Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
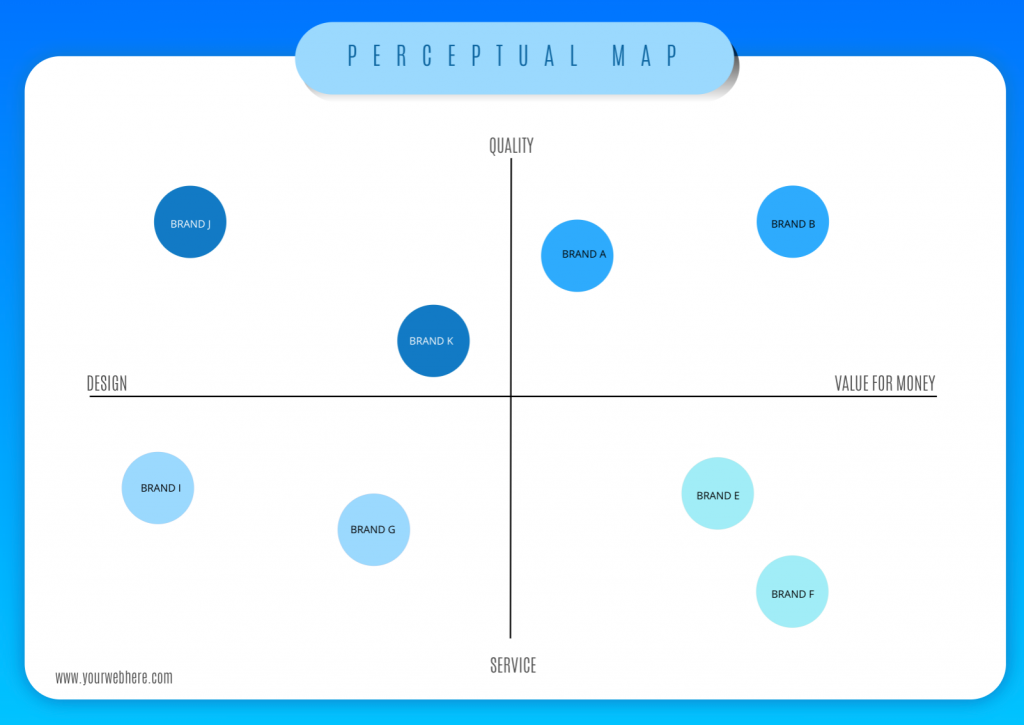
In the competitive arena of business, understanding consumer perception is paramount. Marketers strive to position their products and services in a way that resonates with target audiences, ultimately driving sales and brand loyalty. A powerful tool for achieving this objective is the perceptual map, a visual representation of how consumers perceive different brands or products within a specific market.
Understanding the Concept:
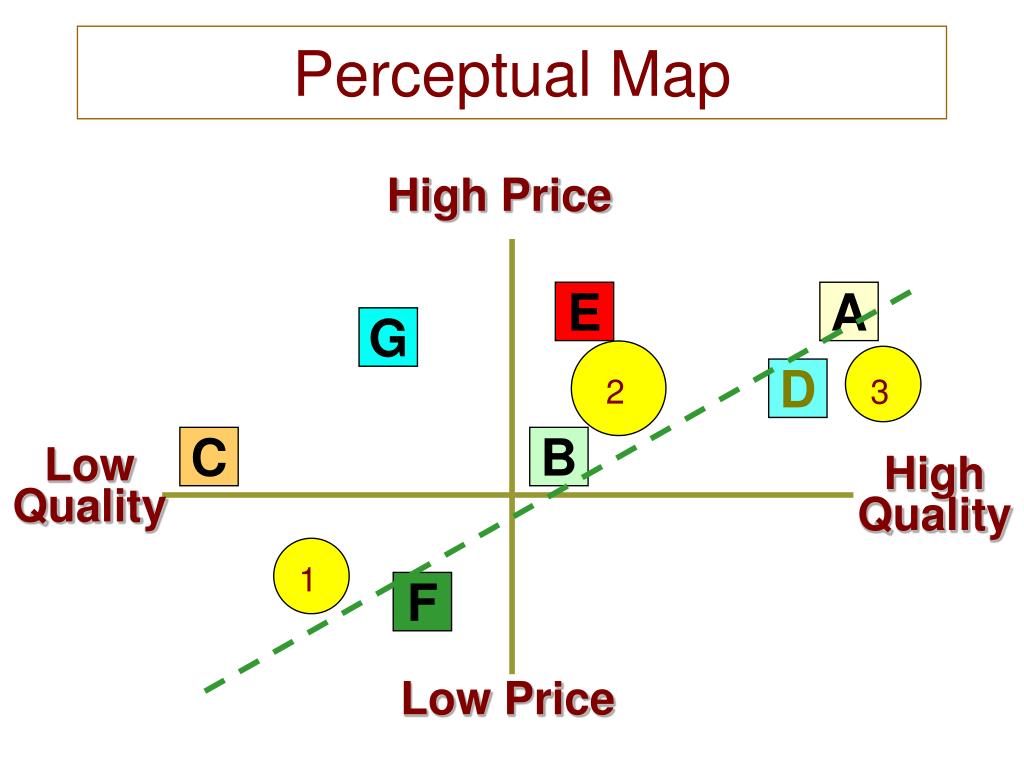
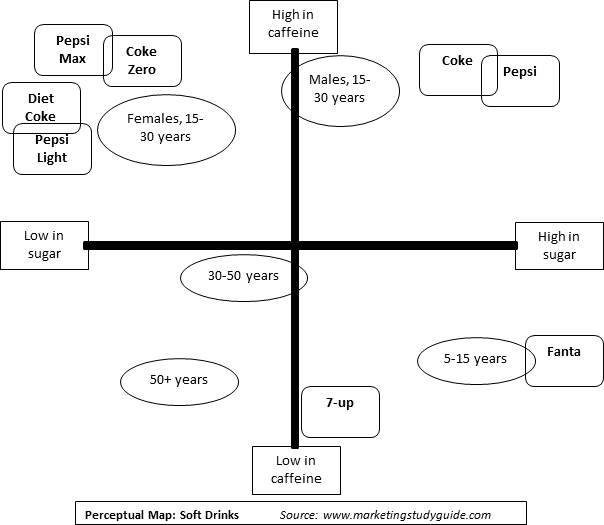
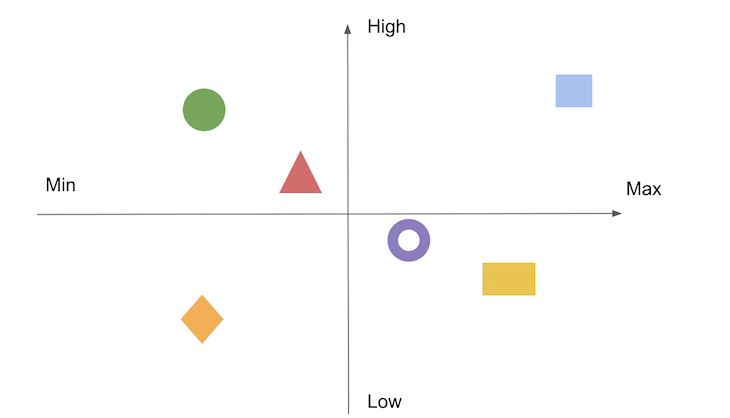
A perceptual map is essentially a graphical representation of consumer perceptions. It plots brands or products on a two-dimensional (or sometimes multi-dimensional) space, using attributes that are relevant to consumers. These attributes can be anything from price and quality to features and benefits, depending on the specific market and target audience.
The axes of the map represent these attributes, allowing for a clear visualization of how brands are perceived in relation to each other. For example, a perceptual map for automobiles might use "price" and "performance" as the axes, with brands like Toyota positioned as affordable and reliable, while BMW might be positioned as luxurious and high-performance.
Construction and Interpretation:
Creating a perceptual map involves a multi-step process:
-
Identifying Relevant Attributes: The first step is to identify the key attributes that consumers consider when making purchasing decisions within a specific market. This can be achieved through market research techniques such as surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis.
-
Data Collection and Analysis: Once the attributes are identified, data is collected from consumers regarding their perceptions of different brands or products on those attributes. This data can be gathered through surveys, interviews, or even online reviews.
-
Plotting the Data: The collected data is then plotted on a graph, with each axis representing a chosen attribute. The position of each brand or product on the map is determined by its average score on each attribute.
-
Interpretation and Insights: The resulting perceptual map provides valuable insights into consumer perceptions. It helps identify:
- Positioning Gaps: Areas on the map where there are no brands or products, suggesting potential opportunities for new product launches or repositioning existing brands.
- Competitive Landscape: The relative positions of competing brands on the map, revealing their strengths and weaknesses.
- Consumer Preferences: The areas of the map where consumers are most concentrated, indicating the most desirable product attributes.
- Brand Perception: How individual brands are perceived by consumers, allowing for the identification of areas for improvement.
Benefits of Utilizing Perceptual Maps:
Perceptual maps offer a range of benefits to businesses, making them a valuable tool for strategic decision-making:
- Enhanced Market Understanding: Perceptual maps provide a clear and concise overview of the competitive landscape, allowing businesses to identify their strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors.
- Effective Positioning Strategies: Understanding consumer perceptions enables businesses to develop effective positioning strategies that differentiate their products and services from competitors.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: By identifying consumer preferences and positioning gaps, businesses can tailor their marketing campaigns to resonate with specific target audiences.
- Product Development and Innovation: Perceptual maps can guide product development by identifying areas where new products or features are most desired by consumers.
- Brand Management: Perceptual maps help monitor brand perception over time, allowing businesses to track changes in consumer sentiment and adjust their strategies accordingly.
FAQs about Perceptual Maps:
Q: What are the limitations of perceptual maps?
A: While powerful, perceptual maps have limitations:
- Subjectivity: Consumer perceptions can be subjective and influenced by personal biases.
- Limited Scope: Perceptual maps typically focus on a limited number of attributes, potentially overlooking other important factors.
- Static Nature: Perceptual maps represent a snapshot in time and may not accurately reflect dynamic market changes.
Q: How can I create a perceptual map?
A: Creating a perceptual map requires expertise in market research and data analysis. It is often best to consult with a professional market research firm or use specialized software designed for this purpose.
Q: How can I use a perceptual map to improve my marketing strategy?
A: A perceptual map can help you:
- Target your messaging: Tailor your marketing messages to appeal to the specific attributes that consumers value in your market.
- Reposition your brand: Identify areas on the map where you can reposition your brand to better appeal to your target audience.
- Develop new products: Identify potential gaps in the market where you can introduce new products that meet unmet consumer needs.
Tips for Utilizing Perceptual Maps Effectively:
- Choose the right attributes: Select attributes that are truly relevant to your target audience and drive their purchasing decisions.
- Use reliable data: Ensure that the data used to create the map is accurate and representative of your target market.
- Regularly update the map: Market dynamics are constantly changing, so it’s crucial to update your perceptual map periodically to reflect these changes.
- Integrate the map with other strategic tools: Use the insights gained from the map to inform your overall marketing strategy, product development, and branding efforts.
Conclusion:
Perceptual maps are a valuable tool for understanding consumer perceptions and navigating the competitive landscape. By providing a visual representation of how brands are perceived, they empower businesses to make informed decisions regarding positioning, marketing, and product development. Utilizing this powerful tool effectively can lead to increased market share, brand loyalty, and ultimately, business success.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!