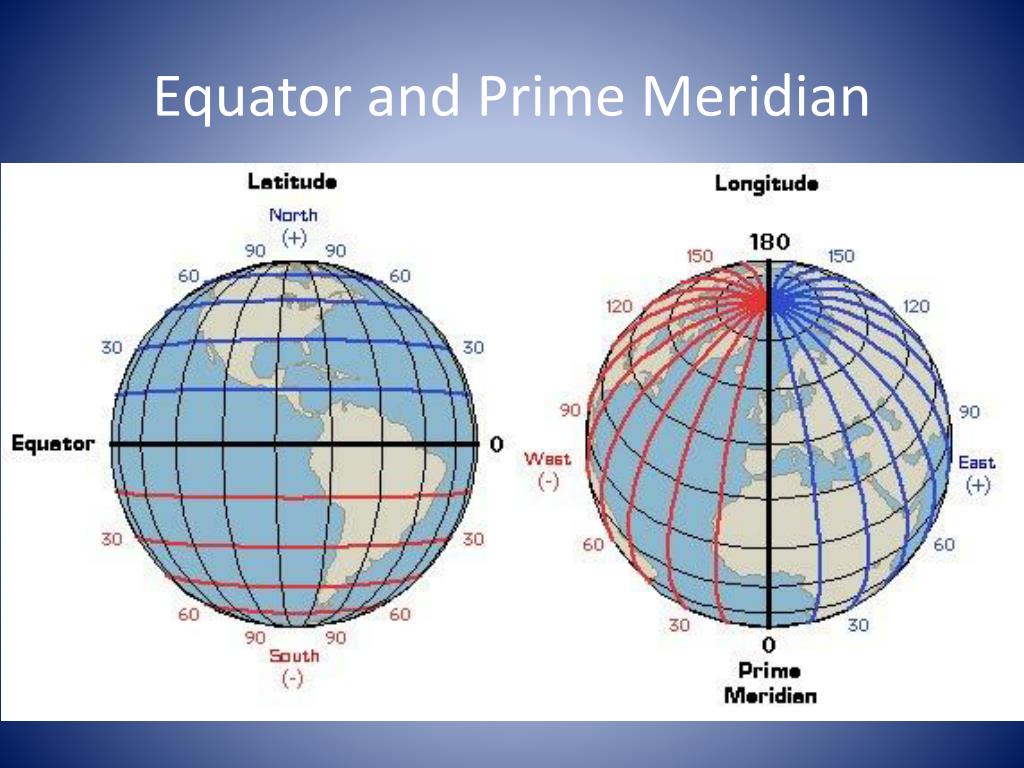
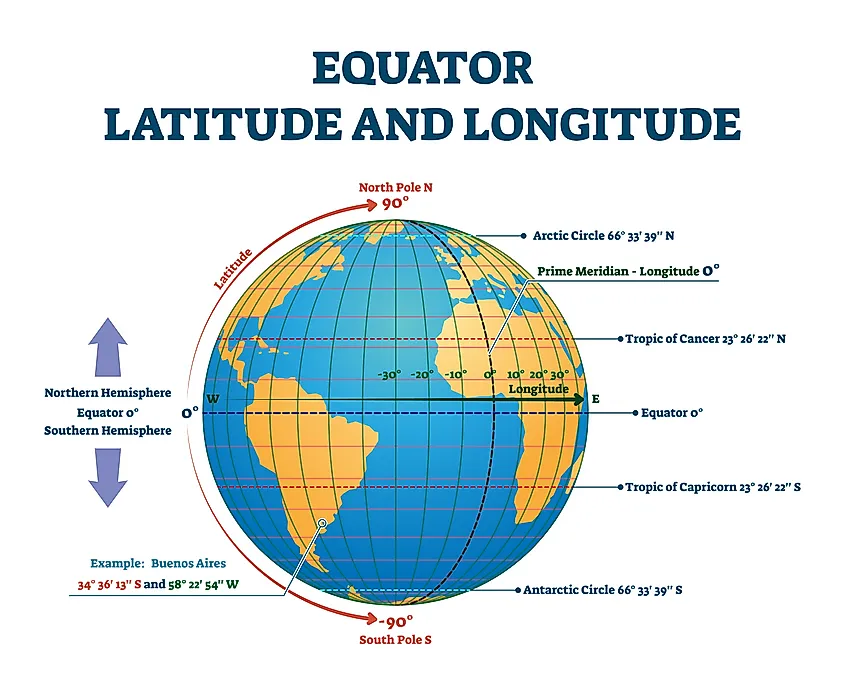
The Equator is not merely a line on a map; it is a fundamental reference point in Earth’s geography. It divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere, with everything north of the Equator residing in the Northern Hemisphere and everything south in the Southern Hemisphere.
Locating the Equator on a Map:
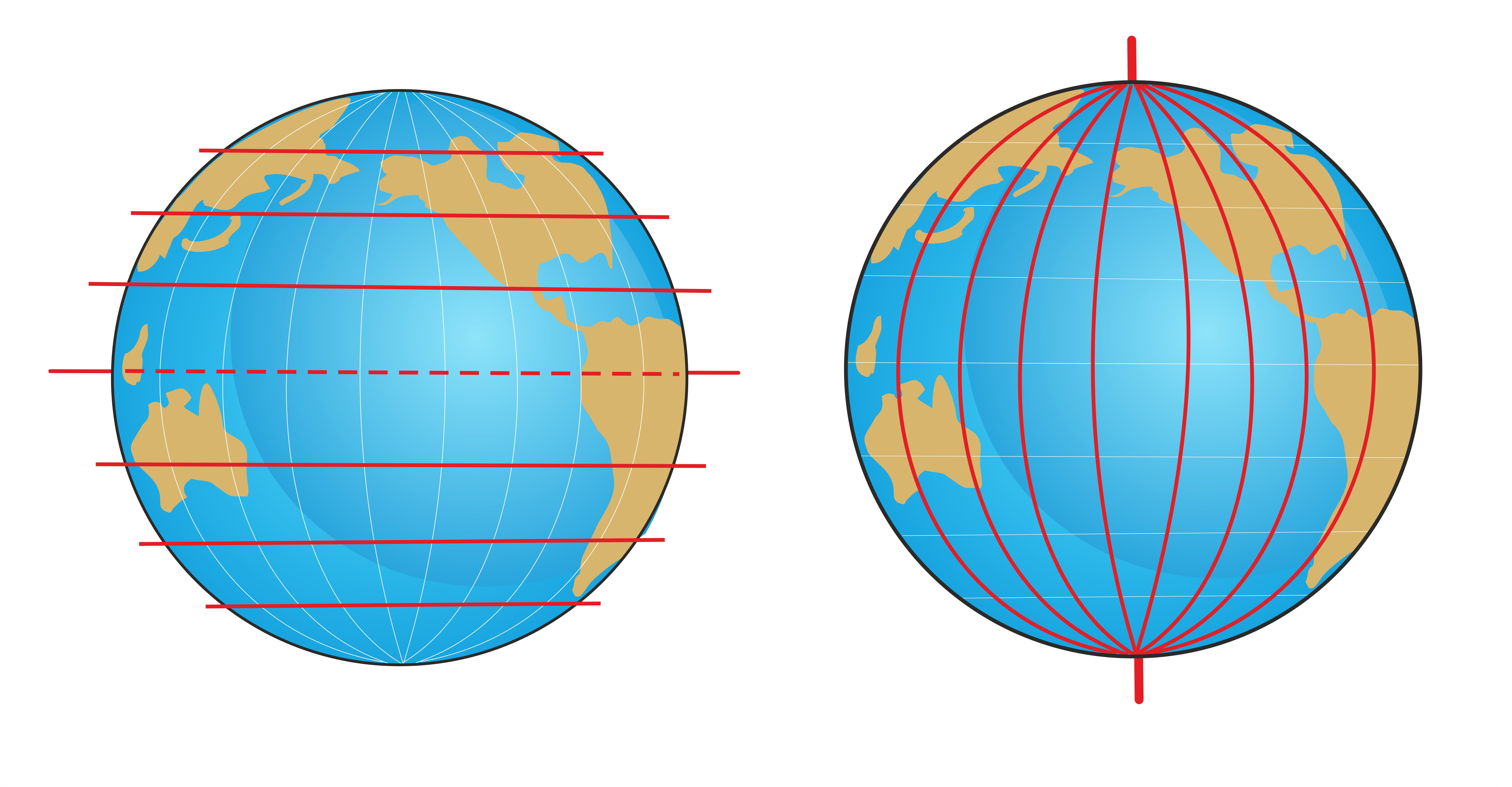
Identifying the Equator on a map is relatively straightforward. It is typically depicted as a thick, solid line that circles the globe horizontally, always at 0° latitude. This line is often accompanied by a label indicating its designation as the "Equator" or "0° Latitude."
The Equator’s Influence on Climate:
The Equator’s position directly influences the Earth’s climate. Due to its location, the Equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and a tropical climate. This constant exposure to solar radiation also fuels the formation of rainforests, which thrive in the humid, warm conditions found along the Equator.
A Tapestry of Cultures:
The Equator runs through diverse landscapes and cultures, showcasing the planet’s rich tapestry of human life. From the vibrant rainforests of the Amazon to the bustling cities of Singapore, the Equator connects people and environments across the globe. This diverse cultural mosaic is reflected in the various traditions, languages, and customs found in equatorial regions.
The Equator’s Role in Navigation:
Navigators and explorers have long relied on the Equator as a vital reference point. It serves as a baseline for measuring latitude, which is the angular distance north or south of the Equator. By knowing their latitude, sailors and pilots can accurately determine their position on Earth.
Exploring the Equator’s Significance:
The Equator’s significance extends beyond its geographical importance. It serves as a powerful symbol of unity, connecting people and cultures across continents. The Equator reminds us that despite our differences, we are all inhabitants of the same planet, sharing a common destiny.
FAQs about the Equator:
Q: What is the length of the Equator?
A: The Equator’s circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
Q: Why is the Equator important?
A: The Equator is crucial for understanding the Earth’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. It serves as a reference point for navigation and provides insights into the planet’s various ecosystems.
Q: What are some countries that the Equator passes through?
A: The Equator passes through numerous countries, including Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Indonesia, Kenya, and Uganda.
Q: What is the difference between the Equator and the Prime Meridian?
A: The Equator is a horizontal line that circles the Earth at 0° latitude, while the Prime Meridian is a vertical line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole at 0° longitude.
Tips for Identifying the Equator on a Map:
- Look for the 0° Latitude Line: The Equator is always depicted as the 0° latitude line on maps.
- Check for Labels: Maps often label the Equator as "Equator" or "0° Latitude."
- Locate the Tropics: The Equator lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Use Online Resources: Online mapping tools and satellite imagery can provide a clear visualization of the Equator’s position.
Conclusion:
The Equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds immense significance in our understanding of the Earth. It shapes our planet’s climate, connects diverse cultures, and provides a vital reference point for navigation. As we continue to explore and learn about our planet, the Equator will remain a fundamental element in our understanding of Earth’s geography and its global interconnectedness.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Earth’s Midline: A Guide to the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!